目录
4.1 提交writeback任务并启动工作队列wb_queue_work
一 、基本概念
bdi(Backing Device Information),从字面理解后台设备信息?主要用于管理“回写”线程。回写是由于内核采用了page cache的延迟写入机制,应用通过write系统调用写时数据并没有真正被写入磁盘介质中,而是只写入到内核page cache中就返回了。因为写内存的速率远远大于写磁盘这种块设备,这样就能够大大的提高应用层效率。当然需要注意的是是否开启这个page cache是由应用open时决定的,如果是以O_DIRECT的标志打开则走的是直接IO,就没有这个page cache,这里先不讨论这个直接IO。
在这种延迟写入的情况下,就需要有回写线程来将在page cache中的数据真正写入到磁盘介质中,而这些需要被写入磁盘的page被称作脏页。
脏页一般在如下三种情况会被写入磁盘,后面具体介绍:
1. 脏页在内存中停留的时间,这个时间会包括两方面,也是可以配置的;
2. 脏页占总可用内存的比例,这个也是可以配置的;
3.调主动刷新脏页的接口:sync、fsync、fdatasync,这三个是有区别的;
二、相关结构体
bdi随着内核版本的变动,也是有一定的变更,本文在linux-4.19.286上分析。在3.10后内核由workqueue来进行实际的回写工作,原先由一个pdflush进程统管所有磁盘的脏页回写,在磁盘数量多时很容易出现IO瓶颈,采用workquene来回写,相当于升级为多线程,提高了IO吞吐量。
内核通过backing_dev_info来管理bdi,定义在include/linux/backing-dev-defs.h。里面比较关键的就是bdi_writeback、struct list_head wb_list;
struct backing_dev_info {
struct list_head bdi_list;
unsigned long ra_pages; /* max readahead in PAGE_SIZE units */
unsigned long io_pages; /* max allowed IO size */
congested_fn *congested_fn; /* Function pointer if device is md/dm */
void *congested_data; /* Pointer to aux data for congested func */
const char *name;
struct kref refcnt; /* Reference counter for the structure */
unsigned int capabilities; /* Device capabilities */
unsigned int min_ratio;
unsigned int max_ratio, max_prop_frac;
/*
* Sum of avg_write_bw of wbs with dirty inodes. > 0 if there are
* any dirty wbs, which is depended upon by bdi_has_dirty().
*/
atomic_long_t tot_write_bandwidth;
struct bdi_writeback wb; /* the root writeback info for this bdi */
struct list_head wb_list; /* list of all wbs */
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK
struct radix_tree_root cgwb_tree; /* radix tree of active cgroup wbs */
struct rb_root cgwb_congested_tree; /* their congested states */
struct mutex cgwb_release_mutex; /* protect shutdown of wb structs */
struct rw_semaphore wb_switch_rwsem; /* no cgwb switch while syncing */
#else
struct bdi_writeback_congested *wb_congested;
#endif
wait_queue_head_t wb_waitq;
struct device *dev;
char dev_name[64];
struct device *owner;
struct timer_list laptop_mode_wb_timer;
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_FS
struct dentry *debug_dir;
struct dentry *debug_stats;
#endif
};
wb_list上面挂载的是需要回写的work,所有需要回写的脏页都会封装成wb_writeback_work,并提交到该链表,定义在./fs/fs-writeback.c。
struct wb_writeback_work {
long nr_pages;
struct super_block *sb;
enum writeback_sync_modes sync_mode;
unsigned int tagged_writepages:1;
unsigned int for_kupdate:1;
unsigned int range_cyclic:1;
unsigned int for_background:1;
unsigned int for_sync:1; /* sync(2) WB_SYNC_ALL writeback */
unsigned int auto_free:1; /* free on completion */
enum wb_reason reason; /* 注明回写的原因why was writeback initiated? */
struct list_head list; /* 挂到backing_dev_info上 pending work list */
struct wb_completion *done; /* 阻塞回写的情况下用以通知回写完成set if the caller waits */
};
reason会标注回写的原因:
num wb_reason {
WB_REASON_BACKGROUND,
WB_REASON_VMSCAN,
WB_REASON_SYNC,/*主动刷新*/
WB_REASON_PERIODIC,/*周期性的*/
WB_REASON_LAPTOP_TIMER,
WB_REASON_FREE_MORE_MEM,/*内存释放*/
WB_REASON_FS_FREE_SPACE,
/*
* There is no bdi forker thread any more and works are done
* by emergency worker, however, this is TPs userland visible
* and we'll be exposing exactly the same information,
* so it has a mismatch name.
*/
WB_REASON_FORKER_THREAD,
WB_REASON_MAX,
};
wb_writeback_work中涉及的需要回写的page及执行写入的工作队列都在bdi_writeback中定义:需要关注的是b_dirty、b_io、b_more_io、delayed_work。
truct bdi_writeback {
struct backing_dev_info *bdi; /* our parent bdi */
unsigned long state; /* Always use atomic bitops on this */
unsigned long last_old_flush; /* last old data flush */
struct list_head b_dirty; /* 当前磁盘上的所有脏页dirty inodes */
struct list_head b_io; /* 需要马上回写的parked for writeback */
struct list_head b_more_io; /* 负载过重时,分担b_io,parked for more writeback */
struct list_head b_dirty_time; /* time stamps are dirty */
spinlock_t list_lock; /* protects the b_* lists */
struct percpu_counter stat[NR_WB_STAT_ITEMS];
struct bdi_writeback_congested *congested;
unsigned long bw_time_stamp; /* last time write bw is updated */
unsigned long dirtied_stamp;
unsigned long written_stamp; /* pages written at bw_time_stamp */
unsigned long write_bandwidth; /* the estimated write bandwidth */
unsigned long avg_write_bandwidth; /* further smoothed write bw, > 0 */
/*
* The base dirty throttle rate, re-calculated on every 200ms.
* All the bdi tasks' dirty rate will be curbed under it.
* @dirty_ratelimit tracks the estimated @balanced_dirty_ratelimit
* in small steps and is much more smooth/stable than the latter.
*/
unsigned long dirty_ratelimit;
unsigned long balanced_dirty_ratelimit;
struct fprop_local_percpu completions;
int dirty_exceeded;
enum wb_reason start_all_reason;
spinlock_t work_lock; /* protects work_list & dwork scheduling */
struct list_head work_list;
struct delayed_work dwork; /*执行回写的延迟工作队列 work item used for writeback */
unsigned long dirty_sleep; /* last wait */
struct list_head bdi_node; /* anchored at bdi->wb_list */
...
}需要注意的是:
1、一个磁盘对应一个bdi,也就只有一个backing_dev_info;
2、每个bdi也只有一个bdi_writeback,期内描述了脏页链表和回写函数(delayed_work调用bdi_writeback_workfn,是在块设备注册时绑定的);
3、b_dirty描述该BDI设备上的所有dirty inode,回写时机到时才移到b_io链表上执行回写;

三、bdi注册
在内核启动过程中会以subsys_initcall的方式初始化一个default_bdi,实现在mm/backing-dev.c。
static int __init default_bdi_init(void)
{
int err;
bdi_wq = alloc_workqueue("writeback", WQ_MEM_RECLAIM | WQ_UNBOUND |
WQ_SYSFS, 0);
if (!bdi_wq)
return -ENOMEM;
err = bdi_init(&noop_backing_dev_info);
return err;
}
subsys_initcall(default_bdi_init);
static int bdi_init(struct backing_dev_info *bdi)
{
int ret;
bdi->dev = NULL;
kref_init(&bdi->refcnt);
bdi->min_ratio = 0;
bdi->max_ratio = 100;
bdi->max_prop_frac = FPROP_FRAC_BASE;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&bdi->bdi_list);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&bdi->wb_list);
init_waitqueue_head(&bdi->wb_waitq);
ret = cgwb_bdi_init(bdi);
return ret;
}
static int cgwb_bdi_init(struct backing_dev_info *bdi)
{
int ret;
INIT_RADIX_TREE(&bdi->cgwb_tree, GFP_ATOMIC);
bdi->cgwb_congested_tree = RB_ROOT;
mutex_init(&bdi->cgwb_release_mutex);
init_rwsem(&bdi->wb_switch_rwsem);
ret = wb_init(&bdi->wb, bdi, 1, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!ret) {
bdi->wb.memcg_css = &root_mem_cgroup->css;
bdi->wb.blkcg_css = blkcg_root_css;
}
return ret;
}
tatic int wb_init(struct bdi_writeback *wb, struct backing_dev_info *bdi,
int blkcg_id, gfp_t gfp)
{
int i, err;
memset(wb, 0, sizeof(*wb));
if (wb != &bdi->wb)
bdi_get(bdi);
wb->bdi = bdi;
wb->last_old_flush = jiffies;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wb->b_dirty);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wb->b_io);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wb->b_more_io);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wb->b_dirty_time);
spin_lock_init(&wb->list_lock);
wb->bw_time_stamp = jiffies;
wb->balanced_dirty_ratelimit = INIT_BW;
wb->dirty_ratelimit = INIT_BW;
wb->write_bandwidth = INIT_BW;
wb->avg_write_bandwidth = INIT_BW;
spin_lock_init(&wb->work_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wb->work_list);
INIT_DELAYED_WORK(&wb->dwork, wb_workfn);
wb->dirty_sleep = jiffies;
wb->congested = wb_congested_get_create(bdi, blkcg_id, gfp);
if (!wb->congested) {
err = -ENOMEM;
goto out_put_bdi;
}
...
}
在其他磁盘介质调用add_disk将磁盘添加到系统的时候,会将创建backing_dev_info加入bdi_list。以emmc为例,具体的emmc 驱动和设备card匹配的过程这里就不分析,mmc_blk匹配成功后在mmc_blk_probe中,进行块设备的相关初始化,其中就包括了bdi的注册过程:
mmc_blk_probe
mmc_blk_alloc
mmc_blk_alloc_req
mmc_init_queue
mmc_mq_init_queue
blk_mq_init_queue
blk_alloc_queue_node
bdi_alloc_node
kmalloc_node ///<申请bdi结构体
bdi_init///<初始化bdi,绑定bdi_writeback,wb->dwork
到了bdi_init则就跟default_bdi是一样的了。上面很多函数都涉及到等待队列的注册,后续分析通用块层和IO调度时再分析。
四、回写触发及流程
触发write_back的两种实现:
4.1 提交writeback任务并启动工作队列wb_queue_work
定义在fs/fs-writeback.c,从定义来看先将wb_writeback_work加入bdi_writeback的work_list,再立即调用bdi_writeback的延时工作队列进行work的回写。
static void wb_queue_work(struct bdi_writeback *wb,
struct wb_writeback_work *work)
{
trace_writeback_queue(wb, work);
if (work->done)
atomic_inc(&work->done->cnt);
spin_lock_bh(&wb->work_lock);
if (test_bit(WB_registered, &wb->state)) {
list_add_tail(&work->list, &wb->work_list);///<将work加入wb的work链表
mod_delayed_work(bdi_wq, &wb->dwork, 0);///<执行delay_work工作队列
} else
finish_writeback_work(wb, work);
spin_unlock_bh(&wb->work_lock);
}
4.2 启动工作队列 wb_wakeup
定义在fs/fs-writeback.c,从wb_wakeup的实现上来看,其只是立即执行bdi_writeback的延时工作队列 。
static void wb_wakeup(struct bdi_writeback *wb)
{
spin_lock_bh(&wb->work_lock);
if (test_bit(WB_registered, &wb->state))
mod_delayed_work(bdi_wq, &wb->dwork, 0);
spin_unlock_bh(&wb->work_lock);
}
4.3 调用流程
列举了如下几种调用流程会调到上述两种方式。
1、应用层调sync接口:
SYSCALL_DEFINE0(sync)
ksys_sync
wakeup_flusher_threads(WB_REASON_SYNC);
__wakeup_flusher_threads_bdi
wb_start_writeback
wb_wakeup
2、write的时候触发脏页平衡
generic_perform_write
balance_dirty_pages_ratelimited
balance_dirty_pages
wb_start_background_writeback
wb_wakeup
3、调清缓存接口,内存回收
4、申请内存不足,释放内存
__alloc_pages_nodemask
__alloc_pages_slowpath
__alloc_pages_direct_reclaim
__perform_reclaim
try_to_free_pages
do_try_to_free_pages
…shrink…
shrink_inactive_list
wakeup_flusher_threads(WB_REASON_VMSCAN);
__wakeup_flusher_threads_bdi
wb_start_writeback
4.4 回写流程
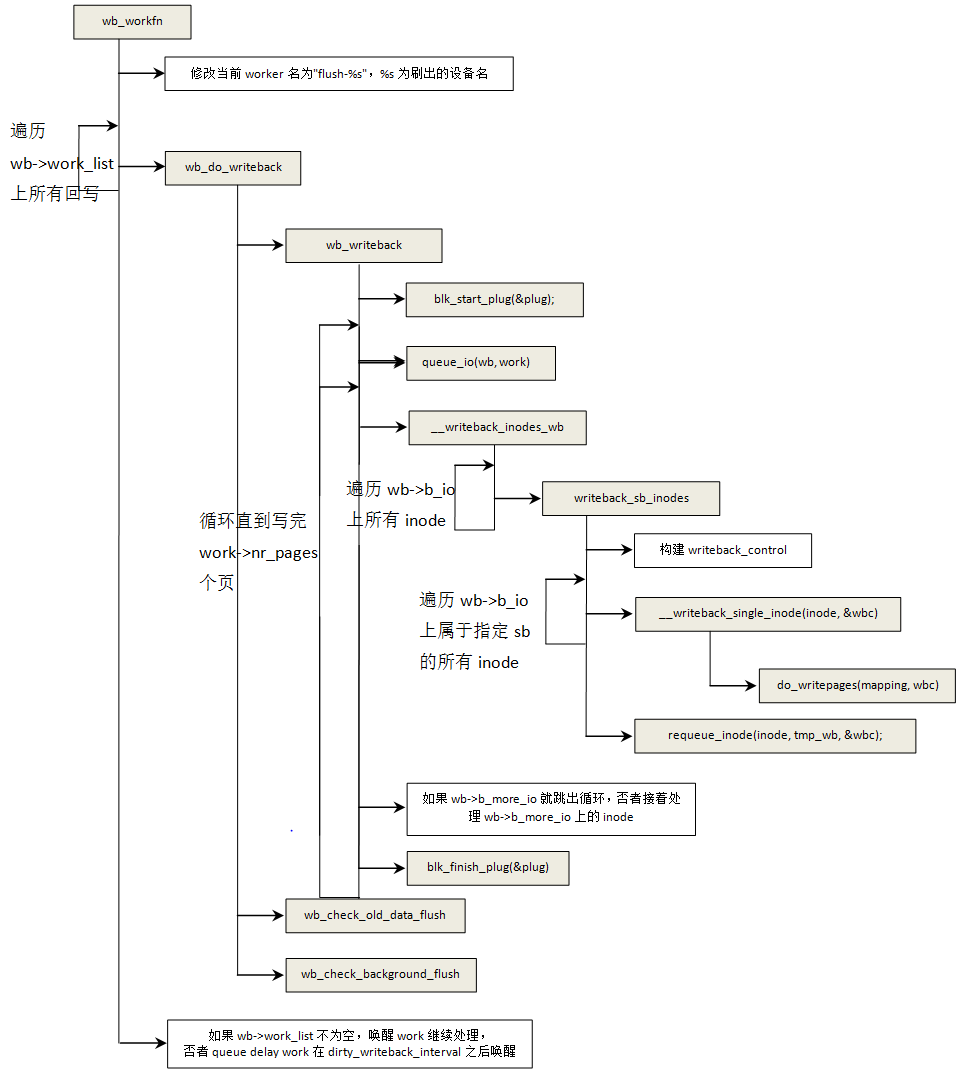
wb_workfn是前面在初始化bdi的时候绑定到延时工作队列上的,其内部主要就是按照提交的work将dirty inode写入介质,在这里我们主要介绍到do_writepages,再往后就是具体的文件系统内建立bio,进而submit_bio到通用块层->io调度层->设备驱动层->介质.
void wb_workfn(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct bdi_writeback *wb = container_of(to_delayed_work(work),
struct bdi_writeback, dwork);
long pages_written;
set_worker_desc("flush-%s", bdi_dev_name(wb->bdi));
current->flags |= PF_SWAPWRITE;
if (likely(!current_is_workqueue_rescuer() ||
!test_bit(WB_registered, &wb->state))) {
/*
* The normal path. Keep writing back @wb until its
* work_list is empty. Note that this path is also taken
* if @wb is shutting down even when we're running off the
* rescuer as work_list needs to be drained.
*/
do {
pages_written = wb_do_writeback(wb);
trace_writeback_pages_written(pages_written);
} while (!list_empty(&wb->work_list));
} else {
/*
* bdi_wq can't get enough workers and we're running off
* the emergency worker. Don't hog it. Hopefully, 1024 is
* enough for efficient IO.
*/
pages_written = writeback_inodes_wb(wb, 1024,
WB_REASON_FORKER_THREAD);
trace_writeback_pages_written(pages_written);
}
if (!list_empty(&wb->work_list))
wb_wakeup(wb);
else if (wb_has_dirty_io(wb) && dirty_writeback_interval)
wb_wakeup_delayed(wb);
current->flags &= ~PF_SWAPWRITE;
}
static long wb_do_writeback(struct bdi_writeback *wb)
{
struct wb_writeback_work *work;
long wrote = 0;
set_bit(WB_writeback_running, &wb->state);
while ((work = get_next_work_item(wb)) != NULL) {
trace_writeback_exec(wb, work);
wrote += wb_writeback(wb, work);
finish_writeback_work(wb, work);
}
/*
* Check for a flush-everything request
*/
wrote += wb_check_start_all(wb);
/*
* Check for periodic writeback, kupdated() style
*/
wrote += wb_check_old_data_flush(wb);
wrote += wb_check_background_flush(wb);
clear_bit(WB_writeback_running, &wb->state);
return wrote;
}





















 3429
3429











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








