我们以一个类作为示例来说明:
class Point{
public:
Point() = default;
Point(const int& m_x, const int& m_y) :m_x(m_x), m_y(m_y) {}
Point(const Point& other) //拷贝构造
{
this->m_x = other.m_x;
this->m_y = other.m_y;
}
private:
int m_x;
int m_y;
};
operator+/- 的操作及注意
重载加运算符,貌似很简单,因为像是普通对象一样:
int a=b+c;
我们只需要返回一个b+c的临时对象就好了:
Point operator+(Point other){
return Point(m_x + other.m_x, m_y + other.m_y);
}
我们确实可以完成 + 的操作:
Point p1{ 20,30 };
Point p2{ 30,40 };
Point p3 = p1 + p2;
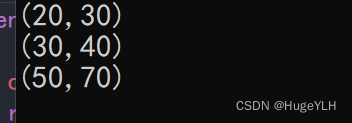
但是,请注意运算符的规则,例如,像这样:
int a,b,c;
(a+b)=10; //ERROR
Point p1{ 20,30 };
Point p2{ 30,40 };
(p1+p2)=Point(50,60); //OK 因为我们+会返回一个普通对象,然后再使用对象的赋值,但是这不符合常理
我们无法完成int类型的先加再赋值的操作,所以我们重载的加运算符也应该满足这一点:
正确:
const Point operator+(const Point& other)const
{
return Point(m_x + other.m_x, m_y + other.m_y);
}
注意点:
- 要符合普通的加法的常理,即不能把相加的返回值当作左值,所以要使用const对象作为返回值。
- 我们要加上const限定符,标记此函数为const成员函数。因为:只有const对象才能调用const成员函数,例如: Point p3=p1+p2+p0 (允许多次相加)
- 将函数写作const引用类型,防止拷贝的产生。
同理:重载的 - 减运算符和+运算符一样,具有相同的道理:
const Point operator-(const Point& other)const
{
return Point(m_x - other.m_x, m_y - other.m_y);
}
Point p1{ 20,30 };
Point p2{ 30,40 };
Point p3;
p3 = p1 - p2 - Point(5, 5); // (-15,-15)
operator+= 的操作及注意
我们一开始的写法:
void operator+=(Point other)
{
m_x += other.m_x;
m_y += other.m_y;
}
直接把相对应的成员变量与other的变量相加,确实,这可以完成最简单的+=操作:
Point p1(10,20)
p1 += Point(10, 10); //20 30
但是当我们想一下,我们的int变量+=的规则:
int a = 0;
(a += 4) = 10; // OK: a=10
把a+=4的返回值(a本身)再赋值为一个值10,这是可以完成的,但是我们重载的+=可以吗?
(p1 += p2) = p3; //ERROR
很显然,不可以,我们的返回值为void,无法进行上面的操作。
正确:
Point& operator+=(const Point& other)
{
m_x += other.m_x;
m_y += other.m_y;
return *this;
}
int main(){
Point p1{ 20,30 };
Point p2{ 30,40 };
p1+=Point(10); //p1=(30,40)
(p1 += p2) = p2; //p1= p2=(30,40)
return 0;
}
注意点:
- 函数返回*this的成员对象,并且我们要返回引用,这样我们就可以完成两个值+=,之后再次赋值,或者多次+=的操作了。
- 函数参数使用const引用,防止不必要的拷贝。
同理:我们的-= 运算符也应该完成一样的操作,并且具有相同规则:
Point& operator-=(const Point& other)
{
m_x -= other.m_x;
m_y -= other.m_y;
return *this;
}
++自增操作
我们都知道,自增,分为前置和后置。
int a=10,b;
b=a++;
b=++a;
前置++:先自增,再赋值
后置++:先赋值,再自增
我们如何区分前置和后置的++呢? 我们使用一个int放在括号里,标记他为一个后置的++
//前置++
Point& operator++()
{
m_x++;
m_y++;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Point& operator++(int)
{
Point temp = *this;
m_x++;
m_y++;
return temp;
}
int main(){
Point p1{ 20,30 };
Point p2{ 30,40 };
++p1; //无参数
p1++; //参数标记为int
return 0;
}

注意点
- 我们要返回对象的引用,因为我们的普通的++允许我们在++后再进行其他的操作,如相加…
- 前置++不带任何参数;后置++设置一个标记int,表示为后置的
- 后置的++的函数体: 一个temp保存当前时刻的对象值,相加后,返回保存的临时值。
同理, --的前置和后置写法,完全一致:
//前置--
Point& operator--()
{
m_x--;
m_y--;
return *this;
}
//后置--
Point& operator--(int)
{
Point temp = *this;
m_x--;
m_y--;
return temp;
}
在这里,不多描述。。。
输入输出重载
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Point& other)
{
cout << "(" << other.m_x << "," << other.m_y << ")";
return cout;
}
friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Point& other)
{
cin >> other.m_x >> other.m_y;
return cin;
}
注意:
- 输出的重载<< 需要设定为友元函数,因为它接受两个参数,一个ostream表示输出,一个istream表示输入
- 重载输出<<中需要指定other为const引用,因为输出并不改变原来的对象的值。
- 重载输入>>中需要指定other为非const引用,因为输入会改变原来的对象的值。
- 记得返回每次的cout和cin,以便可以进行下一次连续的输入和输出,并且返回值为引用类型。
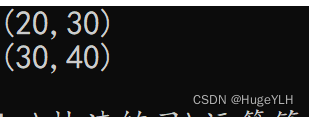
Point p1{ 20,30 };
Point p2{ 30,40 };
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
我们在函数中不要使用endl来换行,因为我们只负责输入和输出,并且不负责格式的变化,因此我们
在外面自己控制格式。
其他重载
==和!=
bool operator!=(const Point& other)
{
return (m_x == other.m_x && m_y != other.m_y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& other)
{
return (m_x == other.m_x && m_y == other.m_y);
}
[] () 运算符…
[] 运算符主要用于数组的访问:
class Foo
{
int* arr;
public:
Foo(int* arr):arr(arr){}
~Foo() { delete[] arr; }
int operator[](int i)
{
return arr[i];
}
};
int main()
{
Foo a(new int[4] {1, 2, 3, 4});
cout << a[3] << endl;
return 0;
}
()运算符的重载主要见于仿函数(函数对象)
class Abc{
public:
bool operator()(int a)
{
return a % 2; //奇数判断条件
}
};
int main(){
vector<int> my{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
vector<int> temp(my.size());
auto it=copy_if(my.begin(), my.end(), temp.begin(), Abc());
temp.resize(distance(temp.begin(), it));
for (auto& x : temp)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
return 0;
}
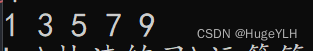
把容器中所有的奇数复制到另一个另一个容器中。
完整操作
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Point
{
public:
Point() = default;
Point(const int& m_x, const int& m_y) :m_x(m_x), m_y(m_y) {}
Point(const Point& other)
{
this->m_x = other.m_x;
this->m_y = other.m_y;
}
// +
const Point operator+(const Point& other)const
{
return Point(m_x + other.m_x, m_y + other.m_y);
}
const Point operator-(const Point& other)const
{
return Point(m_x - other.m_x, m_y - other.m_y);
}
Point& operator+=(const Point& other)
{
m_x += other.m_x;
m_y += other.m_y;
return *this;
}
Point& operator-=(const Point& other)
{
m_x -= other.m_x;
m_y -= other.m_y;
return *this;
}
//前置++
Point& operator++()
{
m_x++;
m_y++;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Point& operator++(int)
{
Point temp = *this;
m_x++;
m_y++;
return temp;
}
//前置++
Point& operator--()
{
m_x--;
m_y--;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Point& operator--(int)
{
Point temp = *this;
m_x--;
m_y--;
return temp;
}
bool operator!=(const Point& other)
{
return (m_x == other.m_x && m_y != other.m_y);
}
bool operator==(const Point& other)
{
return (m_x == other.m_x && m_y == other.m_y);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Point& other)
{
cout << "(" << other.m_x << "," << other.m_y << ")";
return cout;
}
friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Point& other)
{
cin >> other.m_x >> other.m_y;
return cin;
}
private:
int m_x;
int m_y;
};
class Foo
{
int* arr;
public:
Foo(int* arr):arr(arr){}
~Foo() { delete[] arr; }
int operator[](int i)
{
return arr[i];
}
};
class Abc
{
public:
bool operator()(int a)
{
return a % 2; //奇数判断条件
}
};
int main1()
{
Point p1{ 20,30 };
Point p2{ 30,40 };
//++p1; //无参数
//p1++; //参数标记为int
//--p1;
//p1--;
//Point p3 = p1 + p2 + Point(10, 20);
//Point p4 = p1 - p2 - Point(5, 5);
//p1 += Point(10, 10); //30 40
//p1 -= Point(10, 10);
//(p1 += p2) = p3;
//(p1 -= p2) = p4;
//(p1 - p2) = Point(11, 20); //同样和加法一样,不允许
cout << p1 << endl;
cout << p2 << endl;
//cout << p3 << endl;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
Foo a(new int[4] {1, 2, 3, 4});
cout << a[3] << endl;
vector<int> my{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
vector<int> temp(my.size());
auto it=copy_if(my.begin(), my.end(), temp.begin(), Abc());
temp.resize(distance(temp.begin(), it));
for (auto& x : temp)
{
cout << x << " ";
}
return 0;
}























 3262
3262











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










