1、背景介绍
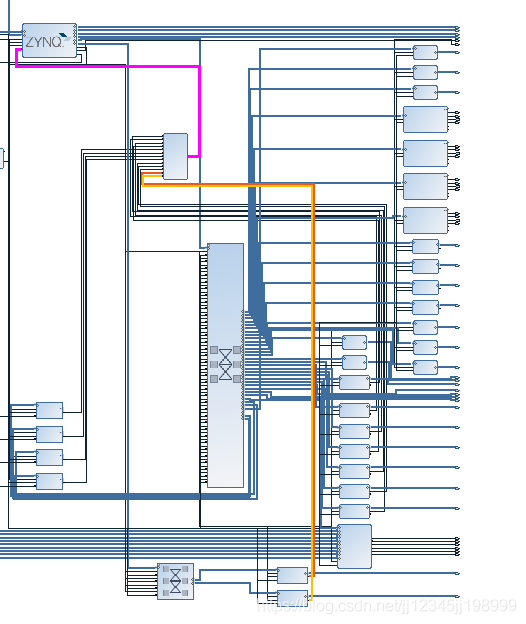
ZYNQ在PL部分使用AXI_QUAD_SPI IP核外挂了8片SPI FLASH,VIVADO示例图如下:
上图中有颜色的线条为IP核的中断到ZYNQ PL-PS中断,由于设备太多,这里使用了中断级联。IP核的地址分配如下:
2、内核配置
内核中需要修改下面文件
增加兼容的硬件spi型号,这里使用的n25q256
完整代码如下:
/*
* MTD SPI driver for ST M25Pxx (and similar) serial flash chips
*
* Author: Mike Lavender, mike@steroidmicros.com
*
* Copyright (c) 2005, Intec Automation Inc.
*
* Some parts are based on lart.c by Abraham Van Der Merwe
*
* Cleaned up and generalized based on mtd_dataflash.c
*
* This code is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 as
* published by the Free Software Foundation.
*
*/
#include <linux/err.h>
#include <linux/errno.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/mtd/mtd.h>
#include <linux/mtd/partitions.h>
#include <linux/spi/spi.h>
#include <linux/spi/flash.h>
#include <linux/mtd/spi-nor.h>
#include <linux/of.h>
static ssize_t m25p80_write(struct spi_nor *nor, loff_t to, size_t len,
const u_char *buf);
static ssize_t m25p80_read(struct spi_nor *nor, loff_t from, size_t len,
u_char *buf);
#define MAX_CMD_SIZE 6
struct m25p {
struct spi_device *spi;
struct spi_nor spi_nor;
u8 command[MAX_CMD_SIZE];
};
static int m25p80_read_reg(struct spi_nor *nor, u8 code, u8 *val, int len)
{
//printk("##################m25p80 read reg\n");
struct m25p *flash = nor->priv;
struct spi_device *spi = flash->spi;
int ret;
//printk("code is 0x%x,len:%d,---%x----\n",code,len,*val);
ret = spi_write_then_read(spi, &code, 1, val, len);
if (ret < 0)
dev_err(&spi->dev, "error %d reading %x\n", ret, code);
return ret;
}
static void m25p_addr2cmd(struct spi_nor *nor, unsigned int addr, u8 *cmd)
{
/* opcode is in cmd[0] */
cmd[1] = addr >> (nor->addr_width * 8 - 8);
cmd[2] = addr >> (nor->addr_width * 8 - 16);
cmd[3] = addr >> (nor->addr_width * 8 - 24);
cmd[4] = addr >> (nor->addr_width * 8 - 32);
}
static int m25p_cmdsz(struct spi_nor *nor)
{
return 1 + nor->addr_width;
}
static int m25p80_write_reg(struct spi_nor *nor, u8 opcode, u8 *buf, int len)
{
struct m25p *flash = nor->priv;
struct spi_device *spi = flash->spi;
flash->command[0] = opcode;
if (buf)
memcpy(&flash->command[1], buf, len);
return spi_write(spi, flash->command, len + 1);
}
static ssize_t m25p80_write(struct spi_nor *nor, loff_t to, size_t len,
const u_char *buf)
{
struct m25p *flash = nor->priv;
struct spi_device *spi = flash->spi;
struct spi_transfer t[2] = {};
struct spi_message m;
int cmd_sz = m25p_cmdsz(nor);
ssize_t ret;
//printk("m25p80_write write len :%d,%x\n",len,*buf);
spi_message_init(&m);
if (nor->program_opcode == SPINOR_OP_AAI_WP && nor->sst_write_second)
cmd_sz = 1;
flash->command[0] = nor->program_opcode;
m25p_addr2cmd(nor, to, flash->command);
t[0].tx_buf = flash->command;
t[0].len = cmd_sz;
spi_message_add_tail(&t[0], &m);
t[1].tx_buf = buf;
t[1].len = len;
spi_message_add_tail(&t[1], &m);
ret = spi_sync(spi, &m);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = m.actual_length - cmd_sz;
if (ret < 0)
return -EIO;
return ret;
}
static inline unsigned int m25p80_rx_nbits(struct spi_nor *nor)
{
switch (nor->flash_read) {
case SPI_NOR_DUAL:
return 2;
case SPI_NOR_QUAD:
return 4;
default:
return 0;
}
}
/*
* Read an address range from the nor chip. The address range
* may be any size provided it is within the physical boundaries.
*/
static ssize_t m25p80_read(struct spi_nor *nor, loff_t from, size_t len,
u_char *buf)
{
struct m25p *flash = nor->priv;
struct spi_device *spi = flash->spi;
struct spi_transfer t[2];
struct spi_message m;
unsigned int dummy = nor->read_dummy;
ssize_t ret;
//printk("m25p80_read read len :%d,%x\n",len,*buf);
/* convert the dummy cycles to the number of bytes */
dummy /= 8;
if (spi_flash_read_supported(spi)) {
struct spi_flash_read_message msg;
memset(&msg, 0, sizeof(msg));
msg.buf = buf;
msg.from = from;
msg.len = len;
msg.read_opcode = nor->read_opcode;
msg.addr_width = nor->addr_width;
msg.dummy_bytes = dummy;
/* TODO: Support other combinations */
msg.opcode_nbits = SPI_NBITS_SINGLE;
msg.addr_nbits = SPI_NBITS_SINGLE;
msg.data_nbits = m25p80_rx_nbits(nor);
ret = spi_flash_read(spi, &msg);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
return msg.retlen;
}
spi_message_init(&m);
memset(t, 0, (sizeof t));
flash->command[0] = nor->read_opcode;
m25p_addr2cmd(nor, from, flash->command);
t[0].tx_buf = flash->command;
t[0].len = m25p_cmdsz(nor) + dummy;
t[0].dummy = nor->read_dummy;
spi_message_add_tail(&t[0], &m);
t[1].rx_buf = buf;
t[1].rx_nbits = m25p80_rx_nbits(nor);
t[1].len = min(len, spi_max_transfer_size(spi));
spi_message_add_tail(&t[1], &m);
ret = spi_sync(spi, &m);
if (ret)
return ret;
ret = m.actual_length - m25p_cmdsz(nor) - dummy;
if (ret < 0)
return -EIO;
return ret;
}
/*
* board specific setup should have ensured the SPI clock used here
* matches what the READ command supports, at least until this driver
* understands FAST_READ (for clocks over 25 MHz).
*/
static int m25p_probe(struct spi_device *spi)
{
struct flash_platform_data *data;
struct m25p *flash;
struct spi_nor *nor;
struct mtd_info *mtd = NULL;
enum read_mode mode = SPI_NOR_NORMAL;
char *flash_name;
int ret;
unsigned int chip_num = 0;
// printk("enter probe ...\n");
data = dev_get_platdata(&spi->dev);
flash = devm_kzalloc(&spi->dev, sizeof(*flash), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!flash)
return -ENOMEM;
nor = &flash->spi_nor;
mtd = &nor->mtd;
/* install the hooks */
nor->read = m25p80_read;
nor->write = m25p80_write;
nor->write_reg = m25p80_write_reg;
nor->read_reg = m25p80_read_reg;
nor->dev = &spi->dev;
spi_nor_set_flash_node(nor, spi->dev.of_node);
nor->priv = flash;
spi_set_drvdata(spi, flash);
flash->spi = spi;
nor->spi = spi;
if (spi->mode & SPI_RX_QUAD)
mode = SPI_NOR_QUAD;
else if (spi->mode & SPI_RX_DUAL)
mode = SPI_NOR_DUAL;
if (data && data->name)
nor->mtd.name = data->name;
/* For some (historical?) reason many platforms provide two different
* names in flash_platform_data: "name" and "type". Quite often name is
* set to "m25p80" and then "type" provides a real chip name.
* If that's the case, respect "type" and ignore a "name".
*/
if (data && data->type)
flash_name = data->type;
else if (!strcmp(spi->modalias, "spi-nor"))
flash_name = NULL; /* auto-detect */
else
flash_name = spi->modalias;
//printk("flash name is %s\n",flash_name);
ret = spi_nor_scan(nor, flash_name, mode);
if (ret)
return ret;
of_property_read_u32(spi->dev.of_node, "chip_num",
&chip_num);
if(chip_num>0)
{
nor->mtd.size = nor->mtd.size*chip_num;
}
//printk("mtd .name = %s, .size = 0x%llx (%lldMiB), "
// ".erasesize = 0x%.8x (%uKiB) .numeraseregions = %d\n",
// nor->mtd.name, (long long)nor->mtd.size, (long long)(nor->mtd.size >> 20),
// nor->mtd.erasesize, nor->mtd.erasesize / 1024, nor->mtd.numeraseregions);
return mtd_device_register(&nor->mtd, data ? data->parts : NULL,
data ? data->nr_parts : 0);
}
static int m25p_remove(struct spi_device *spi)
{
struct m25p *flash = spi_get_drvdata(spi);
/* Clean up MTD stuff. */
return mtd_device_unregister(&flash->spi_nor.mtd);
}
/*
* Do NOT add to this array without reading the following:
*
* Historically, many flash devices are bound to this driver by their name. But
* since most of these flash are compatible to some extent, and their
* differences can often be differentiated by the JEDEC read-ID command, we
* encourage new users to add support to the spi-nor library, and simply bind
* against a generic string here (e.g., "jedec,spi-nor").
*
* Many flash names are kept here in this list (as well as in spi-nor.c) to
* keep them available as module aliases for existing platforms.
*/
static const struct spi_device_id m25p_ids[] = {
/*
* Allow non-DT platform devices to bind to the "spi-nor" modalias, and
* hack around the fact that the SPI core does not provide uevent
* matching for .of_match_table
*/
{"spi-nor"},
/*
* Entries not used in DTs that should be safe to drop after replacing
* them with "spi-nor" in platform data.
*/
{"s25sl064a"}, {"w25x16"}, {"m25p10"}, {"m25px64"},
/*
* Entries that were used in DTs without "jedec,spi-nor" fallback and
* should be kept for backward compatibility.
*/
{"at25df321a"}, {"at25df641"}, {"at26df081a"},
{"mr25h256"},
{"mx25l4005a"}, {"mx25l1606e"}, {"mx25l6405d"}, {"mx25l12805d"},
{"mx25l25635e"},{"mx66l51235l"},
{"n25q064"}, {"n25q128a11"}, {"n25q128a13"}, {"n25q512a"},{"n25q256a"},
{"s25fl256s1"}, {"s25fl512s"}, {"s25sl12801"}, {"s25fl008k"},
{"s25fl064k"},
{"sst25vf040b"},{"sst25vf016b"},{"sst25vf032b"},{"sst25wf040"},
{"m25p40"}, {"m25p80"}, {"m25p16"}, {"m25p32"},
{"m25p64"}, {"m25p128"},
{"w25x80"}, {"w25x32"}, {"w25q32"}, {"w25q32dw"},
{"w25q80bl"}, {"w25q128"}, {"w25q256"},
/* Flashes that can't be detected using JEDEC */
{"m25p05-nonjedec"}, {"m25p10-nonjedec"}, {"m25p20-nonjedec"},
{"m25p40-nonjedec"}, {"m25p80-nonjedec"}, {"m25p16-nonjedec"},
{"m25p32-nonjedec"}, {"m25p64-nonjedec"}, {"m25p128-nonjedec"},
{ },
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(spi, m25p_ids);
static const struct of_device_id m25p_of_table[] = {
/*
* Generic compatibility for SPI NOR that can be identified by the
* JEDEC READ ID opcode (0x9F). Use this, if possible.
*/
{ .compatible = "jedec,spi-nor" },
{ .compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor" },
{}
};
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(of, m25p_of_table);
static struct spi_driver m25p80_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "n25q256a",
.of_match_table = m25p_of_table,
},
.id_table = m25p_ids,
.probe = m25p_probe,
.remove = m25p_remove,
/* REVISIT: many of these chips have deep power-down modes, which
* should clearly be entered on suspend() to minimize power use.
* And also when they're otherwise idle...
*/
};
module_spi_driver(m25p80_driver);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Mike Lavender");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("MTD SPI driver for ST M25Pxx flash chips");
3、devicetree配置
设备树可以用sdk产生,但是生成完后要修改ip核的节点说明,如下:
其中增加了中断描述信息,另外外挂的flash型号也需要描述。
完整的设备树信息如下:
/dts-v1/;
/ {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-7000";
cpus {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
cpu@0 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9";
device_type = "cpu";
reg = <0x0>;
clocks = <0x1 0x3>;
clock-latency = <0x3e8>;
cpu0-supply = <0x2>;
operating-points = <0xa4cb8 0xf4240 0x5265c 0xf4240>;
};
cpu@1 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9";
device_type = "cpu";
reg = <0x1>;
clocks = <0x1 0x3>;
};
};
fpga-full {
compatible = "fpga-region";
fpga-mgr = <0x3>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
ranges;
};
pmu@f8891000 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9-pmu";
interrupts = <0x0 0x5 0x4 0x0 0x6 0x4>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
reg = <0xf8891000 0x1000 0xf8893000 0x1000>;
};
fixedregulator {
compatible = "regulator-fixed";
regulator-name = "VCCPINT";
regulator-min-microvolt = <0xf4240>;
regulator-max-microvolt = <0xf4240>;
regulator-boot-on;
regulator-always-on;
linux,phandle = <0x2>;
phandle = <0x2>;
};
amba {
u-boot,dm-pre-reloc;
compatible = "simple-bus";
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
ranges;
adc@f8007100 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-xadc-1.00.a";
reg = <0xf8007100 0x20>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x7 0x4>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
clocks = <0x1 0xc>;
xlnx,channels {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
channel@0 {
reg = <0x0>;
};
channel@1 {
reg = <0x1>;
};
channel@2 {
reg = <0x2>;
};
channel@3 {
reg = <0x3>;
};
channel@4 {
reg = <0x4>;
};
channel@5 {
reg = <0x5>;
};
channel@6 {
reg = <0x6>;
};
channel@7 {
reg = <0x7>;
};
channel@8 {
reg = <0x8>;
};
channel@9 {
reg = <0x9>;
};
channel@a {
reg = <0xa>;
};
channel@b {
reg = <0xb>;
};
channel@c {
reg = <0xc>;
};
channel@d {
reg = <0xd>;
};
channel@e {
reg = <0xe>;
};
channel@f {
reg = <0xf>;
};
channel@10 {
reg = <0x10>;
};
};
};
gpio@e000a000 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-gpio-1.0";
#gpio-cells = <0x2>;
clocks = <0x1 0x2a>;
gpio-controller;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = <0x2>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x14 0x4>;
reg = <0xe000a000 0x1000>;
};
i2c@e0004000 {
compatible = "cdns,i2c-r1p10-slave";
status = "okay";
clocks = <0x1 0x26>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x19 0x4>;
reg = <0xe0004000 0x1000>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-frequency = <0x61a80>;
};
i2c@e0005000 {
compatible = "cdns,i2c-r1p10-slave";
status = "okay";
clocks = <0x1 0x27>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x30 0x4>;
reg = <0xe0005000 0x1000>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-frequency = <0x61a80>;
};
interrupt-controller@f8f01000 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9-gic";
#interrupt-cells = <0x3>;
interrupt-controller;
reg = <0xf8f01000 0x1000 0xf8f00100 0x100>;
num_cpus = <0x2>;
num_interrupts = <0x60>;
linux,phandle = <0x4>;
phandle = <0x4>;
};
cache-controller@f8f02000 {
compatible = "arm,pl310-cache";
reg = <0xf8f02000 0x1000>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x2 0x4>;
arm,data-latency = <0x3 0x2 0x2>;
arm,tag-latency = <0x2 0x2 0x2>;
cache-unified;
cache-level = <0x2>;
};
memory-controller@f8006000 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-ddrc-a05";
reg = <0xf8006000 0x1000>;
};
ocmc@f800c000 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-ocmc-1.0";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x3 0x4>;
reg = <0xf800c000 0x1000>;
};
serial@e0000000 {
compatible = "xlnx,xuartps", "cdns,uart-r1p8";
status = "okay";
clocks = <0x1 0x17 0x1 0x28>;
clock-names = "uart_clk", "pclk";
reg = <0xe0000000 0x1000>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x1b 0x4>;
device_type = "serial";
port-number = <0x4>;
};
spi@e000d000 {
clock-names = "ref_clk", "pclk";
clocks = <0x1 0xa 0x1 0x2b>;
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-qspi-1.0";
status = "okay";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x13 0x4>;
reg = <0xe000d000 0x1000>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
is-dual = <0x1>;
num-cs = <0x1>;
};
ethernet@e000b000 {
compatible = "xlnx,ps7-ethernet-1.00.a";
reg = <0xe000b000 0x1000>;
status = "okay";
interrupts = <0x0 0x16 0x4>;
clocks = <0x1 0xd 0x1 0x1e>;
clock-names = "ref_clk", "aper_clk";
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
enet-reset = <0x4 0x2f 0x0>;
#local-mac-address = [00 0b 35 11 12 00];
local-mac-address = [00 0b 44 00 3e 16];
phy-mode = "rgmii";
phy-handle = <0x7>;
xlnx,eth-mode = <0x1>;
xlnx,has-mdio = <0x1>;
xlnx,ptp-enet-clock = <0x69f6bcb>;
mdio {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
phy@2 {
compatible = "marvell,88e1111";
device_type = "ethernet-phy";
reg = <0x2>;
linux,phandle = <0x7>;
phandle = <0x7>;
};
};
};
ethernet@e000c000 {
compatible = "xlnx,ps7-ethernet-1.00.b";
reg = <0xe000c000 0x1000>;
status = "okay";
interrupts = <0x0 0x2d 0x4>;
clocks = <0x1 0xe 0x1 0x1f>;
clock-names = "ref_clk", "aper_clk";
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
enet-reset = <0x4 0x2f 0x0>;
local-mac-address = [00 0b 36 11 11 00];
phy-mode = "rgmii";
phy-handle = <0x8>;
xlnx,eth-mode = <0x1>;
xlnx,has-mdio = <0x1>;
xlnx,ptp-enet-clock = <0x69f6bcb>;
mdio {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
phy@1 {
compatible = "marvell,88e1111";
device_type = "ethernet-phy";
reg = <0x1>;
linux,phandle = <0x8>;
phandle = <0x8>;
};
};
};
slcr@f8000000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-slcr", "syscon", "simple-mfd";
reg = <0xf8000000 0x1000>;
ranges;
linux,phandle = <0x5>;
phandle = <0x5>;
clkc@100 {
#clock-cells = <0x1>;
compatible = "xlnx,ps7-clkc";
fclk-enable = <0x3>;
clock-output-names = "armpll", "ddrpll", "iopll", "cpu_6or4x", "cpu_3or2x", "cpu_2x", "cpu_1x", "ddr2x", "ddr3x", "dci", "lqspi", "smc", "pcap", "gem0", "gem1", "fclk0", "fclk1", "fclk2", "fclk3", "can0", "can1", "sdio0", "sdio1", "uart0", "uart1", "spi0", "spi1", "dma", "usb0_aper", "usb1_aper", "gem0_aper", "gem1_aper", "sdio0_aper", "sdio1_aper", "spi0_aper", "spi1_aper", "can0_aper", "can1_aper", "i2c0_aper", "i2c1_aper", "uart0_aper", "uart1_aper", "gpio_aper", "lqspi_aper", "smc_aper", "swdt", "dbg_trc", "dbg_apb";
reg = <0x100 0x100>;
ps-clk-frequency = <0x2faf080>;
linux,phandle = <0x1>;
phandle = <0x1>;
};
rstc@200 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-reset";
reg = <0x200 0x48>;
#reset-cells = <0x1>;
syscon = <0x5>;
};
pinctrl@700 {
compatible = "xlnx,pinctrl-zynq";
reg = <0x700 0x200>;
syscon = <0x5>;
};
};
dmac@f8003000 {
compatible = "arm,pl330", "arm,primecell";
reg = <0xf8003000 0x1000>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupt-names = "abort", "dma0", "dma1", "dma2", "dma3", "dma4", "dma5", "dma6", "dma7";
interrupts = <0x0 0xd 0x4 0x0 0xe 0x4 0x0 0xf 0x4 0x0 0x10 0x4 0x0 0x11 0x4 0x0 0x28 0x4 0x0 0x29 0x4 0x0 0x2a 0x4 0x0 0x2b 0x4>;
#dma-cells = <0x1>;
#dma-channels = <0x8>;
#dma-requests = <0x4>;
clocks = <0x1 0x1b>;
clock-names = "apb_pclk";
};
devcfg@f8007000 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-devcfg-1.0";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x8 0x4>;
reg = <0xf8007000 0x100>;
clocks = <0x1 0xc 0x1 0xf 0x1 0x10 0x1 0x11 0x1 0x12>;
clock-names = "ref_clk", "fclk0", "fclk1", "fclk2", "fclk3";
syscon = <0x5>;
linux,phandle = <0x3>;
phandle = <0x3>;
};
efuse@f800d000 {
compatible = "xlnx,zynq-efuse";
reg = <0xf800d000 0x20>;
};
timer@f8f00200 {
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9-global-timer";
reg = <0xf8f00200 0x20>;
interrupts = <0x1 0xb 0x301>;
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
clocks = <0x1 0x4>;
};
timer@f8001000 {
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0xa 0x4 0x0 0xb 0x4 0x0 0xc 0x4>;
compatible = "cdns,ttc";
clocks = <0x1 0x6>;
reg = <0xf8001000 0x1000>;
};
timer@f8002000 {
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x25 0x4 0x0 0x26 0x4 0x0 0x27 0x4>;
compatible = "cdns,ttc";
clocks = <0x1 0x6>;
reg = <0xf8002000 0x1000>;
};
timer@f8f00600 {
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x1 0xd 0x301>;
compatible = "arm,cortex-a9-twd-timer";
reg = <0xf8f00600 0x20>;
clocks = <0x1 0x4>;
};
watchdog@f8005000 {
clocks = <0x1 0x2d>;
compatible = "cdns,wdt-r1p2";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x9 0x1>;
reg = <0xf8005000 0x1000>;
timeout-sec = <0xa>;
};
};
amba_pl {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
compatible = "simple-bus";
ranges;
i2c@41600000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-names = "ref_clk";
clocks = <0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,xps-iic-2.00.a";
interrupt-names = "iic2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x1f 0x4>;
reg = <0x41600000 0x10000>;
};
i2c@41610000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-names = "ref_clk";
clocks = <0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,xps-iic-2.00.a";
interrupt-names = "iic2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x20 0x4>;
reg = <0x41610000 0x10000>;
i2ctemperature@2 {
compatible = "temperature";
reg = <0x2>;
};
};
i2c@41620000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-names = "ref_clk";
clocks = <0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,xps-iic-2.00.a";
interrupt-names = "iic2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x34 0x4>;
reg = <0x41620000 0x10000>;
i2ctemperature@2 {
compatible = "temperature";
reg = <0x2>;
};
};
i2c@41630000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-names = "ref_clk";
clocks = <0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,xps-iic-2.00.a";
interrupt-names = "iic2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x35 0x4>;
reg = <0x41630000 0x10000>;
i2ctemperature@2 {
compatible = "temperature";
reg = <0x2>;
};
};
i2c@41640000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-names = "ref_clk";
clocks = <0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,xps-iic-2.00.a";
interrupt-names = "iic2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x36 0x4>;
reg = <0x41640000 0x10000>;
i2ctemperature@2 {
compatible = "temperature";
reg = <0x2>;
};
};
i2c@41650000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-names = "ref_clk";
clocks = <0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,xps-iic-2.00.a";
interrupt-names = "iic2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x1d 0x4>;
reg = <0x41650000 0x10000>;
i2ctemperature@2 {
compatible = "temperature";
reg = <0x2>;
};
};
i2c@41660000 {
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
clock-names = "ref_clk";
clocks = <0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,xps-iic-2.00.a";
interrupt-names = "iic2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x1e 0x4>;
reg = <0x41660000 0x10000>;
i2ctemperature@2 {
compatible = "temperature";
reg = <0x2>;
};
};
axi_quad_spi@90000000 {
bits-per-word = <0x8>;
clock-names = "ext_spi_clk", "s_axi_aclk";
clocks = <0x1 0x11 0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,axi_qspi-2.00.a";
fifo-size = <0x100>;
interrupt-names = "ip2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x37 0x1>;
num-cs = <0x4>;
reg = <0x90000000 0x10000>;
xlnx,num-ss-bits = <0x4>;
xlnx,spi-mem-addr-bits = <0x18>;
xlnx,spi-memory = <0x2>;
xlnx,type-of-axi4-interface = <0x0>;
xlnx,use-startup = <0x1>;
xlnx,spi-mode = <0x2>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
is-dual = <0x0>;
flash@0 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x0>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash1";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
flash@1 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x1>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash2";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
flash@2 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x2>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash3";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
flash@3 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x3>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash4";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
};
axi_quad_spi@80000000 {
bits-per-word = <0x8>;
clock-names = "ext_spi_clk", "s_axi_aclk";
clocks = <0x1 0x11 0x1 0xf>;
compatible = "xlnx,axi_qspi-2.00.a";
fifo-size = <0x100>;
interrupt-names = "ip2intc_irpt";
interrupt-parent = <0x4>;
interrupts = <0x0 0x38 0x1>;
num-cs = <0x4>;
reg = <0x80000000 0x10000>;
xlnx,num-ss-bits = <0x4>;
xlnx,spi-mem-addr-bits = <0x18>;
xlnx,spi-memory = <0x2>;
xlnx,type-of-axi4-interface = <0x0>;
xlnx,use-startup = <0x1>;
xlnx,spi-mode = <0x2>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x0>;
is-dual = <0x0>;
flash@0 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x0>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash5";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
flash@1 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x1>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash6";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
flash@2 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x2>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash7";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
flash@3 {
compatible = "n25q256,spi-nor";
reg = <0x3>;
spi-max-frequency = <0x9ef21b0>;
spi-tx-bus-width = <0x1>;
spi-rx-bus-width = <0x1>;
#address-cells = <0x1>;
#size-cells = <0x1>;
partition@0x0000000 {
label = "spi-flash8";
reg = <0x0 0x2000000>;
};
};
};
};
chosen {
bootargs = "earlycon vmalloc=400M";
stdout-path = "serial0:115200n8";
};
aliases {
ethernet0 = "/amba/ethernet@e000b000";
ethernet1 = "/amba/ethernet@e000c000";
serial0 = "/amba/serial@e0000000";
spi0 = "/amba/spi@e000d000";
spi1 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@90000000";
spi2 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@80000000";
flash0 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@90000000/flash@0";
flash1 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@90000000/flash@1";
flash2 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@90000000/flash@2";
flash3 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@90000000/flash@3";
flash4 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@80000000/flash@0";
flash5 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@80000000/flash@1";
flash6 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@80000000/flash@2";
flash7 = "/amba_pl/axi_quad_spi@80000000/flash@3";
};
memory {
device_type = "memory";
reg = <0x0 0x40000000>;
};
};
4、ramdisk配置
Ramdisk中可以在启动脚本中增加挂载文件系统的操作,注意,8个分区启动时全部加载会导致启动速度变慢,最好还是用到多少挂载多少,这里是只挂载了一个,后续的flash分区挂载可以在boot.sh应用启动脚本中让用户自己进行配置。



























 6392
6392











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








