标准C/C++的二个计时函数time()及clock()
time_t time(time_t *timer);
返回以格林尼治时间(GMT)为标准,从1970年1月1日00:00:00到现在的此时此刻所经过的秒数。
time_t实际是个long长整型typedef long time_t;
头文件:#include <time.h>
clock_t clock(void);
返回进程启动到调用函数时所经过的CPU时钟计时单元(clock tick)数,在MSDN中称之为挂钟时间(wal-clock),以毫秒为单位。
clock_t实际是个long长整型typedef long clock_t;
头文件:#include <time.h>
Windows系统API函数
timeGetTime()、GetTickCount()及QueryPerformanceCounter()
DWORD timeGetTime(VOID);
返回系统时间,以毫秒为单位。系统时间是从系统启动到调用函数时所经过的毫秒数。注意,这个值是32位的,会在0到2^32之间循环,约49.71天。
头文件:#include <Mmsystem.h>
引用库:#pragma comment(lib, "Winmm.lib")
DWORD WINAPI GetTickCount(void);
这个函数和timeGetTime()一样也是返回系统时间,以毫秒为单位。
头文件:直接使用#include <windows.h>就可以了。
高精度计时,以微秒为单位(1毫秒=1000微秒)。
先看二个函数的定义
BOOL QueryPerformanceCounter(LARGE_INTEGER *lpPerformanceCount);
得到高精度计时器的值(如果存在这样的计时器)。
BOOL QueryPerformanceFrequency(LARGE_INTEGER *lpFrequency);
返回硬件支持的高精度计数器的频率(次每秒),返回0表示失败。
再看看LARGE_INTEGER
它其实是一个联合体,可以得到__int64 QuadPart;也可以分别得到低32位DWORD LowPart和高32位的值LONG HighPart。
在使用时,先使用QueryPerformanceFrequency()得到计数器的频率,再计算二次调用QueryPerformanceCounter()所得的计时器值之差,用差去除以频率就得到精确的计时了。
头文件:直接使用#include <windows.h>就可以了。
下面给出示例代码,可以在你电脑上测试下。
//Windows系统下time(),clock(),timeGetTime(),GetTickCount(),QueryPerformanceCounter()来计时 by MoreWindows#include <stdio.h>#include <windows.h>#include <time.h> //time_t time() clock_t clock()#include <Mmsystem.h> //timeGetTime()#pragma comment(lib, "Winmm.lib") //timeGetTime()int main(){ //用time()来计时 秒 time_t timeBegin, timeEnd; timeBegin = time(NULL); Sleep(1000); timeEnd = time(NULL); printf("%d\n", timeEnd - timeBegin); //用clock()来计时 毫秒 clock_t clockBegin, clockEnd; clockBegin = clock(); Sleep(800); clockEnd = clock(); printf("%d\n", clockEnd - clockBegin); //用timeGetTime()来计时 毫秒 DWORD dwBegin, dwEnd; dwBegin = timeGetTime(); Sleep(800); dwEnd = timeGetTime(); printf("%d\n", dwEnd - dwBegin); //用GetTickCount()来计时 毫秒 DWORD dwGTCBegin, dwGTCEnd; dwGTCBegin = GetTickCount(); Sleep(800); dwGTCEnd = GetTickCount(); printf("%d\n", dwGTCEnd - dwGTCBegin); //用QueryPerformanceCounter()来计时 微秒 LARGE_INTEGER large_interger; double dff; __int64 c1, c2; QueryPerformanceFrequency(&large_interger); dff = large_interger.QuadPart; QueryPerformanceCounter(&large_interger); c1 = large_interger.QuadPart; Sleep(800); QueryPerformanceCounter(&large_interger); c2 = large_interger.QuadPart; printf("本机高精度计时器频率%lf\n", dff); printf("第一次计时器值%I64d 第二次计时器值%I64d 计时器差%I64d\n", c1, c2, c2 - c1); printf("计时%lf毫秒\n", (c2 - c1) * 1000 / dff); printf("By MoreWindows\n"); return 0;}
下面是本人电脑上的测试结果:
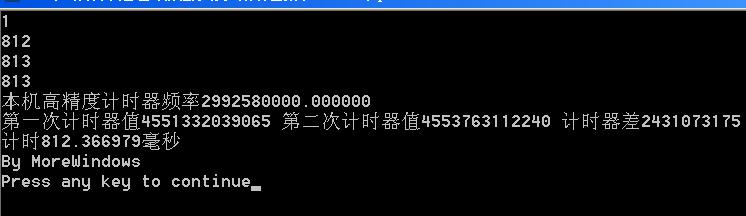
转载请标明出处,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/morewindows/article/details/6854764
再分享一下我老师大神的人工智能教程吧。零基础!通俗易懂!风趣幽默!还带黄段子!希望你也加入到我们人工智能的队伍中来!https://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow





















 4024
4024

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








