转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/abcjennifer/article/details/25912675
本文结合Deep learning的一个应用,Convolution Neural Network 进行一些基本应用,参考Lecun的Document 0.1进行部分拓展,与结果展示(in Python)。
分为以下几部分:
1. Convolution(卷积)
2. Pooling(降采样过程)
3. CNN结构
4. 跑实验
下面分别介绍。
PS:本篇blog为ese机器学习短期班参考资料(20140516课程),本文只是简要讲最naive最simple的思想,重在实践部分,原理课上详述。
1. Convolution(卷积)
类似于高斯卷积,对imagebatch中的所有image进行卷积。对于一张图,其所有feature map用一个filter卷成一张feature map。 如下面的代码,对一个imagebatch(含两张图)进行操作,每个图初始有3张feature map(R,G,B), 用两个9*9的filter进行卷积,结果是,每张图得到两个feature map。
卷积操作由theano的conv.conv2d实现,这里我们用随机参数W,b。结果有点像edge detector是不是?
Code: (详见注释)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat May 10 18:55:26 2014
@author: rachel
Function: convolution option of two pictures with same size (width,height)
input: 3 feature maps (3 channels <RGB> of a picture)
convolution: two 9*9 convolutional filters
"""
from theano.tensor.nnet import conv
import theano.tensor as T
import numpy, theano
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455)
# symbol variable
input = T.tensor4(name = 'input')
# initial weights
w_shape = (2,3,9,9) #2 convolutional filters, 3 channels, filter shape: 9*9
w_bound = numpy.sqrt(3*9*9)
W = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(rng.uniform(low = -1.0/w_bound, high = 1.0/w_bound,size = w_shape),
dtype = input.dtype),name = 'W')
b_shape = (2,)
b = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(rng.uniform(low = -.5, high = .5, size = b_shape),
dtype = input.dtype),name = 'b')
conv_out = conv.conv2d(input,W)
#T.TensorVariable.dimshuffle() can reshape or broadcast (add dimension)
#dimshuffle(self,*pattern)
# >>>b1 = b.dimshuffle('x',0,'x','x')
# >>>b1.shape.eval()
# array([1,2,1,1])
output = T.nnet.sigmoid(conv_out + b.dimshuffle('x',0,'x','x'))
f = theano.function([input],output)
# demo
import pylab
from PIL import Image
#minibatch_img = T.tensor4(name = 'minibatch_img')
#-------------img1---------------
img1 = Image.open(open('//home//rachel//Documents//ZJU_Projects//DL//Dataset//rachel.jpg'))
width1,height1 = img1.size
img1 = numpy.asarray(img1, dtype = 'float32')/256. # (height, width, 3)
# put image in 4D tensor of shape (1,3,height,width)
img1_rgb = img1.swapaxes(0,2).swapaxes(1,2).reshape(1,3,height1,width1) #(3,height,width)
#-------------img2---------------
img2 = Image.open(open('//home//rachel//Documents//ZJU_Projects//DL//Dataset//rachel1.jpg'))
width2,height2 = img2.size
img2 = numpy.asarray(img2,dtype = 'float32')/256.
img2_rgb = img2.swapaxes(0,2).swapaxes(1,2).reshape(1,3,height2,width2) #(3,height,width)
#minibatch_img = T.join(0,img1_rgb,img2_rgb)
minibatch_img = numpy.concatenate((img1_rgb,img2_rgb),axis = 0)
filtered_img = f(minibatch_img)
# plot original image and two convoluted results
pylab.subplot(2,3,1);pylab.axis('off');
pylab.imshow(img1)
pylab.subplot(2,3,4);pylab.axis('off');
pylab.imshow(img2)
pylab.gray()
pylab.subplot(2,3,2); pylab.axis("off")
pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0,0,:,:]) #0:minibatch_index; 0:1-st filter
pylab.subplot(2,3,3); pylab.axis("off")
pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0,1,:,:]) #0:minibatch_index; 1:1-st filter
pylab.subplot(2,3,5); pylab.axis("off")
pylab.imshow(filtered_img[1,0,:,:]) #0:minibatch_index; 0:1-st filter
pylab.subplot(2,3,6); pylab.axis("off")
pylab.imshow(filtered_img[1,1,:,:]) #0:minibatch_index; 1:1-st filter
pylab.show()

2. Pooling(降采样过程)
最常用的Maxpooling. 解决了两个问题:
1. 减少计算量
2. 旋转不变性 (原因自己悟)
PS:对于旋转不变性,回忆下SIFT,LBP:采用主方向;HOG:选择不同方向的模版
Maxpooling的降采样过程会将feature map的长宽各减半。(下面结果图中没有体现出来,python自动给拉到一样大了,但实际上像素数是减半的)
Code: (详见注释)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat May 10 18:55:26 2014
@author: rachel
Function: convolution option
input: 3 feature maps (3 channels <RGB> of a picture)
convolution: two 9*9 convolutional filters
"""
from theano.tensor.nnet import conv
import theano.tensor as T
import numpy, theano
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455)
# symbol variable
input = T.tensor4(name = 'input')
# initial weights
w_shape = (2,3,9,9) #2 convolutional filters, 3 channels, filter shape: 9*9
w_bound = numpy.sqrt(3*9*9)
W = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(rng.uniform(low = -1.0/w_bound, high = 1.0/w_bound,size = w_shape),
dtype = input.dtype),name = 'W')
b_shape = (2,)
b = theano.shared(numpy.asarray(rng.uniform(low = -.5, high = .5, size = b_shape),
dtype = input.dtype),name = 'b')
conv_out = conv.conv2d(input,W)
#T.TensorVariable.dimshuffle() can reshape or broadcast (add dimension)
#dimshuffle(self,*pattern)
# >>>b1 = b.dimshuffle('x',0,'x','x')
# >>>b1.shape.eval()
# array([1,2,1,1])
output = T.nnet.sigmoid(conv_out + b.dimshuffle('x',0,'x','x'))
f = theano.function([input],output)
# demo
import pylab
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib.pyplot import *
#open random image
img = Image.open(open('//home//rachel//Documents//ZJU_Projects//DL//Dataset//rachel.jpg'))
width,height = img.size
img = numpy.asarray(img, dtype = 'float32')/256. # (height, width, 3)
# put image in 4D tensor of shape (1,3,height,width)
img_rgb = img.swapaxes(0,2).swapaxes(1,2) #(3,height,width)
minibatch_img = img_rgb.reshape(1,3,height,width)
filtered_img = f(minibatch_img)
# plot original image and two convoluted results
pylab.figure(1)
pylab.subplot(1,3,1);pylab.axis('off');
pylab.imshow(img)
title('origin image')
pylab.gray()
pylab.subplot(2,3,2); pylab.axis("off")
pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0,0,:,:]) #0:minibatch_index; 0:1-st filter
title('convolution 1')
pylab.subplot(2,3,3); pylab.axis("off")
pylab.imshow(filtered_img[0,1,:,:]) #0:minibatch_index; 1:1-st filter
title('convolution 2')
#pylab.show()
# maxpooling
from theano.tensor.signal import downsample
input = T.tensor4('input')
maxpool_shape = (2,2)
pooled_img = downsample.max_pool_2d(input,maxpool_shape,ignore_border = False)
maxpool = theano.function(inputs = [input],
outputs = [pooled_img])
pooled_res = numpy.squeeze(maxpool(filtered_img))
#pylab.figure(2)
pylab.subplot(235);pylab.axis('off');
pylab.imshow(pooled_res[0,:,:])
title('down sampled 1')
pylab.subplot(236);pylab.axis('off');
pylab.imshow(pooled_res[1,:,:])
title('down sampled 2')
pylab.show()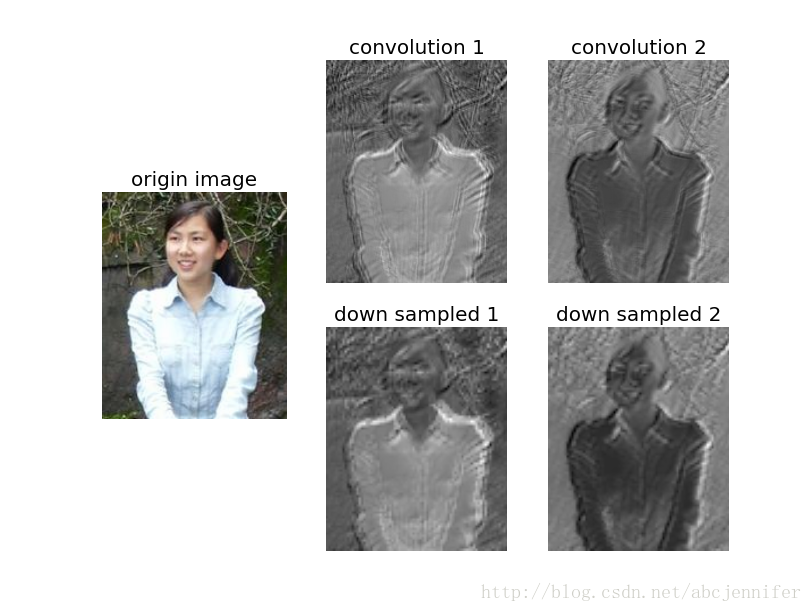 
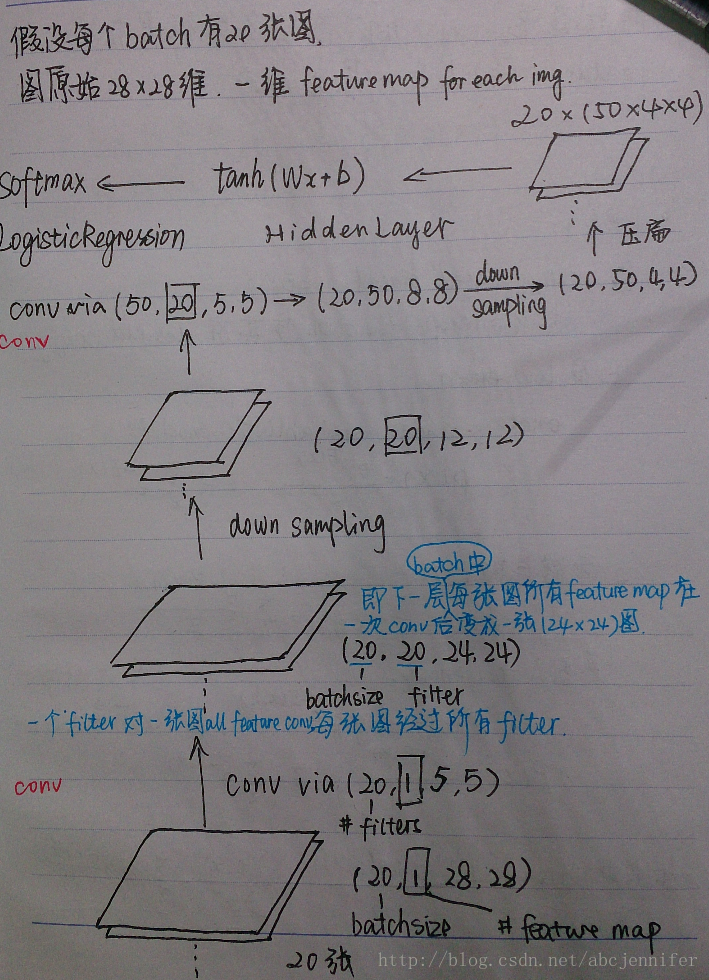
3. CNN结构
想必大家随便google下CNN的图都滥大街了,这里拖出来那时候学CNN的时候一张图,自认为陪上讲解的话画得还易懂(<!--囧-->)
废话不多说了,直接上Lenet结构图:(从下往上顺着箭头看,最下面为底层original input)
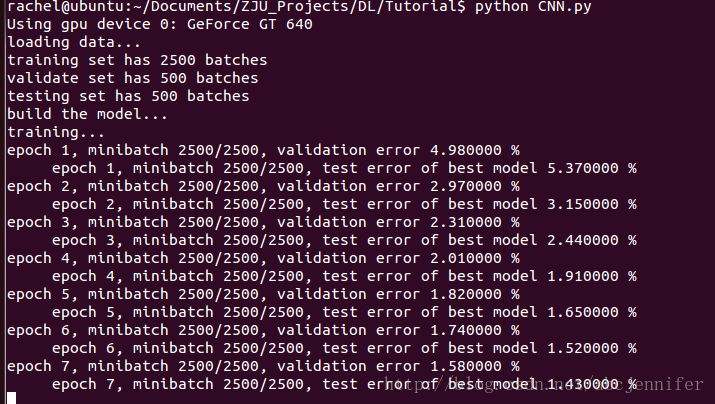
4. CNN代码
rng = numpy.random.RandomState(23455)
# transfrom x from (batchsize, 28*28) to (batchsize,feature,28,28))
# I_shape = (28,28),F_shape = (5,5),
N_filters_0 = 20
D_features_0= 1
layer0_input = x.reshape((batch_size,D_features_0,28,28))
layer0 = LeNetConvPoolLayer(rng, input = layer0_input, filter_shape = (N_filters_0,D_features_0,5,5),
image_shape = (batch_size,1,28,28))
#layer0.output: (batch_size, N_filters_0, (28-5+1)/2, (28-5+1)/2) -> 20*20*12*12
N_filters_1 = 50
D_features_1 = N_filters_0
layer1 = LeNetConvPoolLayer(rng,input = layer0.output, filter_shape = (N_filters_1,D_features_1,5,5),
image_shape = (batch_size,N_filters_0,12,12))
# layer1.output: (20,50,4,4)
layer2_input = layer1.output.flatten(2) # (20,50,4,4)->(20,(50*4*4))
layer2 = HiddenLayer(rng,layer2_input,n_in = 50*4*4,n_out = 500, activation = T.tanh)
layer3 = LogisticRegression(input = layer2.output, n_in = 500, n_out = 10) layer2+layer3:组成一个MLP(ANN)
训练模型:
cost = layer3.negative_log_likelihood(y)
params = layer3.params + layer2.params + layer1.params + layer0.params
gparams = T.grad(cost,params)
updates = []
for par,gpar in zip(params,gparams):
updates.append((par, par - learning_rate * gpar))
train_model = theano.function(inputs = [minibatch_index],
outputs = [cost],
updates = updates,
givens = {x: train_set_x[minibatch_index * batch_size : (minibatch_index+1) * batch_size],
y: train_set_y[minibatch_index * batch_size : (minibatch_index+1) * batch_size]}) 根据cost(最上层MLP的输出NLL),对所有层的parameters进行训练
剩下的具体见代码和注释。
PS:数据为MNIST所有数据





















 245
245

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








