头文件:#include <numeric>
1、accumulate()求和算法,计算一个序列内所有元素之和
accumulate(start迭代器,end迭代器,和的初值)
使用这个算法的前提是该类型可以使用“+”运算,求和的结果保存在第三个参数中
QStringList list;
list <<"aa" <<"bb" <<"cc" << "dd";
auto result = std::accumulate(std::begin(list),std::end(list),QString("xx"));
qDebug()<<result;
初值是“xx”,求和在此基础上加。

这里QString("xx"),不能省略为"xx",因为求和的结果是QString类型,前者显示指明了结果是QString类型,后者实际上是(C语言中的)字符串常量:char * p = "xx"
对于自定义类型,只要重载了“+”运算符,那就能使用此算法。实验:
#include <numeric>
#include <QDebug>
struct ceshi
{
int frist = 0;
int second = 0;
ceshi operator+(const ceshi& b)const
{
ceshi c;
c.frist = this->frist + b.frist;
c.second = this->second + b.second;
return c;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::list<ceshi> list;
ceshi c1;
c1.frist = 10;
c1.second = 20;
list.push_back(c1);
ceshi c2;
c2.frist = 30;
c2.second = 40;
list.push_back(c2);
ceshi c3;
c3.frist = 50;
c3.second = 60;
list.push_back(c3);
ceshi c4;
c4.frist = 70;
c4.second = 80;
list.push_back(c4);
ceshi c0;
auto result = std::accumulate(std::begin(list),std::end(list),c0);
qDebug()<<result.frist<<result.second;
}
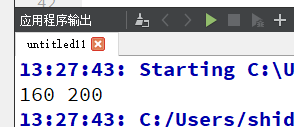
这里自定义一个结构体,然后重载了结构体的“+”运算符,就能使用accumulate()将多个结构体对象按自定义的加法规则进行相加。
可以自定义一个相加函数作为第四个参数。
2、inner_product()求两个序列的内积,即两个元素个数相等的序列对应元素相乘再相加。
#define debug qDebug()<<
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QList<int> list1{26,33,44,66,77};
QList<int> list2{26,33,44,66,777};
int init = 0;
auto result = std::inner_product(list1.begin(),list1.end(),list2.begin(),init);
debug init << result;
}结果 = 初始值init + 对应元素相乘后相加。
还有第一个版本,自定义一个加法操作函数作为第5个参数,自定义一个乘法操作函数作为第6个参数。
3、partial_sum()累加求和
#define debug qDebug()<<
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QList<int> list1{26,33,44,66,77};
QList<int> list2;
std::partial_sum(list1.begin(),list1.end(),std::back_inserter(list2));
debug list2;
}

每个值是从开始到当前值的累加之和。
可自定义加法操作函数作为第4个参数。
4、adjacent_difference() 获取当前每个元素与前一个元素的差
#define debug qDebug()<<
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QList<int> list1{26,33,44,66,77};
QList<int> list2;
std::adjacent_difference(list1.begin(),list1.end(),std::back_inserter(list2));
debug list2;
}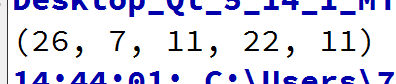

这里使用了int类型的“-”减法操作,还可以自定义减操作函数作为第4个函数。例如:
#define debug qDebug()<<
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QList<int> list1{26,33,44,66,77};
QList<int> list2;
std::adjacent_difference(list1.begin(),list1.end(),std::back_inserter(list2),[](const int & v1, const & v2)
{
return (v1 - v2) * 2;
});
debug list2;
}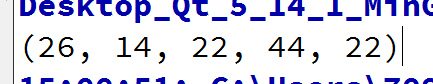
这里自定义操作:相减后乘以2。























 1489
1489











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








