摘要:在使用 ListView 中需要更改点击 item上面的文字颜色和相应 item的背景图片。在使用通过 <selector> 标签一直没有成功。后面搜索到 通过 adapter 的“getView“ 和 “setOnItemClickListener“ 达到效果。借此,把 多布局和合并相同内容一起记录一下
item 的点击效果
注意:在 setOnItemClickListener({ })中一定要使用 notifyDataSetChanged( ) ,进行刷新。不然没有对应的效果。
public class ColorAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context context ;
private List<String> mNames;
private List<String> mNums ;
private LayoutInflater inflater ;
//记录,上一次选中的 item(position)
private int old = -1 ;
private SparseBooleanArray isSelected ;
public ColorAdapter(Context context, List<String> mNames, List<String> mNums) {
super();
this.context = context;
this.mNames = mNames;
this.mNums = mNums;
inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
isSelected = new SparseBooleanArray();
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mNames.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return null;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder holder ;
if(convertView == null){
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_lv, parent, false);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.item = (LinearLayout) convertView.findViewById(R.id.rl_item);
holder.bookNum = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_num);
holder.bookCalss = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_class);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}else{
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
//通过取出存取的值,修改对应的颜色
if(isSelected.get(position)){
holder.item.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor("#ffff8800"));
holder.bookNum .setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#ffaa66cc"));
holder.bookCalss .setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#ff0099cc"));
}else{
holder.item.setBackgroundColor(Color.parseColor("#ff33b5e5"));
holder.bookNum .setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#ff000000"));
holder.bookCalss .setTextColor(Color.parseColor("#ffffffff"));
}
holder.bookNum.setText(mNums.get(position)) ;
holder.bookCalss.setText(mNames.get(position));
return convertView;
}
public void setSelectItem(int selected){
if(old != -1){
//把上次选中的 item(position),存一个 false的变量
this.isSelected.put(old, false);
}
//把当前的存一个 true 变量
this.isSelected.put(selected,true);
//最后把选中的赋给 old,便于下次选中,取消这一次
old = selected ;
}
class ViewHolder{
LinearLayout item;
TextView bookNum;
TextView bookCalss;
}
}listView.setOnItemClickListener(new OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view,
int position, long id) {
colorAdapter.setSelectItem(position);
colorAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
});大致的实现步骤:
- 设置 int old = -1,去记录上一点击的位置。默认为 -1,因为 position从 0 开始。SparseBooleanArray isSelected,记录一个 boolean值。
- 编写 “setSelectItem(int selected)“ 函数,把点击中的 position传递过来
- 在“getView( )“ 函数通过“if(isSelected.get(position)){选中项 }else{未选中项}“
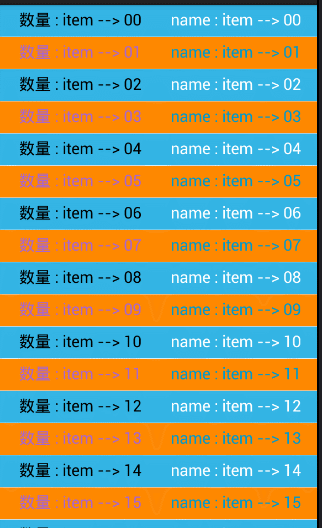
效果图如下:
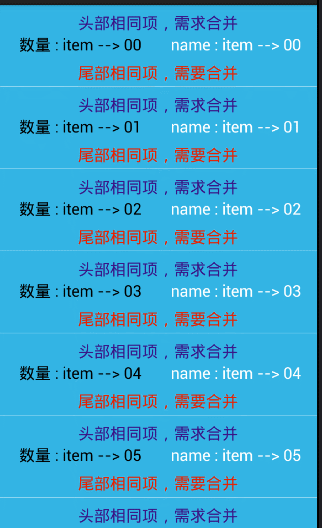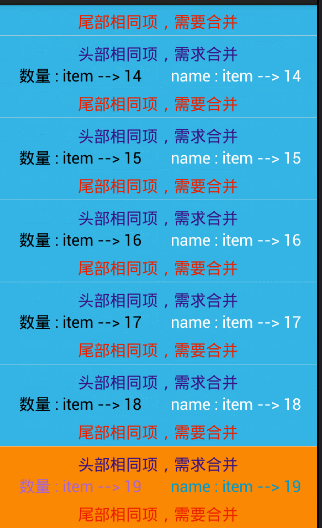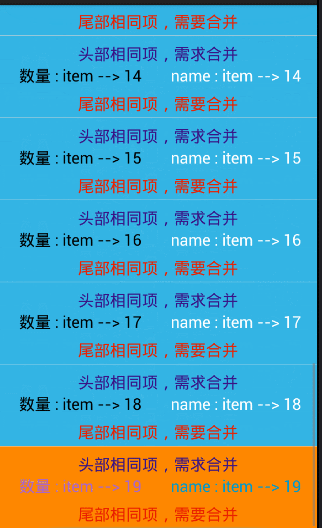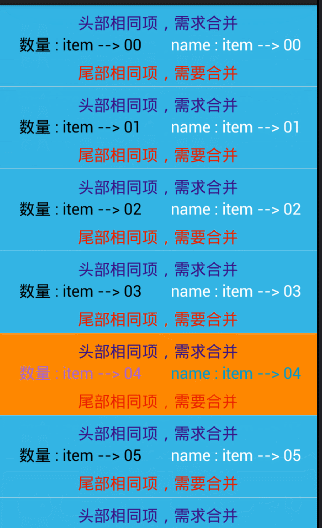
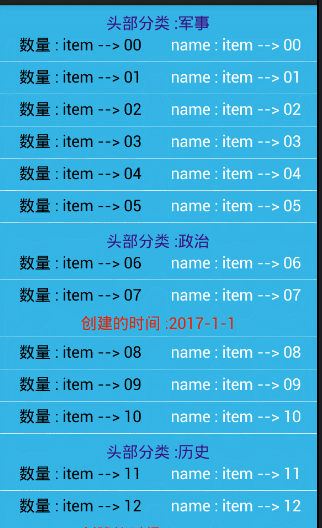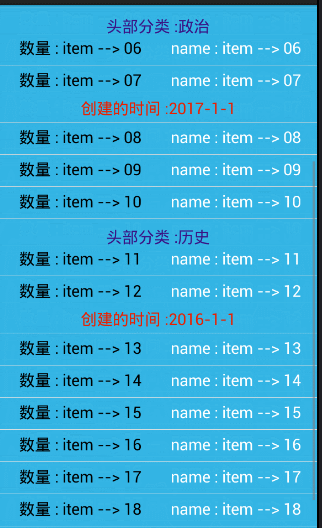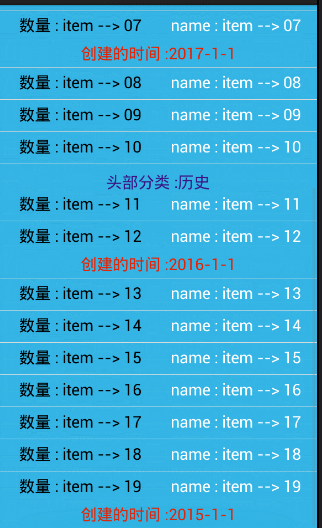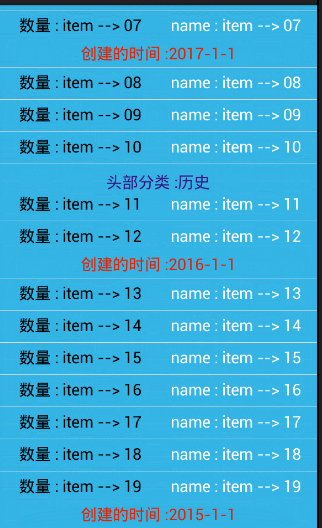
item 相同的合并
public class RepeatAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context context ;
private List<String> mNames;
private List<String> mNums ;
private LayoutInflater inflater ;
//模拟一个头部的分类
private String[] bookHead = {
"军事","政治","历史"
};
//模拟一个尾部的时间
private String[] bookDate = {
"2017-1-1","2016-1-1","2015-1-1"
};
private List<String> date ;
private List<String> head ;
public RepeatAdapter(Context context, List<String> mNames,
List<String> mNums) {
super();
this.context = context;
this.mNames = mNames;
this.mNums = mNums;
inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
date = new ArrayList<>();
head = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < mNames.size(); i++) {
//头部数据
if(i <= 5){
head.add("头部分类 :"+bookHead[0]);
}else if(i <= 10){
head.add("头部分类 :"+bookHead[1]);
}else{
head.add("头部分类 :"+bookHead[2]);
}
//尾部数据
if(i <= 7){
date.add("创建的时间 :"+bookDate[0]);
}else if(i <= 12){
date.add("创建的时间 :"+bookDate[1]);
}else{
date.add("创建的时间 :"+bookDate[2]);
}
}
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mNames.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder holder ;
if(convertView == null){
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_lv, parent, false);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.bookHead = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_head);
holder.bookNum = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_num);
holder.bookCalss = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_class);
holder.bookDate = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_date);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}else{
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
holder.bookHead.setText(head.get(position));
holder.bookNum.setText(mNums.get(position)) ;
holder.bookCalss.setText(mNames.get(position));
holder.bookDate.setText(date.get(position));
// //头部的合并
if(position == 0){//把,第一个去除,避免 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
//显示第一个 内容
holder.bookHead.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
holder.bookHead.setText(head.get(position));
}else{//隐藏后面,相同的内容 item
if(!TextUtils.equals(head.get(position), head.get(position-1))){
holder.bookHead.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
holder.bookHead.setText(head.get(position));
}else{
holder.bookHead.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
// 合并尾部
if(position == date.size()-1){ //把,最后一个去除,避免 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundException
holder.bookDate.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE) ;
holder.bookDate.setText(date.get(position));
}else{
if(!TextUtils.equals(date.get(position), date.get(position+1))){
holder.bookDate.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE) ;
holder.bookDate.setText(date.get(position));
}else{
holder.bookDate.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
return convertView ;
}
class ViewHolder{
TextView bookHead ;
TextView bookNum;
TextView bookCalss;
TextView bookDate;
}
} 相关图片:
item 的多种布局
public class MultiAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private Context context ;
private List<String> mNames;
private List<String> mNums ;
private LayoutInflater inflater ;
private final int ITEM_1 = 0 ;
private final int ITEM_2 = 1 ;
public MultiAdapter(Context context, List<String> mNames, List<String> mNums) {
super();
this.context = context;
this.mNames = mNames;
this.mNums = mNums;
inflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
@Override
public int getItemViewType(int position) {
return position%2 == 0 ? ITEM_1 : ITEM_2;
}
@Override
public int getViewTypeCount() {
return 2;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mNames.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolderOne holderOne = null ;
ViewHolderTwo holderTwo = null;
int type = getItemViewType(position);
if(convertView == null){
switch (type) {
case ITEM_1:
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_lv, parent, false);
holderOne = new ViewHolderOne();
holderOne.bookHead = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_head);
holderOne.bookNum = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_num);
holderOne.bookCalss = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_class);
holderOne.bookDate = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_date);
convertView.setTag(holderOne);
break;
case ITEM_2:
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.item_lv_copy, parent, false);
holderTwo = new ViewHolderTwo();
holderTwo.bookHead = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_head);
holderTwo.bookNum = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_num);
holderTwo.bookCalss = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_class);
holderTwo.bookDate = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_book_date);
convertView.setTag(holderTwo);
break;
}
}else{
switch (type) {
case ITEM_1:
holderOne = (ViewHolderOne) convertView.getTag();
break;
case ITEM_2:
holderTwo = (ViewHolderTwo) convertView.getTag();
break;
}
}
switch (type) {
case ITEM_1:
holderOne.bookHead.setVisibility(View.GONE);
holderOne.bookDate.setVisibility(View.GONE);
holderOne.bookNum.setText(mNums.get(position)) ;
holderOne.bookCalss.setText(mNames.get(position));
break;
case ITEM_2:
holderTwo.bookHead.setVisibility(View.GONE);
holderTwo.bookDate.setVisibility(View.GONE);
holderTwo.bookNum.setText(mNums.get(position)) ;
holderTwo.bookCalss.setText(mNames.get(position));
break;
}
return convertView;
}
class ViewHolderOne{
TextView bookHead ;
TextView bookNum;
TextView bookCalss;
TextView bookDate;
}
class ViewHolderTwo{
TextView bookHead ;
TextView bookNum;
TextView bookCalss;
TextView bookDate;
}
} 相关图片:
listview和Gridview的xml属性使用
| android:cacheColorHint | 表明这个列表的背景始终以单一、 固定的颜色绘制,可以优化绘制过程 |
| android:choiceMode | 为视图指定选着行为。可选的类型有:none、singleChoice、multipleChoice、multipleChoiceModal 默认为 none |
| android:drawSelectorOnTop | 若设为 true,选择器将绘制你在选中条目的上层。默认为 false |
| android:fastScrollEnabled | 设置是否允许使用快速滚动滑块 |
| android:listSelector | 设置选中项的可绘制对象,可以是图片或者颜色属性 |
| android:scrollingCache | 设置在滚动时是否使用绘制缓存,若设为 true,则将使滚动表现更快速。默认为 true |
| android:smoothScrollbar | 为真时,列表会使用更精确的基于条目在屏幕上的可见像素高度的计算方法。默认该属性为真,如果你的适配器需要绘制可变高的条目,他应该设为假。当该属性为真时,你在适配器在显示变高条目时,滚动条的把手会在滚动的过程中改变大小。当设为假时,列表只使用适配器中的条目数和屏幕上的可见条目来决定滚动条的属性 |
| android:stackFromBottom | 设置 GridView和ListView是否将内容从底部开始显示 |
| android:textFilterEnabled | 当设为真时,列表会将结果过滤为用户类型。前提是这个列表的Adapter必须支持Filterable接口 |
| android:transcriptMode | 设置列表的transcriptMode.有如下选项可选:
|
| android:divider | 在列表条目之间显示的drawable或color |
| android:dividerHeight | 用来指定divider的高度 |
| android:entries | 构成ListView的数组资源的引用。对于某些固定的资源,这个属性提供了比在程序中添加资源更加简便的方式 |
| android:footerDividersEnabled | 当设为false时,ListView将不会在各个footer之间绘制divider.默认为true |
| android:headerDividersEnabled | /当设为false时,ListView将不会在各个header之间绘制divider.默认为true |
| android:numColumns | 设置GridView列数,默认为 auto_fit |
| android:columnWidth | 每列的宽度,也就是Item的宽度 |
| android:stretchMode | 列应该如何拉伸以填充可用的空空间,默认为 columnWidth
|
| android:verticalSpacing | 两行之间的边距 |
| android:horizontalSpacing | 两列之间的边距 |
字符分割与比较
在有的时候,我们拿到一个路径的时候,需要进行对立面内容过滤或者需要把后面的毫秒值,截取下来,以便后续的处理。
/**
* Compares the specified string to this string to determine if the
* specified string is a prefix.
*
* @param prefix
* the string to look for.
* @return {@code true} if the specified string is a prefix of this string,
* {@code false} otherwise
* @throws NullPointerException
* if {@code prefix} is {@code null}.
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return startsWith(prefix, 0);
} 给定的字符串和自定义的字符串想比较,看是否前缀相同。eg:A.startsWith(B),A是给定的B是自己定义的字串
/**
* Compares the specified string to this string, starting at the specified
* offset, to determine if the specified string is a prefix.
*
* @param prefix
* the string to look for.
* @param start
* the starting offset.
* @return {@code true} if the specified string occurs in this string at the
* specified offset, {@code false} otherwise.
* @throws NullPointerException
* if {@code prefix} is {@code null}.
*/
public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int start) {
return regionMatches(start, prefix, 0, prefix.count);
} 指定字符串和自定义字符串从指定的 start 位置开始比较会否前缀相同。eg:A.startsWith(B,C),A 是否和B 从 C 位置开始是否前缀相同,A是给定的B是自己定义的字串。
&emsp;&emsp;相对应也用后缀最比较,endsWith(String suffix)
substring
s=s.substring(int begin);截取掉s从首字母起长度为begin的字符串,将剩余字符串赋值给s;
s=s.substring(int begin,int end);截取s中从begin开始至end结束时的字符串,并将其赋值给s;
split
split(String regularExpression)将一个字符串分割为子字符串,然后将结果作为字符串数组返回。
split(String regularExpression, int limit)根据匹配给定的正则表达式来拆分此字符串。
此方法返回的数组包含此字符串的子字符串,每个子字符串都由另一个匹配给定表达式的子字符串终止,或者由此字符串末尾终止。数组中的子字符串按它们在此字符串中出现的顺序排列。如果表达式不匹配输入的任何部分,那么所得数组只具有一个元素,即此字符串。
limit 参数控制模式应用的次数,因此影响所得数组的长度。如果该限制 n 大于 0,则模式将被最多应用n - 1 次,数组的长度将不会大于 n,而且数组的最后一项将包含所有超出最后匹配的定界符的输入。如果 n为非正,那么模式将被应用尽可能多的次数,而且数组可以是任何长度。如果 n 为0,那么模式将被应用尽可能多的次数,数组可以是任何长度,并且结尾空字符串将被丢弃。
split 的实现直接调用的 matcher 类的 split 的方法。“ . ”在正则表达式中有特殊的含义,因此我们使用的时候必须进行转义(\.)截取的效率问题。
数组的排序
<1> .利用Arrays带有的排序方法快速排序
int[] a={5,4,2,4,9,1};
Arrays.sort(a); //进行排序
<2> .冒泡排序算法
public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] args){//冒泡排序算法
for(int i=0;i<args.length-1;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<args.length;j++){
if (args[i]>args[j]){
int temp=args[i];
args[i]=args[j];
args[j]=temp;
}
}
}
return args;
}
<3> .选择排序算法
public static int[] selectSort(int[] args){//选择排序算法
for (int i=0;i<args.length-1 ;i++ ){
int min=i;
for (int j=i+1;j<args.length ;j++ ){
if (args[min]>args[j]){
min=j;
}
}
if (min!=i){
int temp=args[i];
args[i]=args[min];
args[min]=temp;
}
}
return args;
}<4> .插入排序算法
public static int[] insertSort(int[] args){//插入排序算法
for(int i=1;i<args.length;i++){
for(int j=i;j>0;j--){
if (args[j]<args[j-1]){
int temp=args[j-1];
args[j-1]=args[j];
args[j]=temp;
}else break;
}
}
return args;
}
Comparable与Comparator
Comparable与Comparator的区别






















 1869
1869

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








