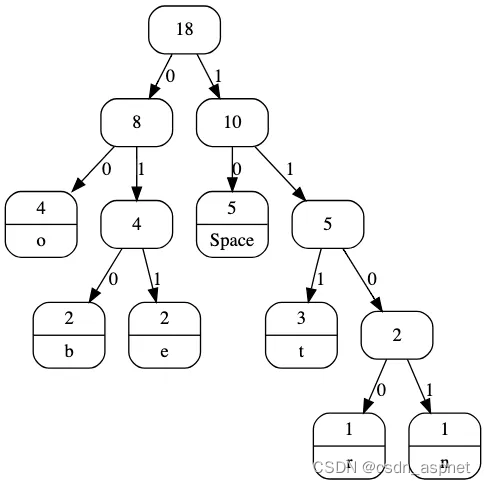
Huffman Tree 进行解码 示例图
c语言:c语言 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)_霍夫曼的贪婪c语言-CSDN博客
c++:c++ 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)_霍夫曼的贪婪算法设计核心代码-CSDN博客
c#:C# 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
c++ STL:c++ STL 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
java:java 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
python:python 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
javascript:JavaScript 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
我们在之前的文章中 讨论了霍夫曼编码。在这篇文章中,我们将讨论解码。
例子:
输入数据: AAAAAABCCCCCCDDEEEEE
频率: A:6,B:1,C:6,D:2,E:5
编码数据: 00000000000011001010101010111111110101010
哈夫曼树: “#”是用于内部节点的特殊字符,因为
内部节点不需要字符字段。
#(20)
/ \
#(12) #(8)
/ \ / \
A(6) C(6) E(5) #(3)
/ \
B(1) D(2)
‘A’ 的代码是 ‘00’,‘C’ 的代码是 ‘01’,..
解码数据: AAAAAAABCCCCCCDDEEEEE
输入数据: GeeksforGeeks
字符 频率为
e 10, f 1100, g 011, k 00, o 010, r 1101, s 111
编码的哈夫曼数据: 01110100011111000101101011101000111
解码的哈夫曼数据: geeksforgeeks
请按照以下步骤解决问题:
注意:要解码编码数据,我们需要霍夫曼树。我们遍历二进制编码数据。要找到与当前位对应的字符,我们使用以下简单步骤:
1、我们从根开始,依次进行,直到找到叶子。
2、如果当前位为 0,我们就移动到树的左节点。
3、如果该位为 1,我们移动到树的右节点。
4、如果在遍历过程中遇到叶节点,我们会打印该特定叶节点的字符,然后再次从步骤 1 开始继续迭代编码数据。
下面的代码将一个字符串作为输入,对其进行编码,并将其保存在变量编码字符串中。然后对其进行解码并打印原始字符串。
下面是上述方法的实现:
// To map each character its huffman value
let codes = {};
// To store the frequency of character of the input data
let freq = {};
// A Huffman tree node
class MinHeapNode {
constructor(data, freq) {
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.data = data;
this.freq = freq;
}
// Define the comparison method for sorting the nodes in the heap
compareTo(other) {
return this.freq - other.freq;
}
}
// Create an empty min-heap
let minHeap = [];
// Utility function to print characters along with their huffman value
function printCodes(root, str) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (root.data !== "$") {
console.log(root.data + " : " + str);
}
printCodes(root.left, str + "0");
printCodes(root.right, str + "1");
}
// Utility function to store characters along with their huffman value in a hash table
function storeCodes(root, str) {
if (!root) {
return;
}
if (root.data !== "$") {
codes[root.data] = str;
}
storeCodes(root.left, str + "0");
storeCodes(root.right, str + "1");
}
// Function to build the Huffman tree and store it in minHeap
function HuffmanCodes(size) {
for (let key in freq) {
minHeap.push(new MinHeapNode(key, freq[key]));
}
// Convert the array to a min-heap using the built-in sort method
minHeap.sort((a, b) => a.compareTo(b));
while (minHeap.length !== 1) {
let left = minHeap.shift();
let right = minHeap.shift();
let top = new MinHeapNode("$", left.freq + right.freq);
top.left = left;
top.right = right;
minHeap.push(top);
// Sort the array to maintain the min-heap property
minHeap.sort((a, b) => a.compareTo(b));
}
storeCodes(minHeap[0], "");
}
// Utility function to store map each character with its frequency in input string
function calcFreq(str) {
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
let char = str.charAt(i);
if (freq[char]) {
freq[char]++;
} else {
freq[char] = 1;
}
}
}
// Function iterates through the encoded string s
// If s[i] == '1' then move to node.right
// If s[i] == '0' then move to node.left
// If leaf node, append the node.data to our output string
function decode_file(root, s) {
let ans = "";
let curr = root;
let n = s.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == "0") {
curr = curr.left;
} else {
curr = curr.right;
}
// Reached leaf node
if (!curr.left && !curr.right) {
ans += curr.data;
curr = root;
}
}
return ans + "\0";
}
// Driver code
let str = "geeksforgeeks";
let encodedString = "";
let decodedString = "";
calcFreq(str);
HuffmanCodes(str.length);
console.log("Character With their Frequencies:")
let keys = Array.from(Object.keys(codes))
keys.sort()
for (var key of keys)
console.log(key, codes[key])
for (var i of str)
encodedString += codes[i]
console.log("\nEncoded Huffman data:")
console.log(encodedString)
// Function call
decodedString = decode_file(minHeap[0], encodedString)
console.log("\nDecoded Huffman Data:")
console.log(decodedString)
输出:
具有以下频率的字符:
e 10
f 1100
g 011
k 00
o 010
r 1101
s 111
编码的哈夫曼数据:
01110100011111000101101011101000111
解码的哈夫曼数据:
geeksforgeeks
时间复杂度:
霍夫曼编码算法的时间复杂度为O(n log n),其中n为输入字符串的字符个数。辅助空间复杂度也是O(n),其中n为输入字符串的字符个数。
在给定的 JavaScript 实现中,时间复杂度主要由使用优先级队列创建 Huffman 树决定,这需要 O(n log n) 时间。空间复杂度主要由用于存储字符频率和代码的映射决定,这需要 O(n) 空间。用于打印代码和存储代码的递归函数也增加了空间复杂度。
比较输入文件大小和输出文件大小:
比较输入文件大小和霍夫曼编码的输出文件。我们可以用一种简单的方法计算输出数据的大小。假设我们的输入是一个字符串“geeksforgeeks”,存储在文件 input.txt 中。
输入文件大小:
输入: “geeksforgeeks”
字符总数即输入长度:13
大小: 13 个字符出现次数 * 8 位 = 104 位或 13 个字节。
输出文件大小:
输入: “geeksforgeeks”
——————————————————
字符 | 频率 | 二进制哈夫曼值 |
——————————————————
e | 4 | 10 |
f | 1 | 1100 |
g | 2 | 011 |
k | 2 | 00 |
o | 1 | 010 |
r | 1 | 1101 |
s | 2 | 111 |
—————————————————
因此要计算输出大小:
e:出现 4 次 * 2 位 = 8 位
f:出现 1 次 * 4 位 = 4 位
g:出现 2 次 * 3 位 = 6 位
k:出现 2 次 * 2 位 = 4 位
o:出现 1 次 * 3 位 = 3 位
r:出现 1 次 * 4 位 = 4 位
s:出现 2 次 * 3 位 = 6 位
总和: 35 位,约 5 字节
由此可见,编码后的数据量是比较大的,上面的方法也可以帮我们确定N的值,也就是编码后数据的长度。























 1385
1385











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








