打开/dev/graphics/fb0节点的过程:
打开/dev/graphics/fb0这个设备的调用过程如下:
1.在HWComposer中,加载module
HWComposer::HWComposer(
const sp<SurfaceFlinger>& flinger,
EventHandler& handler)
{
...
// Note: some devices may insist that the FB HAL be opened before HWC.
int fberr = loadFbHalModule();
loadHwcModule();
...
}1)loadFbHalModule()直接从下面的路径打开fb,初始化并保存framebuffer_device_t类型成员变量mFbDev。
gralloc_device_open()->fb_device_open()->mapFrameBuffer() -> mapFrameBufferLocked()加载module和调用open函数过程如下
这里gralloc_device_open定义在HAL层定义的:
//gralloc.cpp文件中
static struct hw_module_methods_t gralloc_module_methods = {
.open = gralloc_device_open
};
struct private_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.base = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Graphics Memory Allocator Module",
.author = "The Android Open Source Project",
.methods = &gralloc_module_methods
},
.registerBuffer = gralloc_register_buffer,
.unregisterBuffer = gralloc_unregister_buffer,
.lock = gralloc_lock,
.unlock = gralloc_unlock,
},
.framebuffer = 0,
.flags = 0,
.numBuffers = 0,
.bufferMask = 0,
.lock = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER,
.currentBuffer = 0,
};这个Module会在HWComposer::loadFbHalModule()中被加载,调用对应的open函数。
看以下代码注释
int HWComposer::loadFbHalModule()
{
hw_module_t const* module;
//根据GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID这个值,加载对应的module代码,也就是上面说的内容
int err = hw_get_module(GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module);
if (err != 0) {
ALOGE("%s module not found", GRALLOC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID);
return err;
}
return framebuffer_open(module, &mFbDev);
}
//这里methods->open当然就是调用上面module的open函数,也就是gralloc_device_open()
static inline int framebuffer_open(const struct hw_module_t* module,
struct framebuffer_device_t** device) {
return module->methods->open(module,
GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0, (struct hw_device_t**)device);
}
//由于第二个参数是GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0,所以会跑到fb_device_open中
int gralloc_device_open(const hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
hw_device_t** device)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
if (!strcmp(name, GRALLOC_HARDWARE_GPU0)) {
const private_module_t* m = reinterpret_cast<const private_module_t*>(
module);
gpu_context_t *dev;
IAllocController* alloc_ctrl = IAllocController::getInstance();
dev = new gpu_context_t(m, alloc_ctrl);
if(!dev)
return status;
*device = &dev->common;
status = 0;
} else {
status = fb_device_open(module, name, device);
}
return status;
}
//由于name是GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0,会跑到if语句里进行初始化工作,包括打开/dev/graphics/fb0等
int fb_device_open(hw_module_t const* module, const char* name,
hw_device_t** device)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
if (!strcmp(name, GRALLOC_HARDWARE_FB0)) {
alloc_device_t* gralloc_device;
status = gralloc_open(module, &gralloc_device);
if (status < 0)
return status;
/* initialize our state here */
fb_context_t *dev = (fb_context_t*)malloc(sizeof(*dev));
if(dev == NULL) {
gralloc_close(gralloc_device);
return status;
}
memset(dev, 0, sizeof(*dev));
/* initialize the procs */
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = 0;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast<hw_module_t*>(module);
dev->device.common.close = fb_close;
dev->device.setSwapInterval = fb_setSwapInterval;
dev->device.post = fb_post;
dev->device.setUpdateRect = 0;
dev->device.compositionComplete = fb_compositionComplete;
status = mapFrameBuffer((framebuffer_device_t*)dev);
private_module_t* m = (private_module_t*)dev->device.common.module;
if (status >= 0) {
int stride = m->finfo.line_length / (m->info.bits_per_pixel >> 3);
const_cast<uint32_t&>(dev->device.flags) = 0;
const_cast<uint32_t&>(dev->device.width) = m->info.xres;
const_cast<uint32_t&>(dev->device.height) = m->info.yres;
const_cast<int&>(dev->device.stride) = stride;
const_cast<int&>(dev->device.format) = m->fbFormat;
const_cast<float&>(dev->device.xdpi) = m->xdpi;
const_cast<float&>(dev->device.ydpi) = m->ydpi;
const_cast<float&>(dev->device.fps) = m->fps;
const_cast<int&>(dev->device.minSwapInterval) =
PRIV_MIN_SWAP_INTERVAL;
const_cast<int&>(dev->device.maxSwapInterval) =
PRIV_MAX_SWAP_INTERVAL;
const_cast<int&>(dev->device.numFramebuffers) = m->numBuffers;
dev->device.setUpdateRect = 0;
*device = &dev->device.common;
}
// Close the gralloc module
gralloc_close(gralloc_device);
}
return status;
}2)loadHwcModule()函数通过以下路径打开fb,初始化并保存hwc_composer_device_1_t类型的成员变量mHwc。
HWComposer::loadHwcModule()->hw_get_module(HWC_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module)
然后在调用hwc_open_1(module, &mHwc)->hwc_device_open()->initContext()->
CopyBit::CopyBit()[hwc_copybit.cpp]->hw_get_module(COPYBIT_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, &module)
->open_copybit()->open("/dev/graphics/fb0", O_RDWR, 0);这里的module加载以及调用open函数的过程基本和上面的一样,不多说了。
到此可以知道framework层是怎么打开的/dev/graphics/fb0节点,以待后续进行处理的!!
操作/dev/graphics/fb0节点的过程:
在SurfaceFlinger中最后进行数据刷新的函数,我们知道是postFrameBuffer()函数。定义如下:
void SurfaceFlinger::postFramebuffer()
{
ATRACE_CALL();
#ifdef PRODUCT_DEV
if (CC_UNLIKELY(mDebugFps)) {
debugShowFPS();
}
/*
if(CC_UNLIKELY(ATRACE_ENABLED())){
debugShowGPUInfoToSysTrace();
}*/
#endif
const nsecs_t now = systemTime();
mDebugInSwapBuffers = now;
HWComposer& hwc(getHwComposer());
if (hwc.initCheck() == NO_ERROR) {
if (!hwc.supportsFramebufferTarget()) {
getDefaultDisplayDevice()->makeCurrent(mEGLDisplay, mEGLContext);
}
//这个函数当然就是调用HWComposer::commit()函数,,不言而喻~
hwc.commit();
}
...
}
status_t HWComposer::commit() {
int err = NO_ERROR;
if (mHwc) {
...
//这里的mHwc是加载了/hardware/qcom/display/libhwcomposer/Hwc.cpp的内容的
//理由吗,,和上面说的一样,根据id来选择module加载~
//所以set函数就是需要在Hwc.cpp文件中寻找了~
err = mHwc->set(mHwc, mNumDisplays, mLists);
....
}
return (status_t)err;
}
static int hwc_set(hwc_composer_device_1 *dev,
size_t numDisplays,
hwc_display_contents_1_t** displays)
{
int ret = 0;
hwc_context_t* ctx = (hwc_context_t*)(dev);
for (int dpy = 0; dpy < (int)numDisplays; dpy++) {
hwc_display_contents_1_t* list = displays[dpy];
switch(dpy) {
case HWC_DISPLAY_PRIMARY:
//这个就是主屏!!!看hwc_set_primary()函数
ret = hwc_set_primary(ctx, list);
break;
case HWC_DISPLAY_EXTERNAL:
ret = hwc_set_external(ctx, list);
break;
case HWC_DISPLAY_VIRTUAL:
if(ctx->mHWCVirtual)
ret = ctx->mHWCVirtual->set(ctx, list);
break;
default:
ret = -EINVAL;
}
}
return ret;
}
static int hwc_set_primary(hwc_context_t *ctx, hwc_display_contents_1_t* list) {
ATRACE_CALL();
int ret = 0;
const int dpy = HWC_DISPLAY_PRIMARY;
if (LIKELY(list) && ctx->dpyAttr[dpy].isActive
&& !ctx->dpyAttr[dpy].isPause) {
...
//利用copybit或者mdp,每个layer都有几个flags来标记用哪个去画
//以做过的一个平台为例,有以下两种方式
LayerProp::flag values
/* enum {
HWC_MDPCOMP = 0x00000001,
HWC_COPYBIT = 0x00000002,
};
*/
if (ctx->mCopyBit[dpy]) {
if (ctx->mMDP.version < qdutils::MDP_V4_0)
copybitDone = ctx->mCopyBit[dpy]->draw(ctx, list, dpy, &fd);
else
fd = ctx->mMDPComp[dpy]->drawOverlap(ctx, list);
}
...
if (!ctx->mMDPComp[dpy]->draw(ctx, list)) {
ALOGE("%s: MDPComp draw failed", __FUNCTION__);
ret = -1;
}
...
if(!Overlay::displayCommit(ctx->dpyAttr[dpy].fd, lRoi, rRoi)) {
ALOGE("%s: display commit fail for %d dpy!", __FUNCTION__, dpy);
ret = -1;
}
...
}
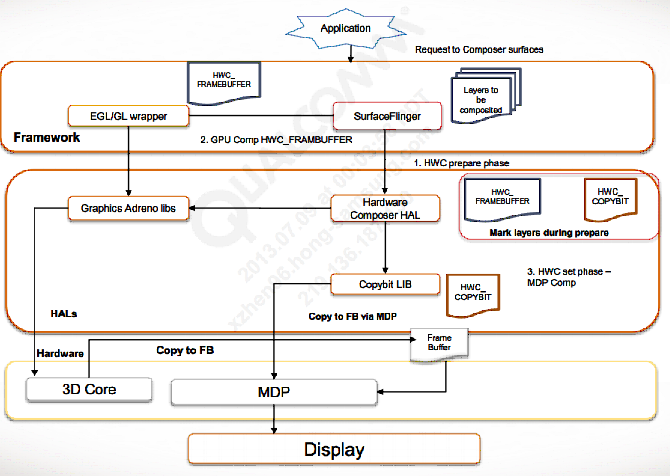
}在加载完fb相关的module之后,SurfaceFlinger就可以通过HWC把Layer画上去。流程如下:
- SurfaceFlinger creates a list of layers and sends them to the HWC in the
prepare phase (hwc_prepare). - HWC sets the compositionType for those layers to be composed by
SurfaceFlinger as HWC_FRAMEBUFFER. - All layers marked as HWC_FRAMEBUFFER and layers whose flag is set
as HWC_SKIP are drawn by SurfaceFlinger. - SurfaceFlinger sends the layer list back to HWC after composing in
Framebuffer. - HWC draws the layers marked for copybit (HWC_COPYBIT) using the
copybit HAL respectively. This is the path taken if MDP composition is set. - The MDP composition mode in the MSM8x25 makes use of the copybit
HAL, which in turn uses the MDP IOCTLs to fill the framebuffer. - HWC invokes eglSwapBuffers.
到这里就可以知道怎么加载的模块,也看了SurfaceFlinger通过HWComposer和HWC.cpp模块的内容进行显示数据的刷写的过程。接下来看一下SurfaceFlinger,,






















 590
590

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








