前面一种方案实际上还是存在一定的问题的, 就是这个避重就轻的初始g(n)值127*s(127表示0-255之间的中间值), 这个东西带来的最直接的问题就是边缘的效果在这个算法下是不咋地的。 其实从这个所谓的"Wellner 1993", 后人又做了很多的改进, 使之效率更高, 效果更好。比方说这个Derek Bradley和Gerhard Roth搞的这个所谓 Adaptive Thresholding Using the Integral Image 在这个网页
http://www.scs.carleton.ca/~roth/iit-publications-iti/docs/gerh-50002.pdf 可以看到一些他的踪迹。
这个算法的基本思想是这样的,为了打破原来算法的初始值问题以及扫描顺序的问题, 这里的像素二值化的时候, 直接使用周围矩形像素的颜色作比较,这样来判断像素值更科学。我们对算法的介绍从求和面积表(Summed-Area Table)开始. 这个求和面积表简单点说就是维护一张表, 表中的元素值就是它左上位置的所有像素的像素值和。(数学公式在这里编辑简直是噩梦!只能放图了无图无真相:))
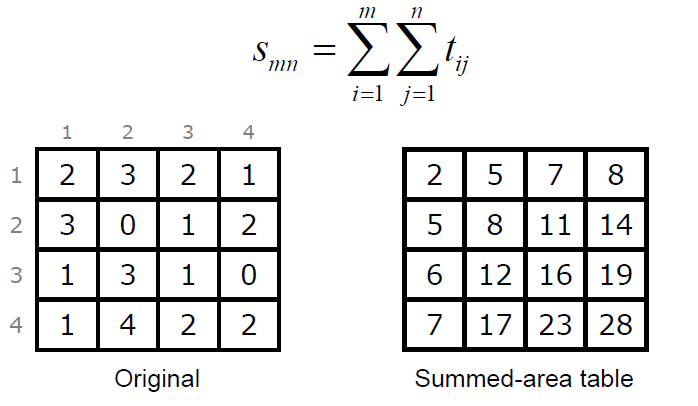
左边就是原始像素值, 右边的就是累加得到的表, 比方说这个表里面的(2,2)位置的8就是通过2+3+3+0得到的, 而这个最大值28就是所有像素的累加和。得到这个和和我们的二值化有什么关联呢?前面我们提到了在新的这个算法里面像素的值以来于周围像素的颜色, 那周围像素的颜色如何表示呢? 我们可以通过这个表轻松获得, 且看下面一张图:
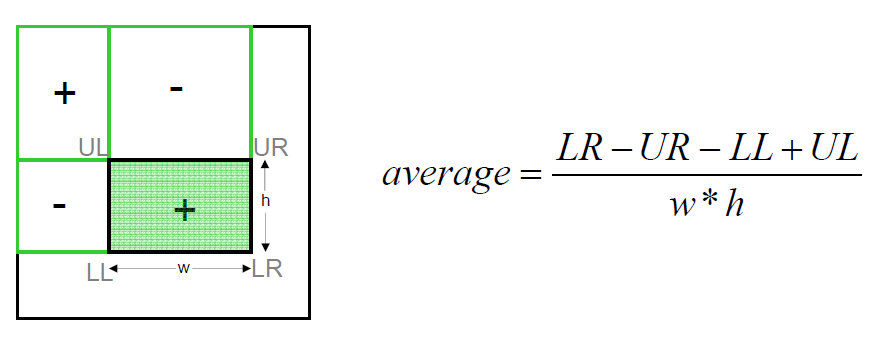
这里的UL, LL, UR, LR表示的就是前面这个求和表里面的值, 如果我们要判断绿色区域中这个+号位置的值, 我们就要计算整个绿色区域的平均像素值, 如何计算呢? 有了新的表就方便了,右边其实给出了这个公式,这里的LR-UR-LL+UL就是整个绿色区域的像素值和。这个什么道理其实已经自己可以推断出来了, 如果还嫌这里不清楚的话,我们就给个更清楚的图:
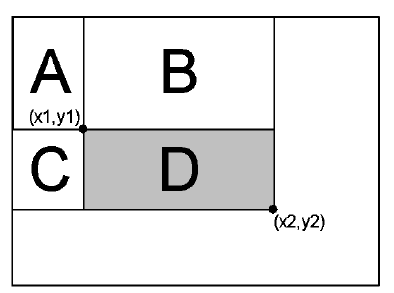
这个图和前面一样,但是如果还是用LR-UR-LL+UL来表示的话,这里就可以写成:
LR-UR-LL+UL = (A+B+C+D)-(A+B)-(A+C)+A = D, 这样就清楚很多了吧。 得到的这个值D就是D这个区域的像素值和, 那D中最中心的像素的颜色就可以用D/(widith*height)来做比较了。 所以算法的流程就是首先得到这个求和面积表, 其次遍历所有的像素, 然后以这些像素为中心点, 计算S*S大小的矩形的平均颜色, 用来和当前像素比较即可。这个流程可以说是相当精炼啊!这里依然用到了原来的S, T, 还保持了一致S是宽度的八分之一, 而T则是15,下面有一段我改过的实现代码:
- void adaptiveThreshold(unsigned char* input, unsigned char*& bin, int width, int height)
- {
- int S = width >> 3;
- int T = 15;
- unsigned long* integralImg = 0;
- int i, j;
- long sum=0;
- int count=0;
- int index;
- int x1, y1, x2, y2;
- int s2 = S/2;
- bin = new unsigned char[width*height];
- // create the integral image
- integralImg = (unsigned long*)malloc(width*height*sizeof(unsigned long*));
- for (i=0; i<width; i++)
- {
- // reset this column sum
- sum = 0;
- for (j=0; j<height; j++)
- {
- index = j*width+i;
- sum += input[index];
- if (i==0)
- integralImg[index] = sum;
- else
- integralImg[index] = integralImg[index-1] + sum;
- }
- }
- // perform thresholding
- for (i=0; i<width; i++)
- {
- for (j=0; j<height; j++)
- {
- index = j*width+i;
- // set the SxS region
- x1=i-s2; x2=i+s2;
- y1=j-s2; y2=j+s2;
- // check the border
- if (x1 < 0) x1 = 0;
- if (x2 >= width) x2 = width-1;
- if (y1 < 0) y1 = 0;
- if (y2 >= height) y2 = height-1;
- count = (x2-x1)*(y2-y1);
- // I(x,y)=s(x2,y2)-s(x1,y2)-s(x2,y1)+s(x1,x1)
- sum = integralImg[y2*width+x2] -
- integralImg[y1*width+x2] -
- integralImg[y2*width+x1] +
- integralImg[y1*width+x1];
- if ((long)(input[index]*count) < (long)(sum*(100-T)/100))
- bin[index] = 0;
- else
- bin[index] = 255;
- }
- }
- free (integralImg);
- }
这里也有一点效果图可以看看, 同时有和前面一个算法的比较:
原始1 wellnar算法 最新


还有一组:
wellnar:
最新算法:
这些个贴图其实还不是特别的具体, 其实这个算法特别适用于光照强度变化很大的像素, 这里有些网页也给出了鲜明的对比:http://www.derekbradley.ca/AdaptiveThresholding/index.html 效果的差距还是很明显的。 总的来说这个算法实现简单, 效率很高,确实是不错的选择。 而且还很新!在07年的杂志上发表的,现在记录下来与君共勉之!
opencv版本
void adaptiveThreshold( const cv::Mat& inImg, cv::Mat& outImg, int step)
{
if (outImg.empty())
{
outImg.create(inImg.size(), inImg.depth());
}
int S = inImg.cols >> step;
int T = 15;
int count=0;
int index;
int row, col, x1, y1, x2, y2;
long double brs, bls, trs, tls, value;
int s2 = S/2;
cv::Mat sum(inImg.rows+1, inImg.cols+1, CV_32FC1);
cv::integral(inImg, sum);
for (row = 0; row < inImg.rows; row++)
{
const uchar* ptr = inImg.ptr<uchar>(row);
uchar* ptr_out = outImg.ptr<uchar>(row);
for (col = 0; col < inImg.cols; col++)
{
// set the SxS region
x1 = col-s2; x2 = col+s2;
y1 = row-s2; y2 = row+s2;
// check the border
if (x1 < 0) x1 = 0;
if (x2 >= inImg.cols) x2 = inImg.cols-1;
if (y1 < 0) y1 = 0;
if (y2 >= inImg.rows) y2 = inImg.rows-1;
count = (x2-x1)*(y2-y1);
brs = sum.at<int>(y2, x2);
bls = sum.at<int>(y2, x1);
trs = sum.at<int>(y1, x2);
tls = sum.at<int>(y1, x1);
value = brs+tls-trs-bls;
if ((ptr[col]*count) < (long)(value*(100-T)/100))
{
ptr_out[col] = 255;
}
else
{
ptr_out[col] = 0;
}
}
}
}
























 3123
3123

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








