Description
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
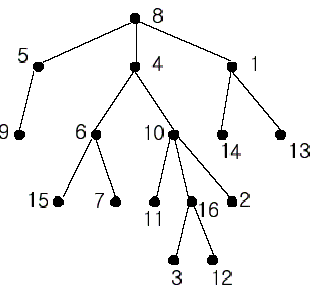
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,…,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,…, N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge –the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Source
大意:
给定t组数据,包括n个点和n-1条边,以及一次询问,求最近公共祖先
思路:
学习了在线的倍增lca,这里补上另一种倍增的做法
2016.9.22补上lca转rmq做法,这里已经是三种了
对有根树T进行DFS,将遍历到的结点按照顺序记下,我们将得到一个长度为2N – 1的序列,称之为T的欧拉序列F
每个结点都在欧拉序列中出现,我们记录结点u在欧拉序列中第一次出现的位置为pos(u)
根据DFS的性质,对于两结点u、v,从pos(u)遍历到pos(v)的过程中经过LCA(u, v)有且仅有一次,且深度是深度序列B[pos(u)…pos(v)]中最小的
即LCA(T, u, v) = RMQ(B, pos(u), pos(v)),并且问题规模仍然是O(N)的(然而还是79MS过感觉体现不出优势啊)
瞎搞:
tarjan版本
#include <stdio.h>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
struct edge
{
int y,next;
}e[10001];
int ls[10001],f[10001],st,ed,maxE=0;
bool vis[10001];
void add(int x,int y)
{
e[++maxE]=(edge){y,ls[x]};
ls[x]=maxE;
}
int find(int x)
{
if (!f[x])
return x;
f[x]=find(f[x]);
return f[x];
}
void dfs(int x)
{
vis[x]=true;
if (x==st&&vis[ed])
printf("%d\n",find(ed));
else
if (x==ed&&vis[st])
printf("%d\n",find(st));
else
for (int i=ls[x];i;i=e[i].next)
{
dfs(e[i].y);
f[find(e[i].y)]=x;
}
}
int main()
{
int t,n;
scanf("%d",&t);
while (t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
maxE=0;
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
memset(ls,0,sizeof(ls));
memset(vis,true,sizeof(vis));
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
vis[y]=false;
add(x,y);
}
scanf("%d%d",&st,&ed);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (vis[i])
{
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
dfs(i);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}倍增版本
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
struct edge
{int y,next;}e[10001];
int ind[10001],dep[10001],ls[10001],f[10001][17],maxE;
void add(int x,int y)
{
e[++maxE]=(edge){y,ls[x]};
ls[x]=maxE;
}
void dfs(int d,int x)
{
dep[x]=d;
for (int i=ls[x];i;i=e[i].next)
dfs(d+1,e[i].y);
}
int LCA(int qx,int qy)
{
if (dep[qx]<dep[qy])
{qx^=qy;qy^=qx;qx^=qy;}
for (int i=16;i>-1;i--)
if (dep[qy]<=dep[f[qx][i]])
qx=f[qx][i];
if (qx==qy)
return qx;
for (int i=16;i>-1;i--)
if (f[qx][i]!=f[qy][i])
{
qx=f[qx][i];
qy=f[qy][i];
}
return f[qx][0];
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while (t--)
{
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
memset(ls,0,sizeof(ls));
memset(ind,0,sizeof(ind));
memset(dep,0,sizeof(dep));
maxE=0;
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
ind[y]++;
add(x,y);
f[y][0]=x;
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (!ind[i])
{
dfs(1,i);
break;
}
for (int j=1;j<=16;j++)
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
f[i][j]=f[f[i][j-1]][j-1];
int qx,qy;
scanf("%d%d",&qx,&qy);
printf("%d\n",LCA(qx,qy));
}
return 0;
}LCA转RMQ版本
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
struct edge{int y,next;}e[10010];
int f[20010][17][2],d[20010],t[20010],pos[20010],ls[10010],maxE,cnt;
bool ind[10010];
void add(int x,int y)
{
e[++maxE]=(edge){y,ls[x]};
ls[x]=maxE;
}
void dfs(int x,int dep)
{
t[++cnt]=x;
d[cnt]=dep;
if (!pos[x])
pos[x]=cnt;
for (int i=ls[x];i;i=e[i].next)
{
dfs(e[i].y,dep+1);
t[++cnt]=x;
d[cnt]=dep;
}
}
int main()
{
int p;
scanf("%d",&p);
while (p--)
{
maxE=cnt=0;
memset(ls,0,sizeof(ls));
memset(pos,0,sizeof(pos));
memset(ind,0,sizeof(ind));
int n,m;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y);
ind[y]=true;
}
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if (!ind[i])
dfs(i,1);
for (int i=1;i<=cnt;i++)
{
f[i][0][0]=d[i];
f[i][0][1]=t[i];
}
for (int j=1;j<=15;j++)
for (int i=1;i<=cnt&&i+(1<<j)-1<=cnt;i++)
if (f[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1][0]<f[i][j-1][0])
{
f[i][j][0]=f[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1][0];
f[i][j][1]=f[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1][1];
}
else
{
f[i][j][0]=f[i][j-1][0];
f[i][j][1]=f[i][j-1][1];
}
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
x=pos[x];
y=pos[y];
if (x>y){x^=y;y^=x;x^=y;}
int v=(int)floor(log10(y-x+1)/log10(2));
if (f[x][v][0]<f[y-(1<<v)+1][v][0])
printf("%d\n",f[x][v][1]);
else
printf("%d\n",f[y-(1<<v)+1][v][1]);
}
return 0;
}























 344
344

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








