提示:整理代码发现了这个小玩意,不知道以后大家会不会用到,放上来算了
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、输入和输出
- 二、代码示例
- 三、使用说明
- 四、补充说明
- 想说的话
前言
在做地平线智能车的前期,在巡线的思路上一直采用的是使用常规思路,即使用resnet18进行黑线的中心点的预测。关于对图片数据的标注其实旭日社区里的各种大佬已经给出的不少,这里我把当时使用的标注代码放上来供大家使用
一、输入和输出
输入:这里需要的是png或jpg格式的彩色图像(由于resnet18分类一般为224*224所以这里使用,但不强制规定具体大小)
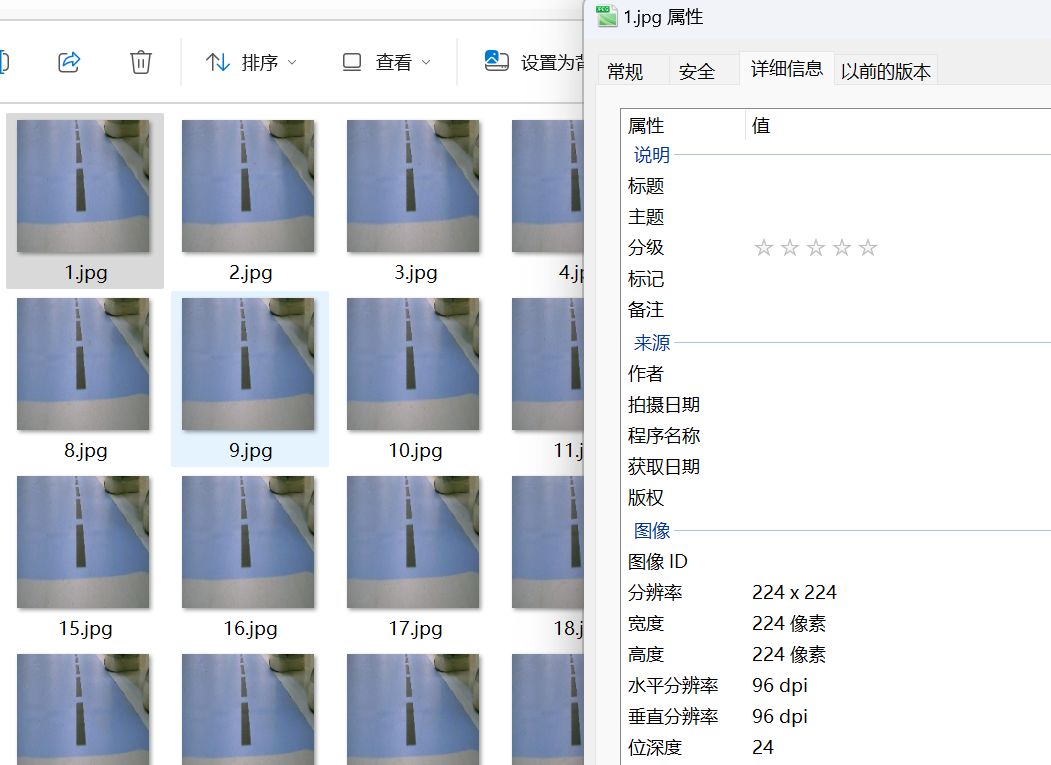
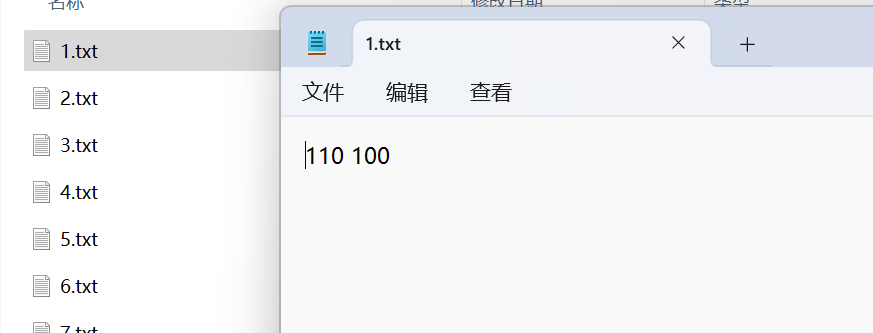
输出:内容为(x y)的txt标签文件
二、代码示例
# coding=utf-8
import os
import cv2
# 全局变量
image_folder = "images" # 图片文件夹路径
output_folder = "labels" # 标注结果保存路径
image_files = [] # 图片文件列表
current_index = 0 # 当前图片索引
current_point = None # 当前标注点
current_image = None # 当前显示的图片
if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
os.makedirs(output_folder)
# 加载图片文件并按数字排序
image_files = sorted([f for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith(('.jpg', '.png', '.jpeg'))],
key=lambda x: int(os.path.splitext(x)[0]))
if not image_files:
print("未找到图片文件!")
exit()
# 获取已存在的标签文件编号
existing_labels = set()
for f in os.listdir(output_folder):
if f.endswith('.txt'):
try:
existing_labels.add(int(os.path.splitext(f)[0]))
except ValueError:
continue
# 自动定位到第一个未标注的图片
found_unlabeled = False
for idx, img_file in enumerate(image_files):
img_num = int(os.path.splitext(img_file)[0])
if img_num not in existing_labels:
current_index = idx
found_unlabeled = True
break
if not found_unlabeled:
current_index = 0 # 全部标注时从第一张开始
print("所有图片均已标注,从第一张开始显示")
else:
print(f"发现未标注图片,从第 {current_index+1} 张开始")
# 鼠标回调函数
def mouse_callback(event, x, y, flags, param):
global current_point, current_image
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
current_point = (x, y)
save_annotation()
image_display = current_image.copy()
if current_point is not None:
cv2.circle(image_display, current_point, 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
display_image_with_progress(image_display)
# 保存标注结果
def save_annotation():
if current_point is not None:
image_name = image_files[current_index]
txt_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(image_name)[0] + ".txt")
with open(txt_path, "w") as f:
f.write(f"{current_point[0]} {current_point[1]}\n")
print(f"已保存标注到 {txt_path}")
# 显示图片和进度
def display_image_with_progress(img):
progress_text = f'{current_index + 1}/{len(image_files)}'
cv2.putText(img, progress_text, (10, 30), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.imshow("Image Annotation", img)
# 加载并显示当前图片
def load_image():
global current_point, current_image
current_point = None # 重要修改:重置标注点状态
if 0 <= current_index < len(image_files):
image_path = os.path.join(image_folder, image_files[current_index])
current_image = cv2.imread(image_path)
# 加载已有标注
txt_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(image_files[current_index])[0] + ".txt")
if os.path.exists(txt_path):
with open(txt_path, "r") as f:
line = f.readline().strip()
if line:
current_point = tuple(map(int, line.split()))
# 更新显示
image_display = current_image.copy()
if current_point is not None:
cv2.circle(image_display, current_point, 5, (0, 255, 0), -1)
display_image_with_progress(image_display)
# 主循环
cv2.namedWindow("Image Annotation")
cv2.setMouseCallback("Image Annotation", mouse_callback)
while True:
load_image()
key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
if key == ord('a'):
current_index = max(0, current_index - 1)
elif key == ord('d'):
current_index = min(len(image_files) - 1, current_index + 1)
elif key == ord('q'):
break
elif key == ord('w'): # 删除键 ASCII 值为 127
image_name = image_files[current_index]
txt_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(image_name)[0] + ".txt")
if os.path.exists(txt_path): # 如果存在对应的标注文件,则删除
os.remove(txt_path)
print(f"已删除标注文件 {txt_path}")
image_path = os.path.join(image_folder, image_name)
os.remove(image_path) # 删除图片文件
print(f"已删除图片文件 {image_path}")
del image_files[current_index] # 从列表中移除该图片文件名
if current_index >= len(image_files): # 如果刚刚是最后一张图片,则回退到上一张
current_index -= 1
# 切换到下一张图片
if len(image_files) > 0:
current_index = min(len(image_files) - 1, current_index + 1)
else:
print("没有更多的图片可供显示")
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
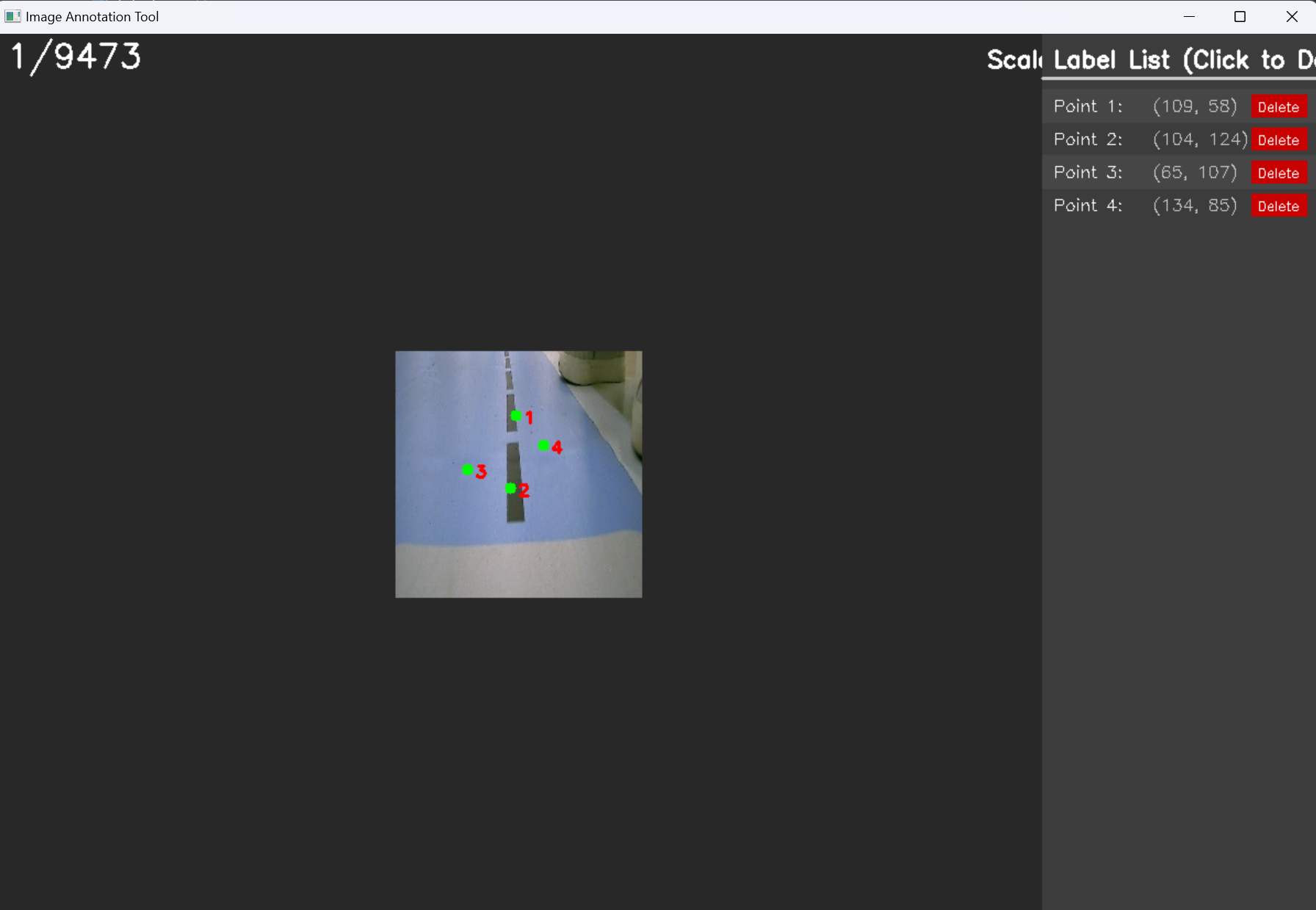
三、使用说明
窗口界面大小与图像大小一致,用鼠标点击图像即可显示绿色目标点,并创建对应图像名称的txt标签文件:
a:切换上一张
d:切换下一张
w:删除当前图像(总数和显示同步更新)
q:退出程序
这个时候就有同学要问了,诶,如果我一次性没有打完标,又没记住从哪开始打标的盖怎么办呢?
诶~,程序执行后会做一个扫描,自动检查已经标注了多少张,窗口会自动从未标注的图像开始显示,如果都标注完毕了,则从文件夹内第一张图像开始显示
四、补充说明
以上是原来备赛使用的功能,那么局限是上面的代码是针对于图像中只标注一个点而设计的,下面的代码可以标注多个点,使用方法也差不多,大家可以自行体验
新增功能
增加标准程序窗口显示和标签栏:可以手动删除对应标签
右键:快速删除最新的标注点
ctrl:加滚轮调节图像大小
左键拖动:按住左键可实现图像拖动
# coding=utf-8
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import sys
# 全局变量
image_folder = "images" # 图片文件夹路径
output_folder = "labels" # 标注结果保存路径
image_files = [] # 图片文件列表
current_index = 0 # 当前图片索引
points = [] # 当前图片的所有标注点
current_image = None # 当前显示的图片
window_name = "Image Annotation Tool" # 使用英文窗口名称避免乱码
sidebar_width = 250 # 侧边栏宽度(像素)
scale = 1.0 # 图像缩放比例
offset_x, offset_y = 0, 0 # 图像偏移量
dragging = False # 是否正在拖动
drag_start_x, drag_start_y = 0, 0 # 拖动起始位置
ctrl_pressed = False # Ctrl键是否按下
# 创建输出文件夹
if not os.path.exists(output_folder):
os.makedirs(output_folder)
# 加载图片文件并按数字排序
image_files = sorted([f for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith(('.jpg', '.png', '.jpeg'))],
key=lambda x: int(os.path.splitext(x)[0]))
if not image_files:
print("No image files found! Please check the image folder path.")
exit()
# 获取已存在的标签文件编号
existing_labels = set()
for f in os.listdir(output_folder):
if f.endswith('.txt'):
try:
existing_labels.add(int(os.path.splitext(f)[0]))
except ValueError:
continue
# 自动定位到第一个未标注的图片
found_unlabeled = False
for idx, img_file in enumerate(image_files):
img_num = int(os.path.splitext(img_file)[0])
if img_num not in existing_labels:
current_index = idx
found_unlabeled = True
break
if not found_unlabeled:
current_index = 0
print("All images are labeled, starting from the first one")
else:
print(f"Found unlabeled images, starting from {current_index + 1}")
# 鼠标回调函数
def mouse_callback(event, x, y, flags, param):
global points, current_image, scale, offset_x, offset_y, dragging, drag_start_x, drag_start_y, ctrl_pressed
# 获取窗口尺寸
window_width = cv2.getWindowImageRect(window_name)[2]
window_height = cv2.getWindowImageRect(window_name)[3]
if current_image is None:
return
img_height, img_width = current_image.shape[:2]
scaled_width = int(img_width * scale)
scaled_height = int(img_height * scale)
# 计算图像在窗口中的实际位置(居中显示)
display_x = int((window_width - scaled_width - sidebar_width) // 2 + offset_x)
display_y = int((window_height - scaled_height) // 2 + offset_y)
# 处理Ctrl+滚轮缩放
if event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEWHEEL:
# 检查Ctrl键是否按下
ctrl_pressed = bool(flags & cv2.EVENT_FLAG_CTRLKEY)
if ctrl_pressed:
old_scale = scale
if flags > 0: # 滚轮上滚 - 放大
scale *= 1.1
else: # 滚轮下滚 - 缩小
scale /= 1.1
# 限制缩放范围
scale = max(0.1, min(scale, 5.0))
# 以鼠标位置为中心缩放
if scaled_width > 0 and scaled_height > 0:
mouse_x_rel = (x - display_x) / scaled_width
mouse_y_rel = (y - display_y) / scaled_height
new_scaled_width = int(img_width * scale)
new_scaled_height = int(img_height * scale)
offset_x += (x - display_x) - mouse_x_rel * new_scaled_width
offset_y += (y - display_y) - mouse_y_rel * new_scaled_height
update_display()
# 处理拖动
elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
# 检查是否在图像区域内
if display_x <= x <= display_x + scaled_width and display_y <= y <= display_y + scaled_height:
# 将点击坐标转换为原始图像坐标
orig_x = int((x - display_x) / scale)
orig_y = int((y - display_y) / scale)
if 0 <= orig_x < img_width and 0 <= orig_y < img_height:
# 左键点击图像区域:添加标注点
points.append((orig_x, orig_y))
save_annotation()
update_display()
else:
# 如果不在图像范围内,开始拖动
dragging = True
drag_start_x, drag_start_y = x, y
else:
# 检查是否在侧边栏区域内
if x >= window_width - sidebar_width and x < window_width:
# 计算点击的标签索引
label_height = 30
label_start_y = 50
label_index = (y - label_start_y) // label_height
if 0 <= label_index < len(points):
points.pop(label_index)
save_annotation()
update_display()
else:
# 如果不在图像或侧边栏区域内,开始拖动
dragging = True
drag_start_x, drag_start_y = x, y
elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE and dragging:
offset_x += x - drag_start_x
offset_y += y - drag_start_y
drag_start_x, drag_start_y = x, y
update_display()
elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP:
dragging = False
# 处理右键点击删除最近的点
elif event == cv2.EVENT_RBUTTONDOWN:
# 检查是否在图像区域内
if display_x <= x <= display_x + scaled_width and display_y <= y <= display_y + scaled_height:
if points:
points.pop()
save_annotation()
update_display()
# 保存标注点到txt文件
def save_annotation():
if not points:
# 删除空标注文件
image_name = image_files[current_index]
txt_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(image_name)[0] + ".txt")
if os.path.exists(txt_path):
os.remove(txt_path)
return
image_name = image_files[current_index]
txt_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(image_name)[0] + ".txt")
with open(txt_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for (x, y) in points:
f.write(f"{x} {y}\n")
print(f"Saved annotation to {txt_path} ({len(points)} points)")
# 创建带侧边栏的完整图像
def create_combined_display():
global current_image, points
if current_image is None:
return None
img_height, img_width = current_image.shape[:2]
# 计算缩放后的图像尺寸
scaled_width = int(img_width * scale)
scaled_height = int(img_height * scale)
# 获取窗口尺寸
window_width = cv2.getWindowImageRect(window_name)[2]
window_height = cv2.getWindowImageRect(window_name)[3]
# 创建组合图像(图像 + 侧边栏)
combined_img = np.zeros((window_height, window_width, 3), dtype=np.uint8)
combined_img[:] = (40, 40, 40) # 设置背景色为深灰色
# 计算图像显示位置(居中)
display_x = int((window_width - scaled_width - sidebar_width) // 2 + offset_x)
display_y = int((window_height - scaled_height) // 2 + offset_y)
# 缩放图像
if scale != 1.0:
scaled_img = cv2.resize(current_image, (scaled_width, scaled_height))
else:
scaled_img = current_image
# 将图像放置到组合图像中(确保索引是整数)
try:
# 确保显示区域在图像范围内
y_start = max(0, display_y)
y_end = min(window_height, display_y + scaled_height)
x_start = max(0, display_x)
x_end = min(window_width, display_x + scaled_width)
# 计算源图像区域
src_y_start = max(0, -display_y)
src_y_end = min(scaled_height, window_height - display_y)
src_x_start = max(0, -display_x)
src_x_end = min(scaled_width, window_width - display_x)
# 确保区域有效
if y_end > y_start and x_end > x_start and src_y_end > src_y_start and src_x_end > src_x_start:
combined_img[y_start:y_end, x_start:x_end] = scaled_img[
src_y_start:src_y_end, src_x_start:src_x_end
]
except Exception as e:
print(f"Image placement error: {e}")
# 在图像上绘制标注点
point_radius = max(3, int(5 * scale))
font_scale = max(0.5, 0.5 * scale)
font_thickness = max(1, int(2 * scale))
for i, (px, py) in enumerate(points):
# 将原始坐标转换为显示坐标
display_px = int(px * scale) + display_x
display_py = int(py * scale) + display_y
# 确保点在图像范围内
if 0 <= display_px < window_width and 0 <= display_py < window_height:
cv2.circle(combined_img, (display_px, display_py), point_radius, (0, 255, 0), -1)
cv2.putText(combined_img, str(i + 1),
(display_px + point_radius + 2, display_py + point_radius + 2),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, font_scale, (0, 0, 255), font_thickness)
# 添加进度信息
progress_text = f'{current_index + 1}/{len(image_files)}'
cv2.putText(combined_img, progress_text, (10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (255, 255, 255), 2)
# 添加缩放比例信息
scale_text = f'Scale: {scale:.2f}x (Ctrl+Wheel)'
cv2.putText(combined_img, scale_text, (window_width - 300, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (255, 255, 255), 2)
# 绘制侧边栏
sidebar_x = window_width - sidebar_width
sidebar_height = window_height
# 侧边栏背景
cv2.rectangle(combined_img,
(sidebar_x, 0),
(sidebar_x + sidebar_width - 1, sidebar_height - 1),
(60, 60, 60), -1)
# 侧边栏标题
title_text = "Label List (Click to Delete)"
cv2.putText(combined_img, title_text, (sidebar_x + 10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.7, (255, 255, 255), 2)
# 分隔线
cv2.line(combined_img,
(sidebar_x, 40),
(sidebar_x + sidebar_width, 40),
(200, 200, 200), 2)
# 如果没有标注点,显示提示
if not points:
no_points_text = "No points labeled"
cv2.putText(combined_img, no_points_text,
(sidebar_x + 10, 80),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.6, (150, 150, 150), 1)
return combined_img
# 显示每个标注点的信息
label_height = 30
label_start_y = 50
for i, (px, py) in enumerate(points):
label_y = label_start_y + i * label_height
# 标签背景(交替颜色提高可读性)
if i % 2 == 0:
cv2.rectangle(combined_img,
(sidebar_x, label_y),
(sidebar_x + sidebar_width, label_y + label_height),
(70, 70, 70), -1)
# 点序号
index_text = f"Point {i + 1}:"
cv2.putText(combined_img, index_text,
(sidebar_x + 10, label_y + 20),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255), 1)
# 点坐标
coord_text = f"({px}, {py})"
cv2.putText(combined_img, coord_text,
(sidebar_x + 100, label_y + 20),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (200, 200, 200), 1)
# 删除按钮
button_x = sidebar_x + sidebar_width - 60
button_y = label_y + 5
cv2.rectangle(combined_img,
(button_x, button_y),
(button_x + 50, button_y + 20),
(0, 0, 200), -1)
cv2.putText(combined_img, "Delete",
(button_x + 5, button_y + 15),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.4, (255, 255, 255), 1)
return combined_img
# 更新显示
def update_display():
combined_img = create_combined_display()
if combined_img is not None:
cv2.imshow(window_name, combined_img)
# 加载并显示当前图片
def load_image():
global points, current_image, scale, offset_x, offset_y
points = [] # 重置当前图片的标注点
scale = 1.0 # 重置缩放比例
offset_x, offset_y = 0, 0 # 重置偏移量
if 0 <= current_index < len(image_files):
image_path = os.path.join(image_folder, image_files[current_index])
current_image = cv2.imread(image_path)
if current_image is None:
print(f"Cannot load image: {image_path}")
return
# 获取窗口尺寸
window_width = cv2.getWindowImageRect(window_name)[2]
window_height = cv2.getWindowImageRect(window_name)[3]
# 如果图像尺寸超过窗口的70%,则进行缩放
img_height, img_width = current_image.shape[:2]
max_display_width = window_width * 0.7
max_display_height = window_height * 0.7
if img_width > max_display_width or img_height > max_display_height:
width_ratio = max_display_width / img_width
height_ratio = max_display_height / img_height
scale = min(width_ratio, height_ratio)
# 加载已有的标注点
txt_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(image_files[current_index])[0] + ".txt")
if os.path.exists(txt_path):
with open(txt_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
for line in f:
line = line.strip()
if line:
try:
x, y = map(int, line.split())
points.append((x, y))
except ValueError:
print(f"Annotation file format error: {txt_path} (skipping invalid line)")
# 更新显示
update_display()
# 主循环
cv2.namedWindow(window_name, cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.setMouseCallback(window_name, mouse_callback)
cv2.resizeWindow(window_name, 1200, 800) # 设置初始窗口尺寸
# 初始显示
load_image()
while True:
key = cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF
# 检查窗口是否已关闭
if cv2.getWindowProperty(window_name, cv2.WND_PROP_VISIBLE) < 1:
break
# 键盘导航控制
if key == ord('a') or key == ord('A'): # 上一张
current_index = max(0, current_index - 1)
load_image()
elif key == ord('d') or key == ord('D'): # 下一张
current_index = min(len(image_files) - 1, current_index + 1)
load_image()
elif key == ord('q') or key == ord('Q'): # 退出
break
elif key == ord('w') or key == ord('W'): # 删除当前图片
image_name = image_files[current_index]
txt_path = os.path.join(output_folder, os.path.splitext(image_name)[0] + ".txt")
if os.path.exists(txt_path):
os.remove(txt_path)
print(f"Deleted annotation file: {txt_path}")
image_path = os.path.join(image_folder, image_name)
os.remove(image_path)
print(f"Deleted image file: {image_path}")
del image_files[current_index]
if current_index >= len(image_files):
current_index -= 1
if len(image_files) > 0:
current_index = min(len(image_files) - 1, current_index + 1)
load_image()
else:
print("No more images to display")
break
# 持续更新显示以响应窗口大小变化
update_display()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
想说的话
下午坐着不知道干点啥,想起来有些比赛时候写的小程序可以放上来,视觉的教程也在写了。






















 1541
1541

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








