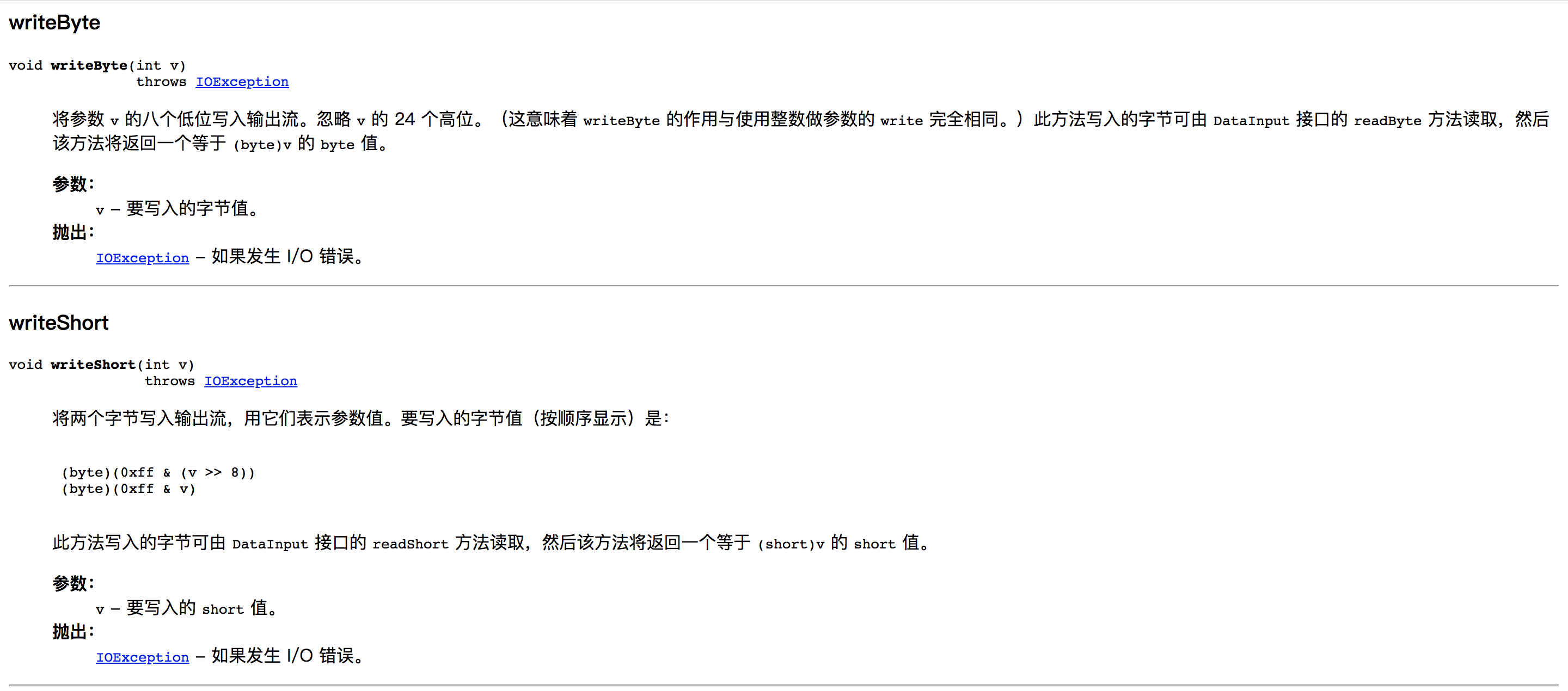
DataOutput接口与前面讲过的DataInput接口相对应,功能基本相反
注释:
/** * The <code>DataOutput</code> interface provides * for converting data from any of the Java * primitive types to a series of bytes and * writing these bytes to a binary stream. * There is also a facility for converting * a <code>String</code> into * <a href="DataInput.html#modified-utf-8">modified UTF-8</a> * format and writing the resulting series * of bytes. * <p> * For all the methods in this interface that * write bytes, it is generally true that if * a byte cannot be written for any reason, * an <code>IOException</code> is thrown. * * @author Frank Yellin * @see java.io.DataInput * @see java.io.DataOutputStream * @since JDK1.0 */
大意如下:
该接口用于将数据从Java基本类型转化为二进制byte流,同时提供了一个将字符串转化为修改版UTF-8并写入所得到的修改版UTF-8字节的工具
对于该接口中的任意方法,如果由于某个原因无法写入某个字节,将抛出IOExpection
该接口中定义了十四个方法:
以上就是该接口所定义的全部方法及其作用(该内容来自官方文档),从中我们可以明显感觉到DataOutput接口与DataInput接口在功能上十分类似,除了数据的流动方向不同外,其他功能基本一样。其实在IO包中,各种相对应的输入输出流基本都是如此,因为其本身就是被设计从相对的输出流来接受数据或向相对的输入流输出数据。
DataOutputStream是DataOutput接口的完整实例
该类继承自FilterOutputStream
该类的作用注释如下
/** * A data output stream lets an application write primitive Java data * types to an output stream in a portable way. An application can * then use a data input stream to read the data back in. * * @author unascribed * @see java.io.DataInputStream * @since JDK1.0 */
大意为:
一个通过便携方法让应用程序写出Java基本类型数据的数据输出流
一个应用程序在稍后可以使用数据输入流来读取刚写出的数据
该类含有两个成员变量
当目前为止已写入输出流的字节数
protected int written;
byte缓冲区(用于writeUTF方法)
private byte[] bytearr = null;
该类含有十五个方法(多一个构造方法)
构造方法
public DataOutputStream(OutputStream out) { super(out); }
修改写入记数
private void incCount(int value) {//value这次写入的字节数 int temp = written + value; if (temp < 0) {//溢出判定 temp = Integer.MAX_VALUE; } written = temp; }
写出单个int值的低八位
public synchronized void write(int b) throws IOException { out.write(b); incCount(1);//增加一次写入记数 }
将数组中特定位置及长度的数据依次写出
public synchronized void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException { out.write(b, off, len); incCount(len); }
刷新流
public void flush() throws IOException { out.flush(); }
写出boolean值(其实默认int值)
public final void writeBoolean(boolean v) throws IOException { out.write(v ? 1 : 0); incCount(1); }
写出低八位(在该类中和write(int)没啥区别)
public final void writeByte(int v) throws IOException { out.write(v); incCount(1); }
写出两个字节(把short值拆分)
public final void writeShort(int v) throws IOException { out.write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF);//低位 out.write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF); incCount(2); }
写出两个字节(拆分char值)
public final void writeChar(int v) throws IOException { out.write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF); out.write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF); incCount(2); }
写出四个字节(拆分int值)
public final void writeInt(int v) throws IOException { out.write((v >>> 24) & 0xFF); out.write((v >>> 16) & 0xFF); out.write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF); out.write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF); incCount(4); }
写出八个字节(拆分long值)
public final void writeLong(long v) throws IOException { writeBuffer[0] = (byte)(v >>> 56); writeBuffer[1] = (byte)(v >>> 48); writeBuffer[2] = (byte)(v >>> 40); writeBuffer[3] = (byte)(v >>> 32); writeBuffer[4] = (byte)(v >>> 24); writeBuffer[5] = (byte)(v >>> 16); writeBuffer[6] = (byte)(v >>> 8); writeBuffer[7] = (byte)(v >>> 0); out.write(writeBuffer, 0, 8); incCount(8); }
写出四个字节(拆分float值)
public final void writeFloat(float v) throws IOException { writeInt(Float.floatToIntBits(v));//进行格式转化 }
写出八个字节(拆分double值)
public final void writeDouble(double v) throws IOException { writeLong(Double.doubleToLongBits(v)); }
字符串按字节顺序写出
public final void writeBytes(String s) throws IOException { int len = s.length(); for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) { out.write((byte)s.charAt(i)); } incCount(len); }
字符串按字符顺序写出
public final void writeChars(String s) throws IOException { int len = s.length(); for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) { int v = s.charAt(i); out.write((v >>> 8) & 0xFF); out.write((v >>> 0) & 0xFF); } incCount(len * 2); }
写出字符串(先写入两个字节的长度信息,然后写入字符串的修改版UTF-8形式,记数)
static int writeUTF(String str, DataOutput out) throws IOException { int strlen = str.length(); int utflen = 0; int c, count = 0; /* use charAt instead of copying String to char array */ for (int i = 0; i < strlen; i++) { c = str.charAt(i); if ((c >= 0x0001) && (c <= 0x007F)) { utflen++; } else if (c > 0x07FF) { utflen += 3; } else { utflen += 2; } } if (utflen > 65535) throw new UTFDataFormatException( "encoded string too long: " + utflen + " bytes"); byte[] bytearr = null; if (out instanceof DataOutputStream) {//没有绑定written,并且后文也没有对记数的修改,所以该方法写出不影响记数-——当前版本为1.8 DataOutputStream dos = (DataOutputStream)out; if(dos.bytearr == null || (dos.bytearr.length < (utflen+2))) dos.bytearr = new byte[(utflen*2) + 2]; bytearr = dos.bytearr; } else { bytearr = new byte[utflen+2]; } bytearr[count++] = (byte) ((utflen >>> 8) & 0xFF); bytearr[count++] = (byte) ((utflen >>> 0) & 0xFF); int i=0; for (i=0; i<strlen; i++) { c = str.charAt(i); if (!((c >= 0x0001) && (c <= 0x007F))) break; bytearr[count++] = (byte) c; } for (;i < strlen; i++){ c = str.charAt(i); if ((c >= 0x0001) && (c <= 0x007F)) { bytearr[count++] = (byte) c; } else if (c > 0x07FF) { bytearr[count++] = (byte) (0xE0 | ((c >> 12) & 0x0F)); bytearr[count++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((c >> 6) & 0x3F)); bytearr[count++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((c >> 0) & 0x3F)); } else { bytearr[count++] = (byte) (0xC0 | ((c >> 6) & 0x1F)); bytearr[count++] = (byte) (0x80 | ((c >> 0) & 0x3F)); } } out.write(bytearr, 0, utflen+2); return utflen + 2;//返回写入长度 }
写出字符串(调用上个方法,用自己的流写出)
public final void writeUTF(String str) throws IOException { writeUTF(str, this); }
获得已写出的数据量
public final int size() { return written; }
DataOutputStream是DataOutput的一个实例,将DataOutput功能的完成方式给我们直观的表现出来。但也发现一些奇怪的地方,比如writerUTF()方法写出的数据竟然不被记录,不知道是本身设计上不需要还是忘了添加































 8859
8859

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








