1. 应用场景
如银行排队系统等
2. 思路
- 队列是 有序列表,可以用数组来存储(地址连续)。
- 因为是数组,所以需要规定 最大容量 “maxSize”。
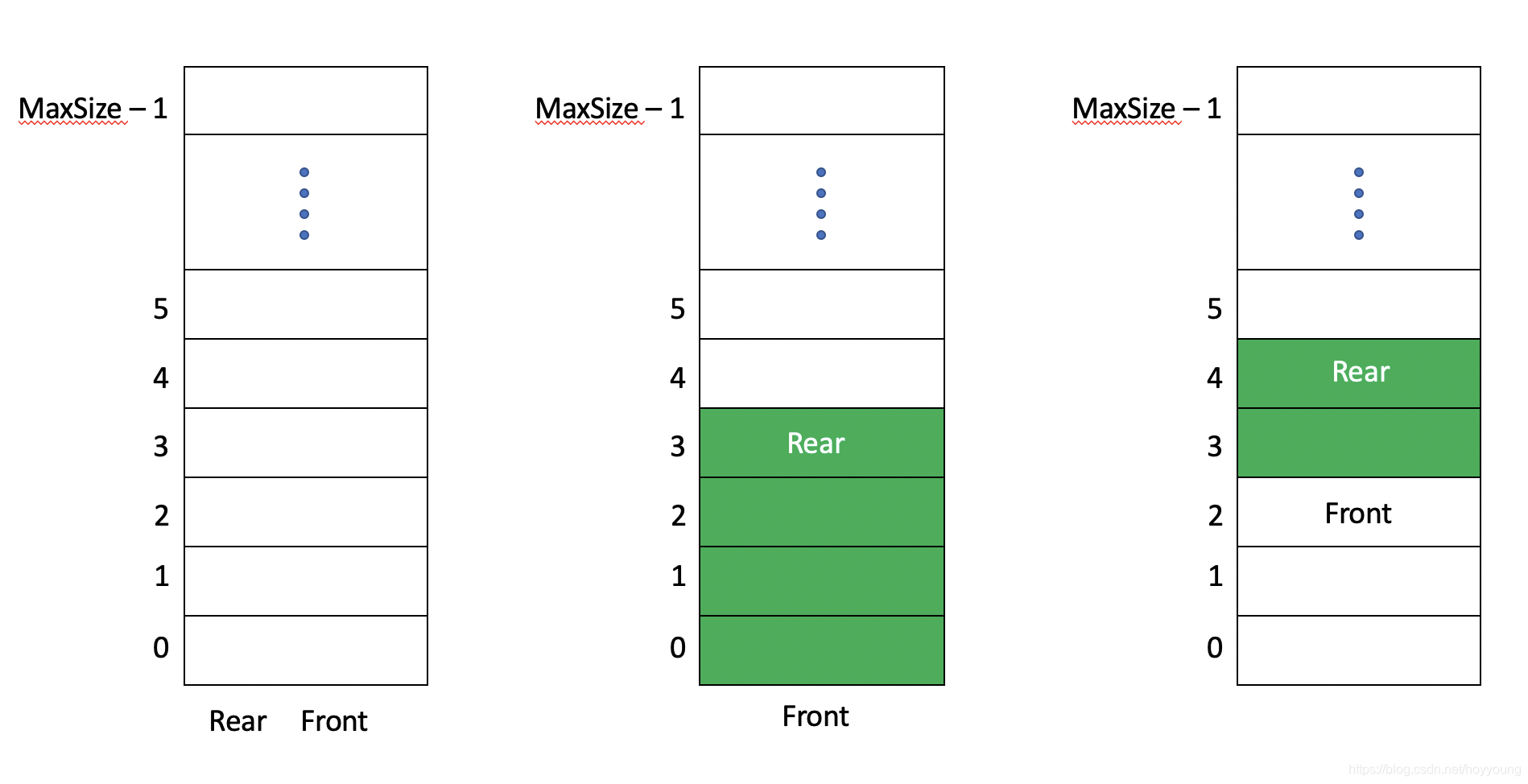
- 因为队列需要前后端的处理,所以需要两个变量 front 和 rear来分别处理前后端数据。
- front 指向队列头的 ** 前一个位置**,随着数据 取出 移动。
- rear 指向队列 尾的位置,随着数据 添加 移动。
- 数组的尾部位置为 maxSize - 1,当 rear 与其相等时,数组不可再添加新的数据(一次性)
3. 数据结构(类结构):
(1)成员变量(Field)
- array: int 数组,用于存放队列 数据
- maxSize: int,队列的 最大容量
- front: int,指向队列 头部数据 的 前一个位置,随着数据 输出 改变
- rear: int,指向队列 尾部数据 的位置,随着数据 输入 改变
private int[] array;
private int maxSize;
private int front;
private int rear;
(2)初始化 / 构造器(Constructor)
- 传入maxSize参数
- 初始化全部成员变量
public ArrayQueue(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.array = new int[maxSize];
this.front = -1;
this.rear = -1;
}
(3)方法(Methods)
- 判断队列是否为空:
isQueueEmpty() -> boolean
- rear 和 front 是否重合
public boolean isQueueEmpty(){
// rear 和 front 是否重合
return this.rear == this.front;
}
- 判断队列是否已满:
isQueueFull() -> boolean
- rear 是否移动到了最后一个位置
public boolean isQueueFull(){
// rear 是否移动到了最后一个位置
return this.rear == this.maxSize - 1;
}
- 添加数据:
addData(int data)
1. 判断队列是否已满,已满则直接return结束方法
2. rear 后移一位: rear + 1
3. 在数组的 rear位置 添加数据
public void addData(int data){
// 1. 判断队列是否已满
if (this.isQueueFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满或已用完,无法添加");
return;
}
// 2. rear后移一位
this.rear++;
// 3. 在数组的rear位置添加数据
this.array[this.rear] = data;
}
- 取出数据:
fetchData() -> int
1. 判断队列是否为空,为空则抛出异常
2. front 后移一位: front + 1
3. 在数组的 front位置 取出数据
public int fetchData(){
// 1. 判断队列是否为空,为空则抛出异常
if (this.isQueueEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无可取出数据");
}
// 2. front后移一位
this.front++;
// 3. 在数组的fornt位置取出数据
return this.array[front];
}
- 显示全部数据:
displayAll()
1. 判断队列是否为空,为空则直接return结束方法
2. 遍历 数组,打印 有效 数据
public void displayAll(){
// 1. 判断队列是否为空,为空则直接return结束方法
if (this.isQueueEmpty()){
System.out.println("队列为空,无可打印数据");
return;
}
// 2. 遍历数组,打印有效数据
for(int i = this.front + 1; i <= this.rear; i++){
System.out.printf("Item d% is: %d\n", i + 1, this.array[i]);
}
}
- 获取头部数据:
peekHeadData() -> int
1. 判断队列是否为空,为空则直接return结束方法
2. array返回位于 front 后一个位置 的数据
public int peekHeadData(){
// 1. 判断队列是否为空,为空则直接return结束方法
if (this.isQueueEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无可获取的头部数据");
}
// 2. array返回位于front后一个位置的数据
return this.array[this.front + 1];
}
4. 完整实现:
// 数组模拟队列,一次性使用
public class OneTimeArrayQueue {
private int[] array; // 储存队列的数组
private int maxSize; // 队列最大容量
private int front; // 指向队列最前面数据的前一个位置
private int rear; // 指向队列最后面数据的位置
// 构造器
public OneTimeArrayQueue(int maxSize){
this.maxSize = maxSize;
this.array = new int[maxSize];
this.front = -1;
this.rear = -1;
}
// 判断队列是否为空
public boolean isQueueEmpty(){
// rear 和 front 是否重合
return this.rear == this.front;
}
// 判断队列是否已满
public boolean isQueueFull(){
// rear 是否位于数组末尾位置
return this.rear == this.maxSize - 1;
}
// 添加数据
public void addData(int data){
// 1. 判断数组是否已满
if (this.isQueueFull()){
System.out.println("队列已满或已用完,无法添加");
}
// 2. rear 后移一位
this.rear++;
// 3. 添加数据到数组的rear位置
this.array[rear] = data;
}
// 取出数据
public int fetchData(){
// 1. 判断数组是否为空
if (this.isQueueEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无可取出数据");
}
// 2. front 后移一位
this.front++;
// 3. 取出位于数组front位置的数据
return this.array[this.front];
}
// 显示全部数据
public void displayAllData(){
// 1. 判断数组是否为空
if (this.isQueueEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无可打印数据");
}
// 2. 遍历数组,打印有效数据
for (int i = this.front + 1; i <= this.rear; i++){
System.out.printf("Item %d is: %d\n", i + 1, this.array[i]);
}
}
// 获取头部数据
public int peekHeadData(){
// 1. 判断数组是否为空
if (this.isQueueEmpty()){
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,无可打印数据");
}
// 2. 返回数组中位于(front+1)位置的数据
return this.array[this.front + 1];
}
}
























 1611
1611











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








