Nearest Common Ancestors
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 10000K | |
| Total Submissions: 14650 | Accepted: 7816 |
Description
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
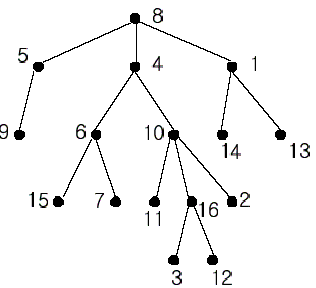
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.

In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,...,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,..., N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge --the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2 16 1 14 8 5 10 16 5 9 4 6 8 4 4 10 1 13 6 15 10 11 6 7 10 2 16 3 8 1 16 12 16 7 5 2 3 3 4 3 1 1 5 3 5
Sample Output
4 3
Source
题意:给n个点,n-1条边,找出2个点的最近公共祖先
题解:本人课件使用,so代码带详细解释
详细版:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int head[10005]; //邻接表头
int fath[10005]; //fath[i]指向i的父节点
int deep[10005]; //deep[i]代表节点i的深度
int all; //all代表邻接表边数
int root; //root是树的根
int n; //n是点的数目
//邻接表存图
struct edge
{
int data;
int next;
} v[10005];
//邻接表增加边操作
void add(int x,int y)
{
v[all].next=head[x];
v[all].data=y;
head[x]=all;
all++;
}
void input()
{
int i;
int x;
int y;
scanf("%d",&n);
//把全部节点的父亲置-1
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
head[i]=-1;
fath[i]=-1;
}
//all是邻接表边数
all=0;
/*
加边,并将儿子的fath数组指向父节点,
由于这是一棵树,所以明显最后只有根节点的fath值是-1
*/
for(i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y);
fath[y]=x;
}
}
//对树进行深搜,并计算出每一个节点的深度deep[i]
void dfs(int x,int d)
{
int i;
for(i=head[x]; i!=-1; i=v[i].next)
{
dfs(v[i].data,d+1);
}
//赋值深度
deep[x]=d;
}
//找出fath[i]==-1的节点即树的根节点
void pre_deal()
{
int i;
for(i=1; i<=n; i++)
{
if(fath[i]==-1)
{
root=i; //root代表根
break;
}
}
//由树的根节点开始深搜
dfs(root,0);
}
void solve()
{
int x;
int y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
//若x的深度比y的深度小,互换x和y,保证x的深度大
if(deep[x]<deep[y])
{
x=x+y;
y=x-y;
x=x-y;
}
//调整x的深度,使其和y一样
while(deep[x]>deep[y])
{
x=fath[x];
}
/*
若x和y相等,则证明这就是他们的最近公共祖先
若不相等,由于他们现在深度相等,则将他们等于他们的父节点,
一定会使其到最近公共祖先的时候2节点相等的
*/
while(x!=y)
{
x=fath[x];
y=fath[y];
}
//输出公共祖先
printf("%d\n",x);
}
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
input(); //录入数据
pre_deal(); //预处理数据
solve(); //输入并求解
}
return 0;
}
精简版:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int head[10005],fath[10005],deep[10005],all,root,n,i;
struct edge{ int data,next; } v[10005];
void add(int x,int y)
{
v[all].next=head[x];
v[all].data=y;
head[x]=all++;
}
void dfs(int x,int d)
{
for(deep[x]=d,i=head[x];i!=-1;i=v[i].next)
dfs(v[i].data,d+1);
}
int main()
{
int t,i,x,y;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1; i<=n; i++) head[i]=fath[i]=-1;
for(all=i=0; i<n-1; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
add(x,y),fath[y]=x;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) if(fath[i]==-1) { root=i; break; }
dfs(root,0);
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
if(deep[x]<deep[y]) x^=y^=x^=y;
while(deep[x]>deep[y]) x=fath[x];
while(x!=y) x=fath[x],y=fath[y];
printf("%d\n",x);
}
return 0;
}

























 341
341

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








