Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary search tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary search tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
The encoded string should be as compact as possible.
Note: Do not use class member/global/static variables to store states. Your serialize and deserialize algorithms should be stateless.
然后给出的方法模板是这样的:/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
public class Codec {
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
}
}
// Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
// Codec codec = new Codec();
// codec.deserialize(codec.serialize(root));如何用字符串来表示一棵树呢?我就想到了用 [ val , ( leftTree , rightTree ) ] 的形式。如果没有左右子树,那么为 [ val ] 。如果没有右子树,那么为 [ val , ( leftTree ) ] 。
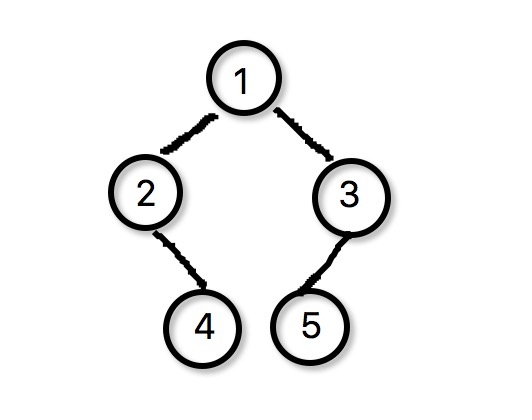
举个例子。下面这张图:
对应的string就是 [1([2(,[4])],[3([5])])]
下面是我的解法:
//Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return "";
}
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null){
return "["+root.val+"]";
}
else if(root.right==null){
return "["+root.val+"("+serialize(root.left)+")]";
}
else{
return "["+root.val+"("+serialize(root.left)+","+serialize(root.right)+")]";
}
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if(data==null||data.equals("")){
return null;
}
if(!data.contains("(")){
data=data.substring(1,data.length()-1);//把两侧的[ ]剥掉
int val=Integer.parseInt(data);
return new TreeNode(val);
}
int index=data.indexOf('(');
String valString=data.substring(1,index);
String subRootString=data.substring(index+1,data.length()-2);//去掉(和)]
int val=Integer.parseInt(valString);
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(val);
int i=0;//i是要得出当前括号所对应逗号的index
int countLeft=0;
while(i<subRootString.length()){
if(subRootString.charAt(i)=='['){
countLeft++;
}
else if(subRootString.charAt(i)==']'){
countLeft--;
}
else if(countLeft==0&&subRootString.charAt(i)==','){
break;
}
i++;
}
if(i==subRootString.length()){//说明当前括号没有对应逗号,即当前只有左结点
root.left=deserialize(subRootString);
}
else{
String left=subRootString.substring(0, i);
String right=subRootString.substring(i+1);
root.left=deserialize(left);
root.right=deserialize(right);
}
return root;
}大神是用先根遍历+队列来做的,思路如下:
BST的先根遍历是先输出根结点,再输出左、右结点。
root left1 left2 leftX right1 rightX
BST的特征是它的左子树的值都小于它,它的右子树的值都大于它。那么我们注意先根遍历的值:
rootValue (<rootValue) (<rootValue) (<rootValue) |separate line| (>rootValue) (>rootValue)
那么,在分割线 | 前面的值都比当前根的值小,在分割线| 后面的值都比当前根的值大。我们根据这个特性来构造左右子树。我们使用队列来获得根节点、左右子树。
public class Codec {
private static final String SEP = ",";
private static final String NULL = "null";
// Encodes a tree to a single string.
public String serialize(TreeNode root) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (root == null) return NULL;
//traverse it recursively if you want to, I am doing it iteratively here
Stack<TreeNode> st = new Stack<>();
st.push(root);
while (!st.empty()) {
root = st.pop();
sb.append(root.val).append(SEP);
if (root.right != null) st.push(root.right);
if (root.left != null) st.push(root.left);
}
return sb.toString();
}
// Decodes your encoded data to tree.
// pre-order traversal
public TreeNode deserialize(String data) {
if (data.equals(NULL)) return null;
String[] strs = data.split(SEP);
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
for (String e : strs) {
q.offer(Integer.parseInt(e));
}
return getNode(q);
}
// some notes:
// 5
// 3 6
// 2 7
private TreeNode getNode(Queue<Integer> q) { //q: 5,3,2,6,7
if (q.isEmpty()) return null;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(q.poll());//root (5)
Queue<Integer> samllerQueue = new LinkedList<>();
while (!q.isEmpty() && q.peek() < root.val) {
samllerQueue.offer(q.poll());
}
//smallerQueue : 3,2 storing elements smaller than 5 (root)
root.left = getNode(samllerQueue);
//q: 6,7 storing elements bigger than 5 (root)
root.right = getNode(q);
return root;
}
}























 3169
3169

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








