5.1 流的继承关系
在C++中,有一个stream这个类,所有的I/O都以这个“流”类为基础的,里面包括了所有的输入输出类,今天我们就来介绍一下sstream.h(字符串流)这个类:
C++引入了ostringstream、istringstream、stringstream这三个类,要使用他们创建对象就必须包含sstream.h头文件。
istringstream类用于执行C++风格的串流的输入操作。
ostringstream类用于执行C风格的串流的输出操作。
strstream类同时可以支持C风格的串流的输入输出操作。
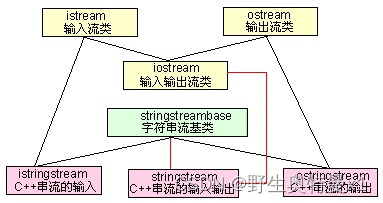
istringstream类是从istream(输入流类)和stringstreambase(c++字符串流基类)派生而来,ostringstream是从ostream(输出流类)和stringstreambase(c++字符串流基类)派生而来,stringstream则是从iostream(输入输出流类)和和stringstreambase(c++字符串流基类)派生而来。
他们的继承关系如下图所示:
5.2 字串流的输入操作
istringstream是由一个string对象构造而来,istringstream类从一个string对象读取字符。
istringstream的构造函数原形如下:
istringstream::istringstream(string str);
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
istringstream istr;
istr.str("1 56.7",);
//上述两个过程可以简单写成 istringstream istr("1 56.7");
cout << istr.str() << endl;
int a;
float b;
istr >> a;
cout << a << endl;
istr >> b;
cout << b << endl;
system("pause");
}
上例中,构造字符串流的时候,空格会成为字符串参数的内部分界,例子中对a,b对象的输入"赋值"操作证明了这一点,字符串的空格成为了整型数据与浮点型数据的分解点,利用分界获取的方法我们事实上完成了字符串到整型对象与浮点型对象的拆分转换过程。
str()成员函数的使用可以让istringstream对象返回一个string字符串(例如本例中的输出操作(cout<<istr.str();)。
5.3 字串流的输出操作
ostringstream同样是由一个string对象构造而来,ostringstream类向一个string插入字符。
ostringstream的构造函数原形如下:
ostringstream::ostringstream(string str);
示例代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ostringstream ostr;
ostr.str("abc");//如果构造的时候设置了字符串参数,那么增长操作的时候不会从结尾开始增加,而是修改原有数据,超出的部分增长
ostr.put('d');
ostr.put('e');
ostr << "fg";
string gstr = ostr.str();
cout << gstr;
system("pause");
}
在上例代码中,我们通过put()或者左移操作符可以不断向ostr插入单个字符或者是字符串,通过str()函数返回增长过后的完整字符串数据,但值得注意的一点是,当构造的时候对象内已经存在字符串数据的时候,那么增长操作的时候不会从结尾开始增加,而是修改原有数据,超出的部分增长。
对于stringstream了来说,不用我多说,大家也已经知道它是用于C++风格的字符串的输入输出的。
stringstream的构造函数原形如下:
stringstream::stringstream(string str);
示例代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stringstream ostr("ccc");
ostr.put('d');
ostr.put('e');
ostr << "fg";
string gstr = ostr.str();
cout << gstr << endl;
char a;
ostr >> a;
cout << a
system("pause");
}
5.4 字串流在数据类型转换中的应用
除此而外,stringstream类的对象我们还常用它进行string与各种内置类型数据之间的转换。
示例代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
stringstream sstr;
//--------int转string-----------
int a = 100;
string str;
sstr << a;
sstr >> str;
cout << str << endl;
//--------string转char[]--------
sstr.clear();//如果你想通过使用同一stringstream对象实现多种类型的转换,请注意在每一次转换之后都必须调用clear()成员函数。
string name = "colinguan";
char cname[200];
sstr << name;
sstr >> cname;
cout << cname;
system("pause");
}
5.5 输入/输出的状态标志
接下来我们来学习一下输入/输出的状态标志的相关知识,C++中负责的输入/输出的系统包括了关于每一个输入/输出操作的结果的记录信息。这些当前的状态信息被包含在io_state类型的对象中。io_state是一个枚举类型(就像open_mode一样),以下便是它包含的值。
goodbit 无错误
Eofbit 已到达文件尾
failbit 非致命的输入/输出错误,可挽回
badbit 致命的输入/输出错误,无法挽回
有两种方法可以获得输入/输出的状态信息。一种方法是通过调用rdstate()函数,它将返回当前状态的错误标记。例如,假如没有任何错误,则rdstate()会返回goodbit.
下例示例,表示出了rdstate()的用法:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a;
cin >> a;
cout << cin.rdstate() << endl;
if (cin.rdstate() == ios::goodbit) {
cout << "输入数据的类型正确,无错误!" << endl;
}
if (cin.rdstate() == ios_base::failbit) {
cout << "输入数据类型错误,非致命错误,可清除输入缓冲区挽回!" << endl;
}
system("pause");
}
//另一种方法则是使用下面任何一个函数来检测相应的输入 / 输出状态:
bool bad();
bool eof();
bool fail();
bool good();
//下例示例,表示出了上面各成员函数的用法:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a;
cin >> a;
cout << cin.rdstate() << endl;
if (cin.good()) {
cout << "输入数据的类型正确,无错误!" << endl;
}
if (cin.fail()) {
cout << "输入数据类型错误,非致命错误,可清除输入缓冲区挽回!" << endl;
}
system("pause");
}
如果错误发生,那么流状态既被标记为错误,你必须清除这些错误状态,以使你的程序能正确适当地继续运行。要清除错误状态,需使用clear()函数。此函数带一个参数,它是你将要设为当前状态的标志值。,只要将ios::goodbit作为实参。
示例代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a;
cin >> a;
cout << cin.rdstate() << endl;
cin.clear(ios::goodbit);
cout << cin.rdstate() << endl;
system("pause");
}
通常当我们发现输入有错又需要改正的时候,使用clear()更改标记为正确后,同时也需要使用get()成员函数清除输入缓冲区,以达到重复输入的目的。
示例代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a;
while (1) {
cin >> a;
if (!cin) { //条件可改写为cin.fail()
cout << "输入有错!请重新输入" << endl;
cin.clear();
cin.get();
} else {
cout << a;
break;
}
}
system("pause");
}
最后再给出一个对文件流错误标记处理的例子,巩固学习,代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ifstream myfile("c:.txt", ios_base::in, 0);
if (myfile.fail()) {
cout << "文件读取失败或指定文件不存在!" << endl;
} else {
char ch;
while (myfile.get(ch)) {
cout << ch;
}
if (myfile.eof()) {
cout << "文件内容已经全部读完" << endl;
}
while (myfile.get(ch)) {
cout << ch;
}
}
system("pause");
}






















 6919
6919











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








