1.管道创建后父进程和子进程都拿到了管道的读写端描述符。各个进程根据所需关闭端口。
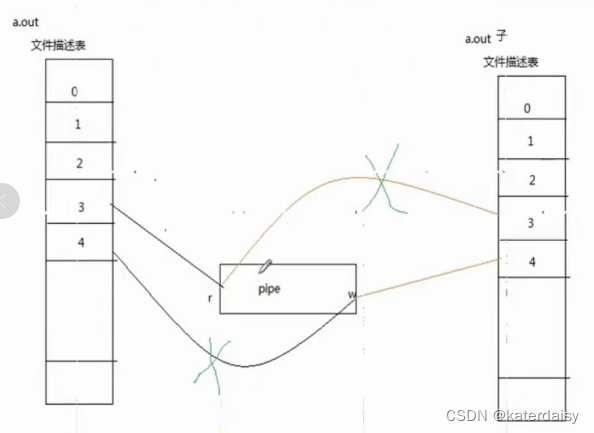
2.不同的读写端关闭情况,会产生不同的读写结果。

3.测试代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <wait.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#if 0
int main(int * argc, const char * agrv[])
{
int fd[2];
pipe(fd);
pid_t pid = fork();
// while(1)
// {
if(pid == 0)//子进程
{
//close(fd[0]);//子进程写pipe,关闭读端
//dup2(STDOUT_FILENO,fd[1]);
dup2(fd[1],STDOUT_FILENO);//ps命令输出到标准输出设备,需要重定向到pipe的写端
execlp(“ps”,“ps”,“aux”,NULL);
}
else if(pid > 0) //父进程
{
//close(fd[1]);//父进程读pipe,关闭写端
//dup2(STDIN_FILENO,fd[0]);
dup2(fd[0],STDIN_FILENO);//grep命令从标准输入接收数据,现在需要从pipe的读端读数据,所有需要把标准输入重定向到pipe的读端p[0]
execlp(“grep”,“grep”,“bash”,NULL);
}
// }
return 0;
}
#endif
#if 0
int main(int * argc, const char * agrv[])
{
pid_t pid;
int fd[2];
pipe(fd);
int i;
for(i = 0; i<2; i++)
{
pid = fork();
if(pid == 0) break;
}
if(pid > 0) //父进程
{
printf("I am father, pid:%d\n",getpid());
close(fd[0]);
close(fd[1]);
// int status;
// while(1) {
// sleep(1);
// int ret = waitpid(-1,&status,WNOHANG);
// //int ret = wait(&status);
// if(WIFEXITED(status)) printf("recycle child , status:%d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
// if(WIFSIGNALED(status)) printf("recycle child , with status:%d\n", WTERMSIG(status));
// }
}
else if( pid == 0)
{
if(i == 0)//子进程1
{
sleep(1);//保证父进程先执行
printf("I am child1, pid:%d\n",getpid());
close(fd[0]);//子进程写pipe,关闭读端
//dup2(STDOUT_FILENO,fd[1]);
dup2(fd[1],STDOUT_FILENO);//ps命令输出到标准输出设备,需要重定向到pipe的写端
execlp("ps","ps","aux",NULL);
close(fd[1]);
exit(1);
}
else if(i == 1) //子进程2
{
sleep(2);//保证父进程和子进程1先执行
printf("I am child2, pid:%d\n",getpid());
close(fd[1]);//子进程2读pipe,关闭写端
//dup2(STDIN_FILENO,fd[0]);
dup2(fd[0],STDIN_FILENO);//grep命令从标准输入接收数据,现在需要从pipe的读端读数据,所有需要把标准输入重定向到pipe的读端p[0]
execlp("grep","grep","bash",NULL);
close(fd[0]);
exit(1);
}
}
return 0;
}
#endif
int main(int * argc, const char * argv[])
{
int fd[2];//
pipe(fd);
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0)
{
sleep(1);
close(fd[0]);//先关闭读端
char buf[] = {"hello world"};
close(fd[1]);//管道写端也关闭
//write(fd[1],buf,sizeof(buf));
//close(fd[1]);//子进程关闭写端
while(1)
{
write(fd[1],buf,sizeof(buf));
perror("write pipe:");
sleep(1);
}
}
else if(pid > 0) //父进程读管道
{
sleep(2);
close(fd[1]);//父进程关闭写端
//close(fd[0]);
char buf[20];
int status;
while(1) {
int ret = read(fd[0],buf,5);//读管道
//printf("read data %s, ret = %d\n",buf, ret);
sleep(1);
int wret = waitpid(-1,&status,WNOHANG);
//int wret = wait(&status);
if(WIFEXITED(status)) printf("recycle child , status:%d\n", WEXITSTATUS(status));
if(WIFSIGNALED(status)) printf("recycle child , with status:%d\n", WTERMSIG(status));
}
}
}





















 426
426











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








