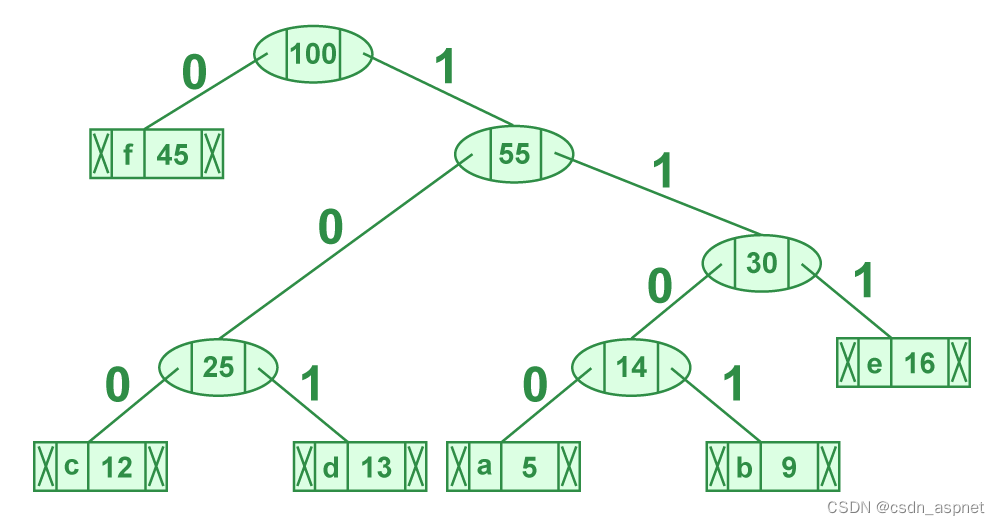
排序输入的高效霍夫曼编码 示例图
建议先阅读下面的文章:
c语言:c语言 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)_霍夫曼的贪婪c语言-CSDN博客
c++:c++ 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)_霍夫曼的贪婪算法设计核心代码-CSDN博客
c#:C# 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
c++ STL:c++ STL 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
java:java 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
python:python 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
javascript:JavaScript 霍夫曼编码 | 贪婪算法(Huffman Coding | Greedy Algo)-CSDN博客
上面讨论的算法的时间复杂度是 O(nLogn)。如果我们知道给定的数组是排好序的(按频率非递减顺序),我们可以在 O(n) 时间内生成霍夫曼码。以下是针对已排序输入的 O(n) 算法。
1.创建两个空队列。
2.为每个唯一字符创建一个叶节点,并按频率非递减顺序将其入队到第一个队列。最初第二个队列是空的。
3.通过检查两个队列的前面,使两个频率最小的节点出队。重复以下步骤两次
1. 如果第二个队列为空,则从第一个队列出队。
2. 如果第一个队列为空,则从第二个队列出队。
3. 否则,比较两个队列的前面,并使最小的节点出队。
4.创建一个新的内部节点,其频率等于两个节点频率之和。将第一个出队节点设为其左子节点,将第二个出队节点设为右子节点。将此节点入队到第二个队列。
5.重复步骤 3 和 4,直到队列中有多个节点。剩下的节点就是根节点,树就完成了。
示例代码:
// JavaScript program for the above approach
// Class for the nodes of the Huffman tree
class QueueNode {
constructor(data = null, freq = null, left = null, right = null) {
this.data = data;
this.freq = freq;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
// Function to check if the following
// node is a leaf node
isLeaf() {
return (this.left == null && this.right == null);
}
}
// Class for the two Queues
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.queue = [];
}
// Function for checking if the
// queue has only 1 node
isSizeOne() {
return this.queue.length == 1;
}
// Function for checking if
// the queue is empty
isEmpty() {
return this.queue.length == 0;
}
// Function to add item to the queue
enqueue(x) {
this.queue.push(x);
}
// Function to remove item from the queue
dequeue() {
return this.queue.shift();
}
}
// Function to get minimum item from two queues
function findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue) {
// Step 3.1: If second queue is empty,
// dequeue from first queue
if (secondQueue.isEmpty()) {
return firstQueue.dequeue();
}
// Step 3.2: If first queue is empty,
// dequeue from second queue
if (firstQueue.isEmpty()) {
return secondQueue.dequeue();
}
// Step 3.3: Else, compare the front of
// two queues and dequeue minimum
if (firstQueue.queue[0].freq < secondQueue.queue[0].freq) {
return firstQueue.dequeue();
}
return secondQueue.dequeue();
}
// The main function that builds Huffman tree
function buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size) {
// Step 1: Create two empty queues
let firstQueue = new Queue();
let secondQueue = new Queue();
// Step 2: Create a leaf node for each unique
// character and Enqueue it to the first queue
// in non-decreasing order of frequency.
// Initially second queue is empty.
for (let i = 0; i < size; i++) {
firstQueue.enqueue(new QueueNode(data[i], freq[i]));
}
// Run while Queues contain more than one node.
// Finally, first queue will be empty and
// second queue will contain only one node
while (!(firstQueue.isEmpty() && secondQueue.isSizeOne())) {
// Step 3: Dequeue two nodes with the minimum
// frequency by examining the front of both queues
let left = findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue);
let right = findMin(firstQueue, secondQueue);
// Step 4: Create a new internal node with
// frequency equal to the sum of the two
// nodes frequencies. Enqueue this node
// to second queue.
let top = new QueueNode("$", left.freq + right.freq, left, right);
secondQueue.enqueue(top);
}
return secondQueue.dequeue();
}
// Prints huffman codes from the root of
// Huffman tree. It uses arr[] to store codes
function printCodes(root, arr) {
// Assign 0 to left edge and recur
if (root.left) {
arr.push(0);
printCodes(root.left, arr);
arr.pop();
}
// Assign 1 to right edge and recur
if (root.right) {
arr.push(1);
printCodes(root.right, arr);
arr.pop();
}
// If this is a leaf node, then it contains
// one of the input characters, print the
// character and its code from arr[]
if (root.isLeaf()) {
let output = root.data + ": ";
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
output += arr[i];
}
console.log(output);
}
}
// The main function that builds a Huffman
// tree and print codes by traversing the
// built Huffman tree
function HuffmanCodes(data, freq, size) {
// Construct Huffman Tree
let root = buildHuffmanTree(data, freq, size);
// Print Huffman codes using the Huffman
// tree built above
let arr = [];
printCodes(root, arr);
}
// Driver code
let arr = ["a", "b", "c", "d", "e", "f"];
let freq = [5, 9, 12, 13, 16, 45];
let size = arr.length;
HuffmanCodes(arr, freq, size);
// This code is contributed by Prince Kumar
输出:
f: 0
c: 100
d: 101
a: 1100
b: 1101
e: 111
时间复杂度: O(n)
如果输入未排序,则需要先对其进行排序,然后才能通过上述算法进行处理。排序可以使用堆排序或合并排序来完成,两者都在 Theta(nlogn) 中运行。因此,对于未排序的输入,总体时间复杂度变为 O(nlogn)。
辅助空间: O(n)























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








