0、AGPS
之前的文章中讲了,AGPS是通过移动网络下载GPS辅助数据来达到快速定位的一种方法。如下为AGPS系统图。
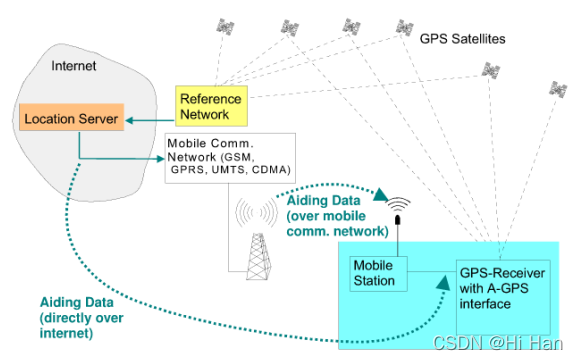
为了传输辅助数据,它有着两种不同的架构:
- 控制层(Control Plane, C-Plane, CP)架构;
- 用户层(User Plane, U-Plane, UP)架构;
关于C-Plane和U-Plane的区别,可以看下面这幅图:

At user plane side, the application creates data packets that are processed by protocols such as TCP, UDP and IP, while in the control plane, the radio resource control (RRC) protocol writes the signalling messages that are exchanged between the base station and the mobile. In both cases, the information is processed by the packet data convergence protocol (PDCP), the radio link control (RLC) protocol and the medium access control (MAC) protocol, before being passed to the physical layer for transmission.
再来看AGPS的C-Plane架构和U-Plane架构
对于C-Plane架构,Location Server和用户终端,通过7号信令系统(SS7)传输控制信号,如下为C-Plane架构的AGPS系统:
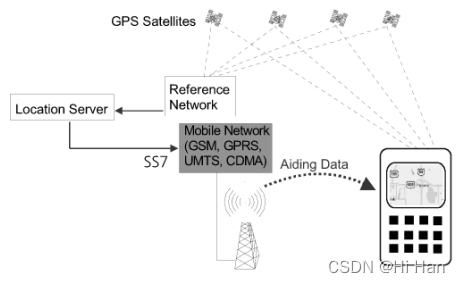
对于 U-Plane架构,Location Server和用户终端通过一套标准的数据传输协议来传输控制信号,例如TCP/IP、UDP,如下 U-Plane架构的AGPS系统:

后来,OMA(Open Mobile Alliance)发布了一个标准协议SUPL,有关U-Plane的标准、协议、规则等都被整合其中,它通过现有的移动通信网络来传输辅助数据。
有关SUPL和C-Plane的对比,可以看博通文档中的一段话:
Two functional entities must be added to the C-Plane network in order to support location services: a Serving Mobile Location Center (SMLC), which controls the coordination and scheduling of the resources required to locate the mobile device; and a Gateway Mobile Location Center (GMLC), which controls the delivery of position data, user authorization, charging, and more. Although simple enough in concept, the actual integration of SMLCs and GMLCs into the Control Plane requires multi-vendor, multi-platform upgrades, as well as modifications to the interfaces between the various network elements. As with any complex endeavor, the larger the scope of the program and the more parties that are involved, the greater the number of points at which failures can occur. LBS through SUPL is much less cumbersome. The SLP takes on most of the tasks that would normally be assigned to the SMLC and GMLC, drastically reducing interaction with Control Plane elements. SUPL supports the same protocols for location data that were developed for the C-Plane, which means little or no modification of C-Plane interfaces is required. Because SUPL is implemented as a separate network layer, MNOs have the choice of installing and maintaining their own SLPs or outsourcing LBS to a Location Services Provider such as Broadcom. The transition from C-Plane location technologies to SUPL AGPS location, where SLPs will assume many of the tasks that are performed by the GMLC or SMLC, is expected to be a process that operators will go through in incremental steps. Broadcom has addressed this by segmenting responsibilities between the Broadcom SLP product and existing GMLCs to avoid duplication of functionality.
1、SUPL
关于supl相关的文档,下载地址:www.openmobilealliance.org - /release/SUPL/
重点看两篇文档,OMA-AD-SUPL和OMA-TS-ULP开头命名的文档。
至于看哪个版本,就看你使用的是哪个版本。如果你只是单纯的学习,可以找Approved Version的,例如我看的这个:
1.1 SUPL定义
先看一下文档关于supl的解释
Secure User Plane Location (SUPL) is an Enabler which utilizes existing standards where available and possible, to transfer assistance data and positioning data over a User Plane bearer, such as IP, to aid network and SUPL Enabled Terminal (SET) based positioning technologies in the calculation of a SET’s position. SUPL includes but is not limited to the definition of a Location User Plane (Lup) Reference Point and corresponding interface between the SUPL Location Platform (SLP) and SET, security functions (e.g., authentication, authorization), charging functions, roaming functions, and privacy functions.
SUPL utilizes existing standards where available and possible, and SUPL should be extensible to enabling more positioning technologies as the need arises so that they utilize the same mechanism.
1.2、SUPL架构
如下图所示,为文档给出的supl的架构图,

SUPL Location Platform(SLP) SUPL定位平台,节点“Location Server”。
- SUPL Location Center(SLC) SUPL定位中心
- SUPL Positioning Center (SPC) SUPL位置中心
SUPL Enabled Terminal(SET)SUPL使能终端,节点“End User Device”。
The MLS Application/SUPL Agent,节点“Location Based Application.”,包含在 “Requesting Applications”。
In generic environments, the required SUPL components are the SET and the network component SLP containing the SLC and SPC systems. The SET communicates with the network over the Lup interface. In environments where SLC and SPC are deployed as separate entities, SLC and SPC communicate with each other over the Llp interface. In environments where the SLC and the SPC are deployed as a single entity, the Llp interface does not apply.
The communication mechanisms for conveying location request notification from the SLP to the SET include OMA Push, SMS, UDP/IP and SIP Push. The protocols involved in OMA Push are PAP (Push Access Protocol) for conveying location request notification from the SLP to the PPG (Push Proxy Gateway), and POTAP (Push Over-The-Air Protocol) and SIP Push for conveying such notification from the PPG to the SET. SMS delivery of notification is another option, and can be initiated either by SMS Trigger from the SLP, or by WAP notification. Protocol interfaces for SMS delivery a specified in the diagram, since the interface between SLP and SMSC/MC is proprietary (e.g., SMPP) and is no 3GPP/3GPP2. The communication path from SMSC/MC to the SET is outside the scope of this document.
In proxy-mode the SUPL application message exchange for service management and positioning determination occurs between the SLP and the SET.
In non-proxy-mode the service management related message exchange occurs between the SLC and the SET, where the positioning determination related message exchange occurs between the SPC and the SET.
The Lup interface is used between the SLP and SET. The Lup carries two types of messaging:
o Messaging destined to the SLC system within the SLP – Lup Location Management Messages,使能SLP,在SLP与SET之间建立会话,执行SLC功能;
o Messaging destined to the SPC system within the SLP – Lup Positioning Determination Messages,在SLP与SET之间传送位置计算信息,执行SPC功能;
1.2.1 SLP
For any SET, a SLP can perform the role of the home SLP (H-SLP), visited SLP (V-SLP) or emergency SLP (E-SLP). A particular SLP may perform one or more of these roles for multiple SETs.
The H-SLP for a particular SET contains the subscription, authentication and privacy related data for the SET and would generally be associated with or part of the SET’s home PLMN.
The E-SLP for a particular SET is an SLP associated with or contained within the PLMN serving the SET that is employed by the serving PLMN to perform positioning in association with an emergency services call initiated by the SET. The E-SLP may be the H-SLP if the SET is not roaming. If the SET is roaming and the E-SLP is not the H-SLP or if the SET is not roaming and the E-SLP is physically or logically separate to the H-SLP, SUPL positioning may occur without interaction with the H-SLP.
The V-SLP for a particular SET would be an SLP chosen by the H-SLP or E-SLP to assist positioning. In the case of an HSLP, the SET would be roaming outside the coverage area of the H-SLP. In the case of an E-SLP, the SET would have initiated an emergency services call outside the coverage area of the E-SLP. Note that the coverage area of an SLP need not be the same as the coverage area of any PLMN with which the SLP is associated.
It should be noted that SUPL roaming will not occur and a V-SLP will not be needed for positioning associated with emergency services calls if calls can only be placed within the service area of an E-SLP.
总结一下,H-SLP是在用户的PLMN下,与SET完成订阅、安全认证、隐私数据传输等操作。E-SLP是针对紧急通话的一种SLP,若用户处于非漫游状态,则可以当H-SLP工作,若用户处于漫游状态并且E-SLP不为H-SLP,或者用户处于非漫游状态并且H-SLP和S-SLP处于物理或者逻辑层面上的分离,SUPL定位可以在E-SLP与SET之间直接进行。V-SLP是用于辅助H-SLP和E-SLP定位的,当用户不在H-SLP或者E-SLP覆盖范围下,则需要V-SLP的协助。
1.2.2 SUPL Location Center (SLC)
SLC 系统协调网络中 SUPL 的操作,并在与SET交互时通过用户平面承载执行以下功能:
- SUPL Privacy Function (SPF)
- SUPL Initiation Function (SIF)
- SUPL Security Function (SSF)
- SUPL Roaming Support Function (SRSF)
- SUPL Charging Function (SCF)
- SUPL Service Management Function (SSMF)
- SUPL Triggering Function (STF)
- SUPL Positioning Calculation Function (SPCF)
- ——SLC可以执行将位置标识符转换为以纬度和经度数据表示的地理位置。 该位置可能满足 SUPL 代理请求的 QoP。 在 MNO 环境中,这通常称为 Cell-ID 位置。
1.2.3 SUPL Positioning Center (SPC)
SPC支持下面的功能:
- SUPL Security Function (SSF)
- SUPL Assistance Delivery Function (SADF)
- SUPL Reference Retrieval Function (SRRF)
- SUPL Positioning Calculation Function (SPCF)
1.2.4 SUPL Enabled Terminal (SET)
SET 支持在 SUPL 中定义的过程,因为它通过用户平面承载与网络交互。 SET 可能支持以下一项或多项功能,具体取决于其功能和 SUPL 提供者的业务规则:
- SUPL Privacy Function (SPF)
- SUPL Security Function (SSF)
- SUPL SET Provisioning Function (SSPF)
- SUPL Initiation Function (SIF)
- SUPL Triggering Function (STF)
如果SET还支持SET-Based或者SET-Assisted 定位计算,那么SET会支持下面的功能:
- SUPL Positioning Calculation Function (SPCF)
- SUPL Assistance Delivery Function (SADF)
1.2.5 Allocation of SUPL Functions to SUPL Subsystems

1.2.6 SUPL Location Services Functional Group
本节标识并描述了 SUPL 位置服务功能组内的逻辑功能实体。 本节的目的是确保识别启用 SUPL 服务所需的所有可能功能。
1.2.6.1 SUPL Privacy Function (SPF)
SPF 是确保 SET 用户的隐私得到尊重的功能。 必须考虑以下几点:
- 遵守目标 SET 用户隐私设置,无论 SUPL 网络发起的服务或 SET 发起的服务如何;
- 遵守目标 SET 用户的通知和验证设置;
- 允许覆盖目标 SET 用户隐私设置,如当地法规要求或允许的,用于紧急服务呼叫定位;
- 允许未来可能适用于目标 SET 用户的合法覆盖规则;
SUPL 可能会使用其他促成因素来实施部分 SPF。 或者,SPF可以在SET中实现。
1.2.6.2 SUPL Initiation Function (SIF)
SIF 为 SUPL 网络提供了一种使用 SET 发起交易的机制。SIF在启用 SUPL 网络启动服务时特别重要。
在 SUPL 网络发起服务的情况下,SUPL 网络使用以下方法之一发起 SUPL 交易:
- OMA Push
- SMS directly in an MNO environment
- UDP/IP
- SIP Push [SIP PUSH]
注意:OMA Push被认为是任何使用推送访问协议 (PAP) 的传递方法,无论是使用 POTAP 还是 SIP 推送来最终传递给 SET。
根据 SET 能力,适用的 SIF 方法被SUPL 网络所应用(确定 SET 能力超出了 SUPL 的范围)。
SET 应支持使用 POTAP、SIP Push 和 SMS 中的至少一种的 SIF。能够使用 IP 承载【1】发起紧急服务呼叫的 SET 还应支持使用 UDP/IP 或 SIP Push 的 SIF。
对于 GSM/WCDMA/TD-SCDMA 部署,SET 和 SLP 都应支持使用 OMA Push 的 SIF。对于 CDMA/CDMA2000 部署,SET 和 SLP 都应支持使用 MT SMS 的 SIF。
对其他传输协议的支持是可选的。
【1】虽然本规范要求 SET 支持与使用 IP 承载发起的紧急服务呼叫相关的定位,但网络运营商可以选择不使用 SUPL——例如,可以使用控制平面定位解决方案。
1.2.6.3 SUPL Security Function (SSF)
SSF 使 SUPL 网络能够认证和授权 SET,并使 SET 能够认证和授权 SUPL 网络。这对于安全启用 SUPL 网络发起的服务和 SET 发起的服务很重要。 SSF 还提供机密性和数据完整性。
1.2.6.4 SUPL Roaming Support Function (SRSF)
对于与紧急服务呼叫无关的定位,SUPL 漫游发生在 SET 离开其 H-SLP 的服务区域时。 对于与紧急服务呼叫相关的定位,当 SET 不在 E-SLP 的服务区域内时会发生 SUPL 漫游。 H-SLP 或 E-SLP 的服务区域包括 H-SLP 或 E-SLP 可以在不联系其他 SLP 的情况下向 SET 提供位置估计或相关辅助数据的区域。 应当注意,H-SLP 或 E-SLP 服务区不一定与底层无线网络的服务区相关联。
SUPL 漫游有多种变体,总结如下:
- H-SLP 或 E-SLP 可以请求 V-SLP 提供初始位置估计,例如,基于位置 ID。
- H-SLP 或 E-SLP 可以请求 V-SLP 提供 Lup 定位确定和 SPC 功能。
应用哪个变体的决定是特定于实现的,并且超出了本规范的范围。 出于参考目的,该决定将取决于以下因素:
- SUPL 提供商之间的漫游协议;
- 位置 ID;
- 缓存信息;
- H-SLP/SET 或 E-SLP/SET 协商参数,例如定位方法。
1.2.6.5 SUPL Charging Function (SCF)
SCF 负责 SLP 内的收费活动。 这包括对 MLS 应用程序、SUPL 代理和 SET 用户的收费。
SCF 的主要任务是收集适当的计费相关数据和 SUPL 提供商之间的计费数据。
此外,SCF 可以基于对可用计费数据的评估授权 SLP 中的活动(例如,辅助数据和位置传递)。 SCF 的更多细节不在 SUPL 的范围内。
1.2.6.7 SUPL SET Provisioning Function (SSPF)
SSPF 是管理 SET 配置的功能。 SET 应配备 Home SLP 的地址。 在 SET 中提供 Home SLP 地址可以使用 OMA 使能器来规定 SET。
1.2.6.8 SUPL Triggering Function (STF)
SUPL 触发功能是在 SLP 和 SET 之间传达周期性和基于事件的触发并评估何时满足这些触发条件的功能。
对于网络发起的触发服务,SLP 向 SET 提供触发标准。 对于 SET 发起的触发服务,SET 将触发标准发送到 SLP。 在某些情况下,SLP 还可以在 SET 发起的触发服务期间向 SET 返回额外的触发标准(例如,如果 SET 已请求具有地理目标区域的基于事件的触发,则返回区域 ID 列表)。
SET 有责任确定何时满足这些触发标准。
对于周期性触发,标准可能包括:
- Fix的数量;
- Fix之间的间隔;
- 触发器的开始时间;
对于基于事件的触发器,标准可能包括:
- 区域事件的类型(进入、离开、内部或外部)
- 地理目标区域列表;
- 区域 ID 列表;
- 指示 SET 是否可以重复使用触发器以及重复使用多少次以及以什么最小间隔重复的报告信息;
- 开始和停止时间。
当基于事件的触发器中存在区域 id 列表但不存在地理目标区域列表时,区域 id 列表将用作触发器的目标区域。当存在地理目标区域列表但没有区域id列表时,将地理目标区域列表作为目标区域。当基于事件的触发器中同时存在地理目标区域列表和区域 id 列表时,将地理目标区域作为实际目标区域,并使用区域 id 列表帮助 SET 避免不必要的定位尝试。
这个基于事件的触发器,概念类似于地理围栏,设定一个区域,当用户进出地理围栏时给予通知。
(1)Repeated reporting and event triggers
当基于事件的触发器与重复报告相结合时,必须指定最小间隔和报告数量。 无论事件类型如何,SLP 和 SET 应继续触发事件会话,直到:
- 已返回请求数量的报告;
- 停止时间(如果存在)已过;
- 已收到 SUPL TRIGGERED STOP 或 SUPL END 以取消会话;
(2)Event trigger types
“Entering”和“Inside”触发器类型都意味着 SET 应在检测到它在目标区域内时立即报告。
这些触发器类型之间的区别在于它们与重复报告结合时的行为。 通过重复报告,“Entering”触发器将在 SET 第一次检测到它在目标区域内时完成。 为了再次满足触发条件,SET必须随后检测到它已经离开目标区域然后重新进入。
每当 SET 发送报告时,它必须等待最小报告间隔,然后再检查是否再次满足触发条件。
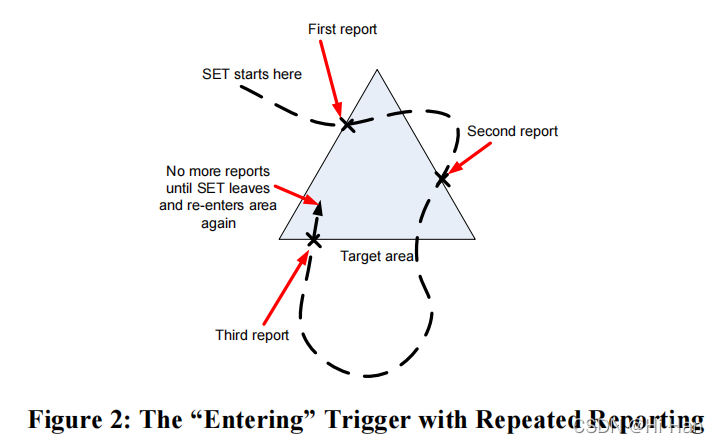
相比之下,“Inside”触发器与重复报告结合使用时,只要 SET 检测到它在该区域内,就会导致重复报告。

请注意,“Entering”和“Inside”触发器类型,如果 SET 在触发器激活时在目标区域内开始(即,如果没有指定开始时间,则在收到触发条件时;如果指定,则在适当的开始时间),触发条件将被满足。 在发送第一份报告之前,SET 无需验证它是否曾在该区域之外。
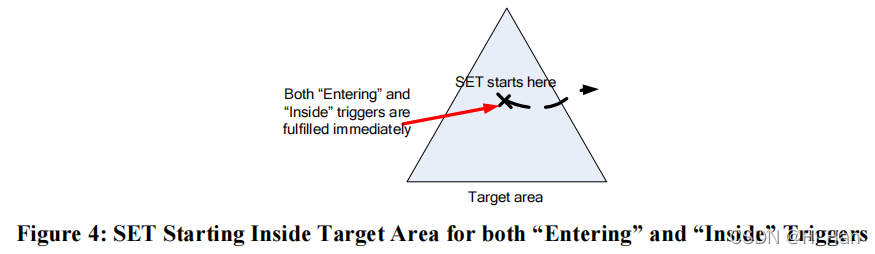
“Leaving”和“Outside”触发器类型的行为方式类似,但仅在 SET 位于目标区域之外时才会执行。 与“Entering”和“Inside”触发器类型一样,“Leaving”和“Outside”触发器在不使用重复报告时具有相同的行为。 当 SET 第一次检测到它在目标区域之外时,它们都被满足。
通过重复报告,离开触发在SET第一次检测到它在目标区域之外时完成,然后每次SET检测到它已经重新进入目标区域然后再次退出。 每当 SET 发送报告时,它必须等待最小报告间隔,然后再检查是否再次满足触发条件。

“Outside”触发器与重复报告结合使用时,只要 SET 保持在目标区域之外,就会以最小报告间隔重复报告。
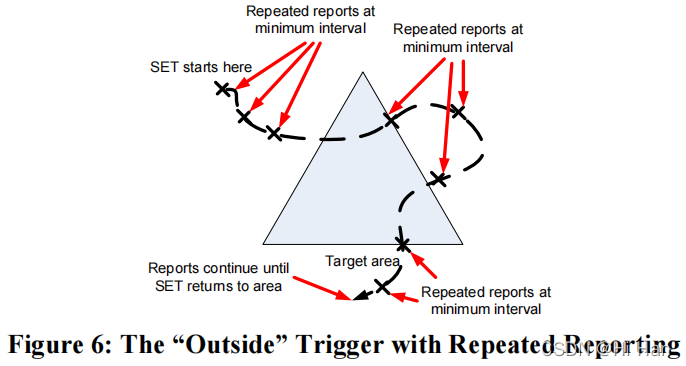
1.2.7 SUPL Positioning Functional Group
1.2.7.1 SUPL Assistance Delivery Function (SADF)
SADF 选择、生成和传递可用的辅助数据,用于测量或计算 SET 位置。 辅助数据传递可以基于从 SRRF 功能检索到的 GPS 或 GANSS 参考数据的选定子集、SET 和网络的能力以及目标 SET 的大致位置信息。
1.2.7.2 SUPL Reference Retrieval Function (SRRF)
SRRF 是从 GPS 或 GANSS 参考网络检索 GPS 或 GANSS 参考数据的功能。 需要参考数据来生成辅助数据。
1.2.7.3 SUPL Position Calculation Function (SPCF)
SPCF选择定位协议和协议版本,并执行计算SET位置的功能。 SUPL服务可以支持以下一种或多种定位计算模式。
- A-GPS SET assisted
- A-GPS SET based
- A-GANSS SET assisted
- A-GANSS SET based
- Autonomous GPS or Autonomous GANSS
- Enhanced Cell/Sector
- AFLT
- EOTD
- OTDOA
- Location ID – SHALL be supported——将位置标识符转换为以纬度和经度表示的地理位置。 在 MNO 环境中,这通常称为 Cell-ID 位置。
1.2.8 SUPL Reference Point Definitions
这节介绍SUPL架构中的参考点。
1.2.8.1 Lup Reference Point
Lup参考点的功能在逻辑上分为定位服务管理和定位确定。
(1)Lup Location Service Management Messages
该参考点用于使 SLP 能够与 SET 建立会话并执行表 1 中位置服务功能组中列出的功能。

(2)Lup Positioning Determination Messages
Lup 定位确定参考点用于在 SET 和 SLP 之间传输信息以计算位置。 定位确定功能组的功能如表1所示。表 3 列出了 Lup Positioning Determination 消息。

1.2.8.2 Llp Reference Point
Llp 引用在逻辑上将定位控制功能和定位数据功能分开。
(1)Llp Positioning Control Function Messages
定位控制功能用于SLC和SPC之间会话的建立、维护和清除。 定位控制功能使 SLC 和 SPC 能够执行位置计算功能。 表 4 列出了 Llp 定位控制功能消息。

(2)Llp Positioning Data Function Messages
定位数据功能用于传输用于位置计算的数据。 定位数据功能接口仅用于代理模式。

1.3 Lup Reference Point Flows
本章显示的流程显示了 Lup 接口消息交换。 流程可以分为两种场景,网络发起和SET发起。
当网络中的 SUPL 代理请求定位时,会发生网络发起的流。
当 SET 请求定位时,会出现 SET 发起的流程。
下面通过显示每个场景的典型流程给出高级描述。 这些流程旨在说明基本概念,而不是详尽的列表。 这些流程只是说明性的。 有关详细流程,请参阅 [OMA ULP]。
1.3.1 SET Initiated flows – Proxy Mode – Immediate Service
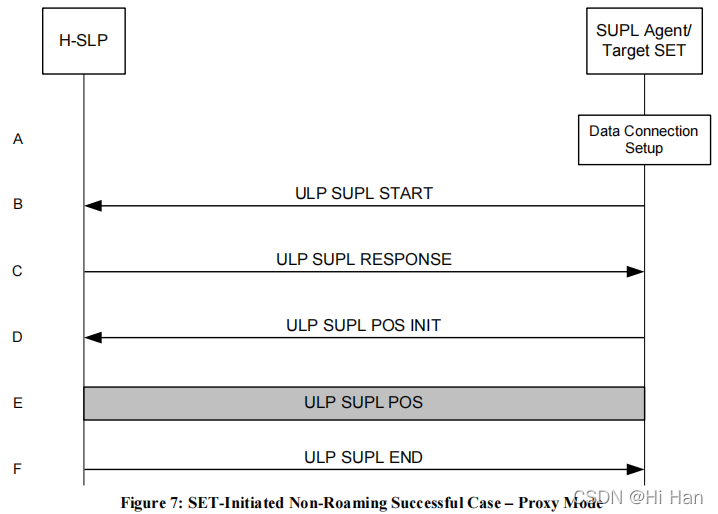
A. The SUPL Agent on the SET receives a request for position from an application running on the SET. The SET establishes secure connection to the H-SLP.
B. The SET sends a ULP SUPL START message to start a SUPL Session with the H-SLP. The ULP SUPL START message contains SET capabilities and location identifier.
C. The H-SLP responds with a ULP SUPL RESPONSE message to the SET. The message contains the requested positioning method. It may also contain location information that does not meet the QoP requested by the SUPL Agent, but gives a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START
message.D. The SET then sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities and the location identifier.
E. The H-SLP then determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages, containing the used positioning protocol (i.e., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801), as needed to determine the position.
F. When the position calculation is complete the H-SLP sends the ULP SUPL END message to the SET informing it that the SUPL Session is finished. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SLP.
1.3.2 SET Initiated flows – Non-Proxy Mode – Immediate Service
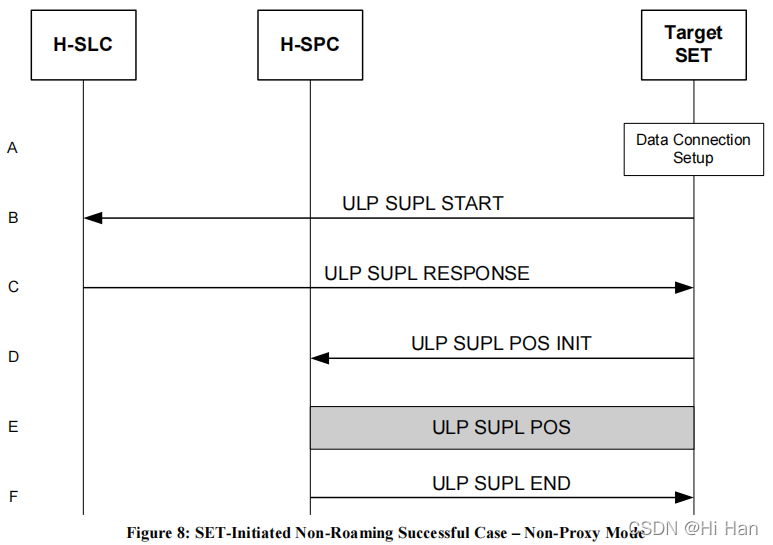
H-SLC和H-SPC内部通信并没有展示在图8中。
A. The SUPL Agent on the SET receives a request for position from an application running on the SET. The SET establishes a secure connection to the H-SLC.
B. The SET sends an ULP SUPL START message to start a SUPL Session with the H-SLC. The ULP SUPL START message contains SET capabilities and location identifier.
C. The H-SLC responds with a ULP SUPL RESPONSE message to the SET. The message contains the requested positioning method. It also contains key information required for the SET to establish a secure connection to the H- SPC. It MAY also contain location information not meeting the QoP requested by the SUPL Agent, but giving a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START message.
D. The SET establishes a secure connection to the H-SPC and sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SPC. The message contains the SET capabilities and the location identifier.
E. The H-SPC then determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages, containing the used positioning protocol (i.e., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801), as needed to determine the position.
F. When the position calculation is complete the H-SPC sends the ULP SUPL END message to the SET informing it that the SUPL Session is finished. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SPC.
1.3.3 Network Initiated flows – Non-Proxy Mode – Immediate Service

H-SLC和H-SPC内部通信并没有展示在图9中。
A. The SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR message to the H-SLC.
B. The H-SLC initiates the SUPL Session with the SET by sending a ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains requested positioning method and SPC address.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMSC network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.C. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it establishes a secure connection to the H-SLC.
D. For authentication purposes, the SET sends an ULP SUPL AUTH REQ message to the H-SLC.
E. The H-SLC responds with an ULP SUPL AUTH RESP message to the SET. The SET releases the secure connection to the H-SLC.
F. The SET establishes a secure connection to the H-SPC and sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SPC. The message contains the SET capabilities.
G. The H-SPC then determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages, containing the used positioning protocol (i.e., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801), as needed to determine the position.
H. When the position calculation is complete the H-SPC sends the ULP SUPL END message to the SET informing it that the SUPL Session is finished. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SPC.、
I. The H-SLC sends the position estimate back to the SUPL Agent in an MLP SLIA message.
1.3.4 Network Initiated flows – Proxy Mode – Immediate Service

A. The SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR message to the H-SLP.
B. The H-SLP initiates the SUPL Session with the SET by sending a ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains requested positioning method.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMSC network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.C. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLP.
D. The SET then sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities.
E. The H-SLP then determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages, containing the used positioning protocol (i.e., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801), as needed to determine the position.
F. When the position calculation is complete the H-SLP sends the ULP SUPL END message to the SET informing it that the SUPL Session is finished. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SLP.
G. The H-SLP sends the position estimate back to the SUPL Agent in an MLP SLIA message.
1.3.5 Network Initiated Proxy Mode – Triggered Services: Periodic Triggers

A. The SUPL Agent issues an MLP TLRR to the H-SLP.
B. The H-SLP initiates the periodic trigger session with the SET using the ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains the intended positioning method.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMSC network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
C. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLP.
D. The SET then sends a ULP SUPL TRIGGERED START message to start a periodic triggered session with the H-SLP.
E. The H-SLP selects the positioning method to be used for the periodic triggered session and responds with a ULP SUPL TRIGGERED RESPONSE message. This message contains the positioning method and periodic trigger parameters.
F. The H-SLP informs the SUPL Agent in an MLP TLRA message that the triggered location response request has been accepted. The SET and the H-SLP may release the secure IP connection.
G. When the periodic trigger in the SET indicates that the first position fix has to be performed, the SET sends a SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. Note: if there is no secure connection between the SET and the H-SLP, the SET establishes a secure connection before sending the SUPL POS INIT to the H-SLP.
H. The SET and the H-SLP MAY exchange several successive positioning procedure messages (e.g., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801) as needed to determine the position.
I. If the reporting mode is batch reporting and SET Assisted mode is used, the position calculated by the H-SLP is reported back to the SET for storage.
J. When the position calculation is complete the H-SLP sends a MLP TLREP message to the SUPL Agent. This message contains the positioning result. The SET and the H-SLP may release the secure IP connection.
K. If the SET cannot communicate with the H-SLP (e.g. no radio coverage available) and if batch reporting or quasi-real time reporting is used, the SET performs either SET Based position fixes or enhanced cell/sector measurements.
L. The SET sends the stored position estimates and/or the stored enhanced cell/sector measurements in an unsolicited ULP SUPL REPORT message to the H-SLP. This message contains the position result(s). Note: if there is no secure connection between the SET and the H-SLP, the SET establishes a secure connection before sending the ULP SUPL REPORT to the H-SLP.
M. If enhanced cell/sector measurements are received in step L, the H-SLP calculates corresponding position estimates. The H-SLP forwards the reported and/or calculated position estimate(s) to the SUPL Agent in an MLP TLREP message.
Steps N-to-P are a repeat of steps G-to-I. Step K might be repeated if necessary.
Q. The SET sends the stored position estimates and/or the stored enhanced cell/sector measurements in an unsolicited ULP SUPL REPORT message to the H-SLP. This message contains the stored position result(s) and/or stored enhanced cell/sector measurements not previously reported to the H-SLP. Note: if there is no secure connection between the SET and the H-SLP, the SET establishes a secure connection before the sending ULP SUPL REPORT to the H-SLP.
R. If enhanced cell/sector measurements are received in step Q, the H-SLP calculates corresponding position estimates. The H-SLP forwards the reported and/or calculated position estimate(s) to the SUPL Agent in an MLP TLREP message.
S. After the last position result has been reported to the SUPL Agent in step R, the H-SLP ends the periodic triggered session by sending a SUPL END message to the SET. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SLP.
1.3.6 Network Initiated Proxy Mode – Triggered Services: Event Triggers

A. SUPL Agent issues an MLP TLRR to the H-SLP.
B. The H-SLP initiates the area event trigger session with the SET using the ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains the intended positioning method.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMSC network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
C. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLP.
D. The SET then sends a ULP SUPL TRIGGERED START message to start an area event triggered session with the H-SLP.
E. The H-SLP selects a positioning method to be used for the area event triggered session and responds with a ULP SUPL TRIGGERED RESPONSE message. This message contains the positioning method and area event trigger parameters. The SUPL TRIGGERED RESPONSE message may contain the area ids of the specified area for the
area event triggered sessionF. The H-SLP informs the SUPL Agent in an MLP TLRA message that the triggered location response request has been accepted. The SET and the H-SLP may release the secure IP connection.
G. When the area event trigger mechanism in the SET or the comparison of the current area id to the downloaded area ids (if any) indicates that a position fix is to be executed, the SET sends a SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. Note: if there is no secure connection between the SET and the H-SLP, the SET establishes a secure connection before the sending the SUPL POS INIT to the H-SLP.
H. The SET and the H-SLP MAY exchange several successive positioning procedure messages (e.g., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801) as needed to determine the position.
I. When the positioning procedure is complete the H-SLP sends a ULP SUPL REPORT message to the SET. This message may contain the positioning result. The SET and the H-SLP may release the secure IP connection.
J. The SET compares the calculated position estimate with the event area to check if the event trigger condition has been met. In this case no area event is triggered.
Whenever the area event trigger mechanism in the SET indicates that a new position fix has to be performed, steps G-to-J are repeated (e.g., steps K-to-N are a repeat of steps G-to-J).
R. The SET compares the calculated position with the event area to check if the event trigger condition has been met. In this case the area event is triggered.
S. If there is no secure connection between the SET and the H-SLP, the SET establishes a secure connection with the H-SLP. The SET sends a ULP SUPL REPORT message to the H-SLP. This message contains the position estimate.
T. The H-SLP sends a MLP TLREP message to the SUPL Agent. This message contains the position estimate.
U. The H-SLP ends the area event triggered session by sending a ULP SUPL END message to the SET. The SET then releases the secure IP connection.
1.3.7 Network Initiated flows – Roaming Proxy Mode with H-SLP Positioning – Immediate Service

A. SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR message to the R-SLP.
B. The R-SLP forwards the location request to the H-SLP of the target subscriber, using an RLP SRLIR. The message contains the requested QoP.
C. The H-SLP initiates the location session with the SET using the ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains the requested positioning method.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMSC network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
D. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLP.
E. The SET then sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities.
F. The H-SLP then decides that the H-SLP will provide assistance/position calculation and the H-SLP sends an RLP SRLIR to the V-SLP to determine a coarse position for further exchange of ULP SUPL POS messages between SET and H-SLP.
G. The V-SLP returns an RLP SRLIA. This message contains the position result (e.g., coarse position for A-GPS positioning).
H. The H-SLP then determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages.
These messages contain the used positioning protocol messages (e.g., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801) as needed to determine the position.I. When the position calculation is complete the H-SLP sends the ULP SUPL END message to the SET. The SET then releases the secure IP connection to the H-SLP.
J. The H-SLP sends an RLP SRLIA message to the R-SLP. This message contains the position estimate.
K. The R-SLP sends an MLP SLIA message to the SUPL Agent. This message contains the position estimate.
1.3.8 Network Initiated flows – Roaming Proxy Mode with V-SLP Positioning – Immediate Service

A. A SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR message to the R-SLP
B. The R-SLP forwards the location request to the H-SLP of the target subscriber, using an RLP SRLIR. The message contains requested QoP.
C. The H-SLP sends an RLP SSRLIR to the V-SLP to inform the V-SLP that the target SET will initiate a SUPL positioning procedure. The message contains the requested QoP.
D. The V-SLP acknowledges that it is ready to initiate a SUPL positioning procedure with an RLP SSRLIA Answer back to the H-SLP.
E. The H-SLP initiates the location session with the SET using the ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains the intended positioning method.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMSC network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
F. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLP.
G. The SET then sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities.
H. The H-SLP then tunnels the ULP SUPL POS INIT message to the V-SLP.
I. The V-SLP then determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages, tunneled over RLP via the H-SLP. These messages contain the used positioning protocol (e.g., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801) as needed to determine the position.
J. When the position calculation is complete the V-SLP sends the ULP SUPL END message towards the SET, tunneled over RLP via the H-SLP.
K. The H-SLP forwards the ULP SUPL END to the SET informing it that the SUPL Session is finished. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SLP.
L. When the position calculation is complete the H-SLP sends an RLP SRLIA message to the R-SLP. This message contains the position estimate.
M. The R-SLP sends an MLP SLIA message to the SUPL Agent. This message contains the position estimate.
1.3.9 Network Initiated flows – Roaming Non Proxy Mode with H-SPC Positioning – Immediate Service

A. A SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR message to the R-SLP.
B. The R-SLP then forwards the location request to the H-SLC of the target subscriber, using an RLP SRLIR. The message contains the requested QoP.
C. The H-SLC informs the H-SPC of the pending SUPL positioning session.
D. The H-SLC initiates the location session with the SET using the ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains the intended positioning method.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMSC network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
E. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLC.
F. The SET sends a ULP SUPL AUTH REQ message to the H-SLC.
G. The H-SLC creates a key to be used for mutual H-SPC/SET authentication. The H-SLC forwards the key to the H-SPC and returns a ULP SUPL AUTH RESP message to the SET.
H. The SET then sends a SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SPC. The message contains the SET capabilities.
I. The H-SPC informs the H-SLC that the target SET has established the session and informs the H-SLC of the location id.
J. The H-SLC sends an RLP SRLIR to the V-SLP to determine a coarse position for further exchange of ULP SUPL POS messages between SET and H-SPC.
K. The V-SLP returns a RLP SRLIA. This message contains the position result (e.g., coarse position for A-GPS positioning).
L. The H-SLC informs the H-SPC of the initial position.
M. The H-SPC then determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages.These messages contain the used positioning protocol messages (e.g., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801) as needed to determine the position.
N. When the position calculation is complete the H-SPC sends the ULP SUPL END message to the SET.
O. The H-SPC informs the H-SLC that the positioning procedure is completed and returns the position result.
P. The H-SLC sends an RLP SRLIA message to the R-SLP. This message contains the position estimate.
Q. The R-SLP sends an MLP SLIA message to the SUPL Agent. This message contains the position estimate.
1.3.10 Network Initiated flows – Roaming Non Proxy Mode with V-SPC Positioning – Immediate Service

A. A SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR to the R-SLP.
B. The R-SLP then forwards the location request to the H-SLP of the target subscriber, using an RLP SRLIR. The message contains the requested QoP.
C. The H-SLP then decides that the V-SPC will provide assistance data or perform the position calculation. The H-SLP sends an RLP SSRLIR to the V-SLC to inform the V-SLC that the target SET will initiate a SUPL positioning procedure.
D. The V-SLC informs the V-SPC of an incoming SUPL positioning session.
E. The V-SLC returns an RLP SSRLIA. The message contains the requested positioning method.
F. The H-SLP initiates the location session with the SET using the ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains the address of the V-SPC.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMS-C network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
G. When the SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLP.
H. The SET sends a ULP SUPL AUTH REQ message to the H-SLP.
I. The H-SLP creates a key to be used for mutual V-SPC/SET authentication. The H-SLP forwards the key to the V-SLC through an RLP SSRP message. The V-SLC forwards the key to the V-SPC through internal communication.
J. The H-SLP returns a ULP SUPL AUTH RESP to the SET.
K. The SET establishes a secure IP connection to the V-SPC. The SET sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a SUPL positioning session with the V-SPC. The message contains the SET capabilities. The SET releases the secure IP connection to the H-SLP. The V-SPC informs the V-SLC that the positioning procedure is started.
L. The V-SPC determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive positioning procedure messages(e.g., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801) with the SET as needed to determine the position.
M. When the position calculation is complete the V-SPC sends the ULP SUPL END message. The SET then releases the secure IP connection to the V-SPC.
N. The V-SPC informs the V-SLC that the positioning procedure is completed and returns the position result.
O. The V-SLC sends a RLP SSRP message to the H-SLP. This message contains the position estimate.
P. The H-SLP sends an RLP SRLIA message to the R-SLP. This message contains the position estimate.
Q. The R-SLP sends an MLP SLIA message to the SUPL Agent. This message contains the position estimate.
1.3.11 Historical Positions

A. The SUPL Agent issues an MLP HLIR message to the H-SLP, which may contain selection criteria such as QoP, positioning methods.
B. The H-SLP initiates the retrieval of historical positions with the SET using the ULP SUPL INIT message. The ULP SUPL INIT message contains criteria for selecting stored historical position estimates and/or stored enhanced cell/sector measurements.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMS-C network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
C. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure data connection to the H-SLP.
D. The SET selects historical position estimates and/or historic enhanced cell/sector measurements and sends the positions and/or measurements in a ULP SUPL REPORT message to the H-SLP.
E. The H-SLP reports the historical position estimates to the SUPL Agent in a MLP HLIA message.
1.3.12 SET-Initiated Request for Transfer of Location to a Third party

A. The SUPL Agent on the SET receives a request from an application running on the SET for transfer of the SET's location to a third party. The Target SET establishes a secure connection to the H-SLP.
B. The SUPL Agent on the Target SET sends a ULP SUPL START message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities, including the supported positioning methods, location identifier and third party identity.
C. The H-SLP responds with the ULP SUPL RESPONSE message to the SET. The message contains the positioning method determined by the H-SLP.
D. The SET sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities, including the supported positioning methods, and location identifier.
E. The SET and the H-SLP may exchange several successive positioning procedure messages. The H-SLP or the SET calculates the position depending on positioning calculation mode (SET-based or SET-assisted).
F. The H-SLP sends the ULP SUPL END message to the Target SET informing it that no further positioning procedure will be started and that the session is ended. The SET then releases the secure connection.
G. The H-SLP delivers the SET location information to the third party
1.4 Llp Reference Point Flows
本章中显示的流程显示了 Llp 接口消息交换。 流程可以分为两种情况:
网络启动和 SET 启动。 仅显示单个定位成功的非漫游场景。 漫游和触发场景没有在这里介绍,因为它们遵循相同的架构概念。
当网络中的 SUPL 代理请求定位时,会发生网络发起的流。当 SET 请求定位时,会出现 SET 发起的流程。
下面通过显示每个场景的典型流程给出高级描述。 这些流程旨在说明基本概念,并非详尽的清单。 这些流程只是说明性的。 有关详细流程,请参阅 [OMA ILP]。
1.4.1 SET Initiated Proxy Mode flows – Non-Roaming
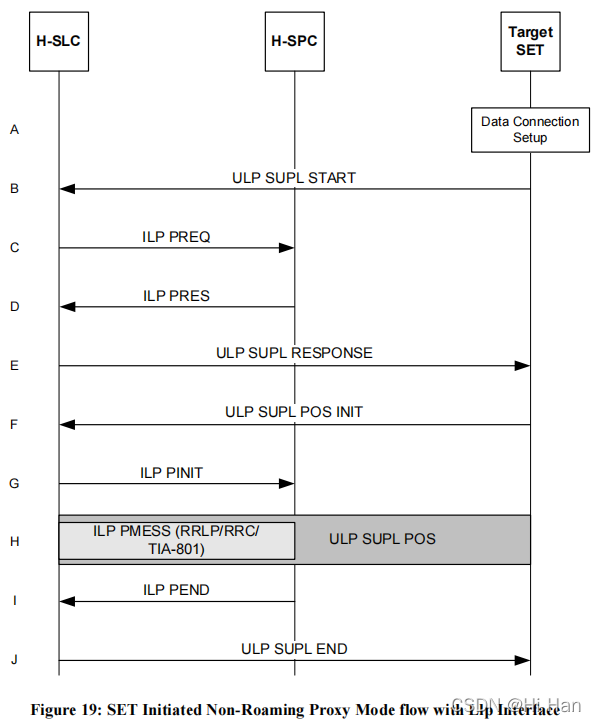
A. The SUPL Agent on the SET receives a request for position from an application running on the SET. The SET establishes secure connection to the H-SLC.
B. The SET sends a ULP SUPL START message to start a SUPL Session with the H-SLP. The ULP SUPL START message contains SET capabilities and location identifier.
C. The H-SLC requests service from the H-SPC. It MAY also request location information not meeting the QoP, but giving a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START message.
D. The H-SPC responds to the service request from the H-SLC. It MAY also contain location information not meeting the QoP, but giving a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START message.
E. The H-SLC sends a ULP SUPL RESPONSE message to the SET. The message contains the requested positioning method and QoP. It MAY also contain location information not meeting the QoP, but giving a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START message.
F. The SET sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities and location identifier.
G. The H-SLC sends an ILP PINIT message to the H-SPC to start the SUPL POS session.
H. The H-SPC determines the positioning method and engages in a SUPL POS session with the SET. Thereby the positioning payload (RRLP/RRC/TIA-801) is transferred between the H-SPC and the H-SLC using ILP PMESS messages, and between the H-SLC and the SET using SUPL POS messages.
I. When the position calculation is complete the H-SPC sends an ILP PEND message to the H-SLC.
J. The H-SLC sends a ULP SUPL END message to the SET. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SLC.
1.4.2 SET Initiated Non-Proxy Mode flows – Non-Roaming

A. The SUPL Agent on the SET receives a request for position from an application running on the SET. The SET establishes secure connection to the H-SLC.
B. The SET sends a ULP SUPL START message to start a SUPL Session with the H-SLP. The ULP SUPL START message contains SET capabilities and location identifier.
C. The H-SLC requests service from the H-SPC. It MAY also request location information not meeting the QoP, but giving a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START message.
D. The H-SPC responds to the service request from the H-SLC. It MAY also contain location information not meeting the QoP, but giving a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START message.
E. The H-SLC sends a ULP SUPL RESPONSE message to the SET. The message contains the requested positioning method, the H-SPC address and the QoP, and the key to be used for mutual SET/H-SPC authentication. The message MAY also contain location information not meeting the QoP, but giving a coarse approximation of the position, based on information received in the ULP SUPL START message. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SLC.
F. The SET establishes a secure connection to the H-SPC using the key received from the H-SLC. The SET sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SPC. The message contains the SET capabilities and location identifier.
G. The H-SPC determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages with the SET, containing the used positioning protocol (i.e., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801), as needed to determine the position.
H. When the position calculation is complete, the H-SPC sends a ULP SUPL END message to the SET. The ULP SUPL END message is to inform the SET that the SUPL Session is finished. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SPC.
I. The H-SPC informs the H-SLC about the end of the SUPL Session.
1.4.3 Network Initiated Proxy Mode flows – Non-Roaming

A. SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR message to the H-SLC.
B. The H-SLC requests service from the H-SPC.
C. The H-SPC responds to the service request from the H-SLC.
D. The H-SLC initiates the SUPL Session with the SET by sending a ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains requested positioning method and QoP.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMS-C network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
E. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLC.
F. The SET sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SLP. The message contains the SET capabilities and location identifier.
G. The H-SLC sends an ILP PINIT message to the H-SPC to start the SUPL POS session.
H. The H-SPC determines the positioning method and engages in a SUPL POS session with the SET. Thereby the positioning payload (RRLP/RRC/TIA-801) is transferred between the H-SPC and the H-SLC using ILP PMESS messages, and between the H-SLC and the SET using SUPL POS messages.
I. When the position calculation is complete the H-SPC sends an ILP PEND message to the H-SLC including the position estimate.
J. The H-SLC sends a ULP SUPL END message to the SET. The SET then releases the secure connection to the H-SLC.
K. The H-SLC sends the position estimate back to the SUPL Agent by means of an MLP SLIA.
1.4.4 Network Initiated Non-Proxy Mode flows – Non-Roaming
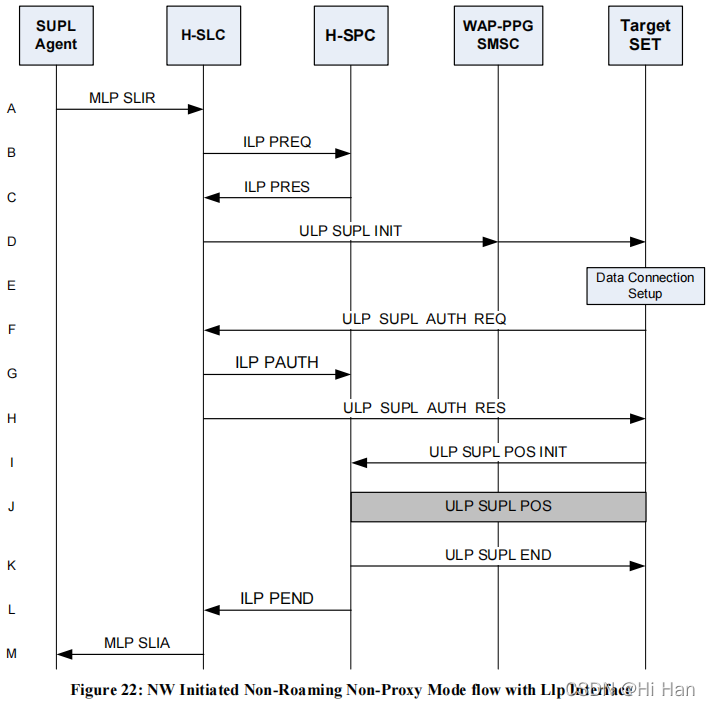
A. SUPL Agent issues an MLP SLIR message to the H-SLC.
B. The H-SLC requests service from the H-SPC.
C. The H-SPC responds to the service request from the H-SLC.
D. The H-SLC initiates the SUPL Session with the SET by sending a ULP SUPL INIT message. The message contains requested positioning method and QoP.
Note: the WAP-PPG/SMS-C network element is only involved if OMA Push or MT SMS is used for delivering the ULP SUPL INIT message to the SET.
E. When the ULP SUPL INIT is received by the SET it will establish a secure connection to the H-SLC.
F. For authentication purposed, the SET sends a ULP SUPL AUTH REQ message to the H-SLC.
G. The H-SLC generates an authentication key that it sends to the H-SPC.
H. The H-SLC responds with a ULP SUPL AUTH RES message including the authentication keys required for SET communication with the H-SPC.
I. The SET sends a ULP SUPL POS INIT message to start a positioning session with the H-SPC. The message contains the SET capabilities and location identifier.
J. The H-SPC determines the positioning method and exchanges several successive ULP SUPL POS messages with the SET, containing the used positioning protocol (i.e., RRLP, RRC, TIA-801), as needed to determine the position.
K. When the position calculation is complete, the H-SPC sends a ULP SUPL END message to the SET. The ULP SUPL END message is to inform the SET that the SUPL Session is finished.
L. The H-SPC informs the H-SLC about the end of the SUPL Session and includes the position estimate.
M. The H-SLC sends the position estimate to the SUPL Agent in an MLP SLIA.
3、缩写及释义
AD Architecture Document
AFLT Advanced Forward Link Trilateration
A-GANSS Assisted Galileo and Additional Navigation Satellite Systems
A-GNSS Assisted Global Navigation Satellite System
A-GPS Assisted GPS
API Application Programming Interface
D-SLP Discovered SLP
EOTD Enhanced Observed Time Difference
E-SLP Emergency SLP
FQDN Fully Qualified Domain Name
GNSS Global Navigation Satellite System
GPS Global Positioning System
ILP Internal Location Protocol
HLIA Historical Location Immediate Request
HLIR Historical Location Immediate Answer
H-SLC Home SLC
H-SLP Home SLP
H-SPC Home SPC
HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol
HTTPS HTTP Secure
IETF Internet Engineering Task Force
IMSI International Mobile Subscriber Identity
IP Internet Protocol
LCS Location Services
LTE Long Term Evolution
Lup Location User Plane
MAC Message Authentication Code
MC Message Center
MLP Mobile Location Protocol
MLS Mobile Location Services
MNO Mobile Network Operator
MSISDN Mobile Subscriber ISDN Number
OMA Open Mobile Alliance
OTDOA Observed Time Difference of Arrival
PAP Push Access Protocol
PC Personal Computer
PLMN Public Land Mobile Network
POTAP WAP Push Over The Air Protocol
PPG Push Proxy Gateway
PSK-TLS Pre-Shared Key Ciphersuites for Transport Layer Security
QoP Quality of Position
RD Requirement Document
RLP Roaming Location Protocol
RRC Radio Resource Control
RRLP Radio Resource LCS Protocol
R-SLP Requesting SLP
SADF SUPL Assistance Delivery Function
SCF SUPL Charging Function
SET SUPL Enabled Terminal
SIF SUPL Initiation Function
SIP Session Initiation Protocol
SLC SUPL Location Center
SLIA Standard Location Immediate Answer
SLIR Standard Location Immediate Request
SLIRep Standard Location Immediate Report
SLP SUPL Location Platform
SMLC Serving Mobile Location Center
SMPP Short Message Peer to peer Protocol
SMS Short Message Service
SMSC Short Message Service Center
SPC SUPL Positioning Center
SPCF SUPL Position Calculation Function
SPF SUPL Privacy Function
SRLIA Standard Roaming Location Immediate Answer
SRLIR Standard Roaming Location Immediate Request
SRRF SUPL Reference Retrieval Function
SRSF SUPL Roaming Support Function
SSF SUPL Security Function
SSMF SUPL Service Management Function
SSPF SUPL SET Provisioning Function
SSRLIA Standard SUPL Roaming Location Immediate Answer
SSRLIR Standard SUPL Roaming Location Immediate Request
SSRP Standard SUPL Roaming Position
SUPL Secure User Plane Location
TD-SCDMA Time Division-Synchronous Code Division Multiple Access
TLS Transport Layer Security
UDP User Datagram Protocol
UE User Equipment
UICC Universal Integrated Circuit Card
UMB Ultra Mobile Broadband
URL Uniform Resource Locator
V-SLC Visited SLC
V-SPC Visited SPC
V-SLP Visited SLP
WAP Wireless Application Protocol
WCDMA Wideband Code Division Multiple Access
Context Model:A model that identifies all contextual items relevant to understanding architecture.
Control Plane:This plane has a layered structure and performs the call control and connection control functions; it dealswith the signaling necessary to set up, supervise and release calls and connections.
Emergency IMS Core:IMS core network supporting emergency IMS call. The main components of Emergency IMS Core areP-CSCF and E-CSCF.
End User Device:See [OMA AD].
ImmediateService:Location service where a single location information is needed immediately.
Interface:The common boundary between two associated systems. See [OMA-DICT]
Location Based Application:See [3GPP TS 23.271].
Location (Based) Service:See [3GPP TS 23.271] [3GPP GSM LCS][3GPP WCDMA LCS][ 3GPP2 X.S0024-0].
MLS Application:An application that requests and consumes the location information.
Non-Proxy Mode:The SPC system will have direct communication with the SET.
Periodic Triggered Service:Location service where a multiple periodic location information is needed.
Proxy Mode:The SPC system will not have direct communication with the SET. In this environment the SLC systemwill act as a proxy between the SET and the SPC.
Quality of Position:A set of attributes associated with a request for the geographic position of a SET. The attributes includethe required horizontal accuracy, vertical accuracy, maximum location age, and response time of the SET position.
Reference Point:See [OMA-DICT]
SET Initiated Services:SET Initiated Services are services that originate from the SET. For these services the SUPL Agent resides within the SET.
SET User:The user of a SET.
SIP/IP Core:A network of servers such as proxies and/or registrars that support a variety of SIP based services.
SUPL Agent:A Software and/or hardware entity accessing the SUPL enabler in order to obtain location information.
SUPL Session:Session established between the SET and the SLP using ULP protocol.
SUPL Enabled Terminal(SET):A logical entity in a device that is capable of communicating with a SUPL Network. Examples of thiscould be a UE in UMTS, a MS in GSM or IS-95, or a PC over an IP-based transport.
SUPL Location Center(SLC):Coordinates the operations of SUPL in the network and interacts with the SET over User Plane bearer.
SUPL Location Platform(SLP):The entity responsible for Location Service Management and Position Determination. The SLP containsthe SLC and SPC Functions.
SUPL Network:Access network which facilitates the Location determination functionality and provides the SUPL bearer
SUPL Network Initiated Services:SUPL Network Initiated Services are services, which originate from within the SUPL Network as opposed to the SET. For these services the SUPL Agent resides in the Network.
SUPL Position Calculation:The position calculation function performs the function of calculating the position of a SET. Variouspositioning calculation modes may be supported by a SUPL service.
SUPL Positioning Center(SPC):Entity in the SUPL Network responsible for all messages and procedures required for position calculation and for the delivery of assistance data.
SUPL Provider:Location information is sensitive personal information and requires specific care with privacy and security. In the case of a Mobile Network Operator it is important that whatever policy the Network Operator decides to implement SUPL functionality cannot be breached. Valid scenarios for MNO controlled SUPL would be:
- The network operator is the single SUPL Provider.
- The network operator and roaming partners are the only SUPL Providers.
- The network operator out-sources the SUPL functionality and there is a single 3rd party SUPL Provider.
- The network operator has an open policy on the provision of SUPL functionality and there are multiple 3rd party SUPL Providers.
The SUPL Provider may be independent of an MNO.
SUPL Security Function:SUPL Security Function manages the Authentication and Authorization for SUPL Agents and MLS Applications to access SUPL Services. This function also provides confidentiality and data integrity.
SUPL Service Management:SUPL Service Management is the function of managing locations of SETs. The function stores, extracts,and modifies the location information of a target SET.
System:A functional entity
User Plane:The User Plane, with its layered structure, provides for user information flow transfer, along with associated controls (e.g., flow control, and recovery from errors, etc).







 本文深入探讨了AGPS(辅助全球定位系统)和SUPL(安全用户平面定位)两种移动定位技术。AGPS通过移动网络获取GPS辅助数据以加速定位,而SUPL是OMA制定的一个标准,利用用户平面传输定位数据,支持更快更安全的位置服务。SUPL通过H-SLP(家庭定位平台)和V-SLP(拜访定位平台)提供定位服务,并有控制面和用户面两种架构。文章还详细介绍了SUPL的架构、功能组件、工作流程以及不同启动模式下的消息交互过程。
本文深入探讨了AGPS(辅助全球定位系统)和SUPL(安全用户平面定位)两种移动定位技术。AGPS通过移动网络获取GPS辅助数据以加速定位,而SUPL是OMA制定的一个标准,利用用户平面传输定位数据,支持更快更安全的位置服务。SUPL通过H-SLP(家庭定位平台)和V-SLP(拜访定位平台)提供定位服务,并有控制面和用户面两种架构。文章还详细介绍了SUPL的架构、功能组件、工作流程以及不同启动模式下的消息交互过程。


















 546
546

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










