在软件项目中,最重要的就是测量质量,成本, 项目和流程的有效性。如果没有测量,项目不能算真正的完成。 这篇文章,我们将会结合例子和图表—学习软件测试度量和测量指标以及怎样在软件测试流程中使用它们。
这里有一句名言:“我们无法测量我们不能控制的东西”。
其中, 可控制的项目指的是:一个项目管理者/领导从测试计划中能发现偏差并且有效的采取行动。根据项目需要生成测量指标是实现令被测软件达到要求的重要的指标。
什么是软件测量指标?
软件测量指标是指对一个拥有指定属性的系统、 系统组件或过程处在何种程度的定量测量。可以被定义为“测量的标准”
软件指标被用于测量项目的质量。简单的说,指标是一个被用于描述一个属性的单位,是一种测量的尺度。
假设,在一般情况下,公斤是一个描述重量的属性的指标,同样的,在软件工程中,在成千行的代码中有多少问题被发现?这里问题的数量是一个测量,而代码行数是另一个测量。 指标就是由这两个测量定义的。
测试指标举例:
- 模块中有多少缺陷存在?
- 人均执行多少测试用例?
- 测试覆盖率是多少?
- 软件测试测量的是什么?
测量是产品或过程的一些属性的量化指示,如程度、数量、尺寸、容量,规模等。
测试度量举例: 缺陷的总数。
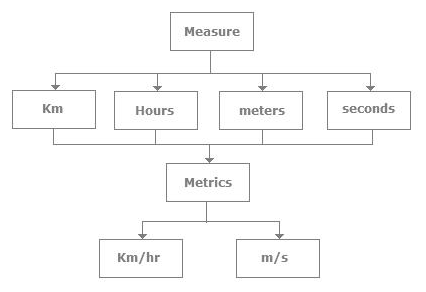
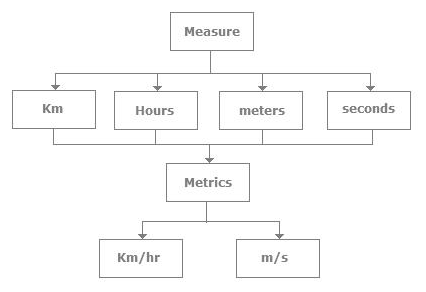
请参考下图来清楚的了解测量与指标的区别。
为什么要有测试指标?
制定软件测试指标是软件测试经理最重要的责任。 测试指标往往能决定下一阶段的活动,比如:预估未来项目的成本和进度。- 了解促进项目的成功需要何种改进。
- 对待改善的过程或是技术做出决策。
软件测试指标的重要性:
正如前面所说的,测试指标是测量软件质量最重要的因素。 现在,我们如何通过指标来测量软件的质量呢? 假设,如果一个项目没有一个指标,测试分析师所作的工作的质量要怎么被定量? 例如:一个测试分析师需要做:- 为 5 个需求设计测试用例
- 执行设计的测试用例
- 记录缺陷以及需求和执行失败的相关用例
- 缺陷解决后, 重新验证缺陷,再次执行相应的失败的用例
- 每个需求设计多少个测试用例?
- 有多少测试用例没有设计(设计不完善)?
- 有多少测试用例被执行?
- 多少用例通过/失败/中断?
- 多少测试用例没有被执行?
- 有多少缺陷被发现,这些缺陷的严重程度是什么?
- 有多少失败的测试用例是因为同一个缺陷等。
指标的生命周期:
➢ 分析:- 识别指标
- 定义指标
- 给利益相关者以及测试团队解释指标的需求
- 培训测试团队在处理测试指标时需要获取的关键数据点
- 获取、验证数据
- 使用获取的数据计算指标值
- 报告中衍生出有效结论
- 将报告发送给给利益相关者和各位代表
- 记录利益相关者的反馈
手动测试指标的类型:
测试指标主要分为两个类别: 计算指标和基础指标。 **基础指标**是由测试分析师在测试用例编写和执行期间收集的数据派生来的指标。 这个数据将贯穿整个测试周期。 收集的数据譬如为, 某一项目所开发的测试案例的总数、 需要被执行的 测试用例的数量或是通过/失败/受阻的测试用例计数。 **计算指标**是通过收集基础指标数据而派生的。这些指标通常由测试经历为测试报告等目的而进行追踪。软件测试指标的例子:
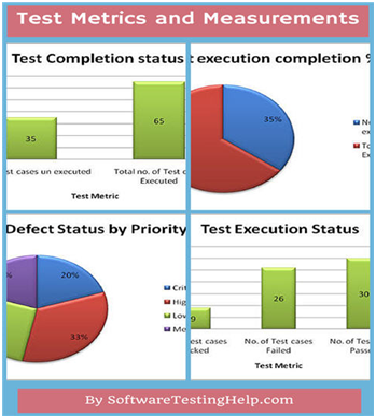
这里来举一个例子来计算各种各样被用于软件测试报告中的指标:
以下表格中的数据来自真正参与到测试中的测试分析师:
| 序号 | 测试指标 | 个数 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 需求个数 | 5 |
| 2 | 平均每个需求所写的测试用例个数 | 20 |
| 3 | 总的测试用例个数 | 100 |
| 4 | 被执行的用例的个数 | 65 |
| 5 | 通过的用例个数 | 30 |
| 6 | 失败的用例个数 | 26 |
| 7 | 中断的用例的个数 | 9 |
| 8 | 没有被执行的用例个数 | 35 |
| 9 | 确定的缺陷数 | 30 |
| 10 | 严重的缺陷数 | 6 |
| 11 | 优先级较高的缺陷数 | 10 |
| 12 | 一般的缺陷数 | 6 |
| 13 | 轻微的缺陷数 | 8 |
原文如下:
In software projects, it is most important to measure the quality, cost and effectiveness of the project and the processes. Without measuring these, project can’t be completed successfully.
In today’s article we will learn with examples and graphs – Software test metrics and measurementsand how to use these in software testing process.
There is a famous statement: “We can’t control things which we can’t measure”.
Here controlling the projects means, how a project manager/lead can identify the deviations from the test plan ASAP in order to react in the perfect time. Generation of test metrics based on the project needs is very much important to achieve the quality of the software being tested.
What are Software Testing Metrics?
A Metric is a quantitative measure of the degree to which a system, system component, or process possesses a given attribute.Metrics can be defined as “STANDARDS OF MEASUREMENT”.
Software Metrics are used to measure the quality of the project. Simply, Metric is a unit used for describing an attribute. Metric is a scale for measurement.
Suppose, in general, “Kilogram” is a metric for measuring the attribute “Weight”. Similarly, in software, “How many issues are found in thousand lines of code?”, here No. of issues is one measurement & No. of lines of code is another measurement. Metric is defined from these two measurements.
Test metrics example:
- How many defects are existed within the module?
- How many test cases are executed per person?
- What is the Test coverage?
- What is Software Test Measurement?
Measurement is the quantitative indication of extent, amount, dimension, capacity, or size of some attribute of a product or process.
Test measurement example: Total number of defects.
Please refer below diagram for clear understanding of the difference between Measurement & Metrics.
Why Test Metrics?
Generation of Software Test Metrics is the most important responsibility of the Software Test Lead/Manager. Test Metrics are used to take the decision for next phase of activities such as, estimate the cost & schedule of future projects.- Understand the kind of improvement required to success the project
- Take decision on process or technology to be modified etc.
Importance of Software Testing Metrics:
As explained above, Test Metrics are the most important to measure the quality of the software. Now, how can we measure the quality of the software by using Metrics? Suppose, if a project does not have any metrics, then how the quality of the work done by a Test analyst will be measured? **For Example:** A Test Analyst has to,- Design the test cases for 5 requirements
- Execute the designed test cases
- Log the defects & need to fail the related test cases
- After the defect is resolved, need to re-test the defect & re-execute the corresponding failed test case.
- How many test cases have been designed per requirement?
- How many test cases are yet to design?
- How many test cases are executed?
- How many test cases are passed/failed/blocked?
- How many test cases are not yet executed?
- How many defects are identified & what is the severity of those defects?
- How many test cases are failed due to one particular defect? etc.
Metrics Life Cycle:
➢ Analsis- Identifiation of the Metrics
- Define the identified Metrics
- Explain the need of metric to stakeholder and testing tean
- Educate the testing team about the data points need to be captured for processing the metric
- Capture & verify the data
- Calculating the metric(s) value using the data capyured
- Develop the report with effective conclsion
- Didtribute report to the stakeholder and respective representative
- Take feedback from stakeholder
Types of Manual Test Metrics:
Testing Metrics are mainly divided into 2 categories. Base Metrics Calculated MetricsBase Metrics:
Base Metrics are the Metrics which are derived from the data gathered by the Test Analyst during the test case development and execution. This data will be tracked throughout the Test Life cycle. I.e. collecting the data like, Total no. of test cases developed for a project (or) no. of test cases need to be executed (or) no. of test cases passed/failed/blocked etc.Calculated Metrics:
Calculated Metrics are derived from the data gathered in Base Metrics. These Metrics are generally tracked by the test lead/manager for Test Reporting purpose.Examples of Software Testing Metrics:
Let’s take an example to calculate various test metrics used in software test reports: Below is the table format for the data retrieved from the test analyst who is actually involved in testing:| S.NO | Testng Metric | Data retrieved during test case development&execution |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | NO.of Requirements | 5 |
| 2 | Avg.NO.of Test cases written per Requirement | 20 |
| 3 | Total no.of Test cases written for all requirements | 100 |
| 4 | Total no.of Test cases Executed | 65 |
| 5 | No.of Test cases Passed | 30 |
| 6 | No.of Test cases Failed | 26 |
| 7 | No.of Test cases Blocked | 9 |
| 8 | No.of Test cases unexecuted | 35 |
| 9 | No.of Test Defects identified | 30 |
| 10 | Critical Defects count | 6 |
| 11 | High Defects count | 10 |
| 12 | Medium Defects count | 6 |
| 13 | Low Defects count | 8 |

























 565
565

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








