摘要
- The dominant sequence transduction models 显性序列转换模型。
- complex recurrent 复杂的递归。
- convolutional neural networks 卷积神经网络。
- an encoder and a decoder 编码器和解码器。
- The best performing models性能最佳的模型
- the encoder → \rightarrow → an attention mechanism → \rightarrow → decoder。
- a new simple network architecture: 新的简单的网络架构。
- , the Transformer :完全基于注意力机制:
- recurrence and convolutions 免除了递归和卷积。
- Experiments on two machine translation tasks: 两个机器翻译任务上的实验表明:
- 这些模型能够在质量上最优和要求并行化 在训练时间上所需的时间更少。
- WMT 2014 Englisht-o-German translation task: 2014年WMT英德翻译任务上,
- the existing best results 现有的最佳结果。
- BLEU
- On the WMT 2014 English-to-French translation task
- eight GPUs 八块GPU上。
- a new single-model :一个新的单模型。
- state-of-the-art BLEU score:最先进的BLEU scores.
- a small fraction of the training costs 培训成本的一个小部分。
- the literature 文献中。
- English constituency parsing :英语选民分析。
- large and limited training data:大量有限训练数据。
介绍
- Recurrent neural networks:递归神经网络
- long short-term memory 长短时记忆。
- gated recurrent 门控递归
- neural networks 神经网络
- firmly 牢固地。
- state of the art approaches in sequence modeling and transduction problems最先进序列模型的方法转换问题。
- language modeling and machine translation: 语言模式和机器翻译。
- Numerous efforts:无数的努力
- recurrent language models 循环语言模型
- encoder-decoder architectures:编解码器架构。
- Recurrent models typically factor computation along the symbol positions of the input and output sequences:
- 训练模型通常沿输入输出序列的符号位置进行计算。
- Aligning the positions to steps in computation time 将计算时间内的位置与步骤对齐。
(隐藏状态) (先前的隐藏状态) - generate a sequence of hidden states h t h_t ht.
- a function of the previous hidden state h t − 1 h_{t - 1} ht−1
- the input for position t t t
- at longer sequence lengths. (更长的序列长度)
- memory constraints 内存约束。
- batching across examples 跨示例批处理。
- factorization tricks 因式分解。
- conditional computation 条件计算:模型压缩的一个子方向。
- sequential computation 连续计算
- compelling:引人注目。
- with regrad to 不考虑。
- eschewing recurrence 避免复发。
- eight P100 GPUs. 八个P100GPUS.
背景
- the Extended Neural GPU G P U 图 形 GPU图形 GPU图形
- ByteNet
- ConvS2S
- convolutional neural networks: 作为基础的构建模块。
- computing hidden representations in parallel for all input and output positions
- 在所有输入和输出位置上并行的计算隐藏层表示。
- two arbitrary input or output positions 两个任意输入输出位置。
- linearly for ConvS2S and logarithmically for ByteNet
- albeit 尽管。
- averaging attention-weighted positions, 平均注意力权重位置。
- counteract 抵消。
- Multi-Head Attention 多头注意力机制 in section 3.2.
- Self-attention 自注意力机制。
- reading comprehension 阅读理解。
- abstractive summarization 抽象总结。
- textual entailment: 文本蕴涵:两个文本片段有指向关系。
- task-independent sentence representations:任务依赖句子表示。
- End-to-end memory networks: 端到端的记忆网络。
(基于循环注意力机制:a recurrent attention mechanism) -
- simple-language question answerin : 简单的语言问答系统。
- simple-language question answerin 语言模型任务。
- To the best of our knowledge 据我们所知。
模型架构
Most competitive neural sequence transduction models: 最具有竞争力的神经序列转换模型。
an encoder-decoder structure 编码和解码架构。
- the encoder:
maps an input sequence of symbol representation:
( x 1 , x 2 , ⋯ x n ) (x_1,x_2,\cdots x_n) (x1,x2,⋯xn) - a sequence of continuous representations
z = ( z 1 , ⋯ , z n ) z = (z_1,\cdots,z_n) z=(z1,⋯,zn) Given z: - the decoder then generates an output sequence:
( y 1 , ⋯ , y n ) (y_1,\cdots,y_n) (y1,⋯,yn) - At each step the model is auto-regressive.
- 在生成下一个时,先前的符号作为一个额外输入。tha additional input.
- Transformer: stacked self-attention 堆积自我注意力。
- Point-wise 按照点操作属性和规则的集合。
fully connected layers: 全连接层。

Encoder and Decoder Stacks
Encoder
- a stack of N = 6 N = 6 N=6 idential layers.
- Each layer has two sub-layers.
分别为:
-
a multi-head self-attention mechanism
-
a simple position-wise fully connected feed-forward network.
-
a multi-head self-attention mechanism (残差链接): around each of the two sub-layers. followed by layer normalization
-
the output of each sub-layer is layerNorm,:
l a y e r N o r m ( x + S u b l a y e r ( x ) ) layerNorm(x + Sublayer(x)) layerNorm(x+Sublayer(x)) -
S u b l a y e r ( x ) Sublayer(x) Sublayer(x)
-
is the function implemented by the sub-layer itself.
为了促进这些残差链接,模型中的所有的副层,还有嵌入层产生
d m o d e l = 512 d_{model} = 512 dmodel=512的产出维度。
Decoder
- a stack of N = 6 N = 6 N=6 idential layers. (相同图层)
Attention
- An attention function can be described as mapping a query and a set of key-value pairs to an output,
- the query,keys,values and output are all vectors.
- The output is a weighted sum of the values.(值的权重和)
- 计算每个值得权重:使用一个函数,通过相应得键进行查询。
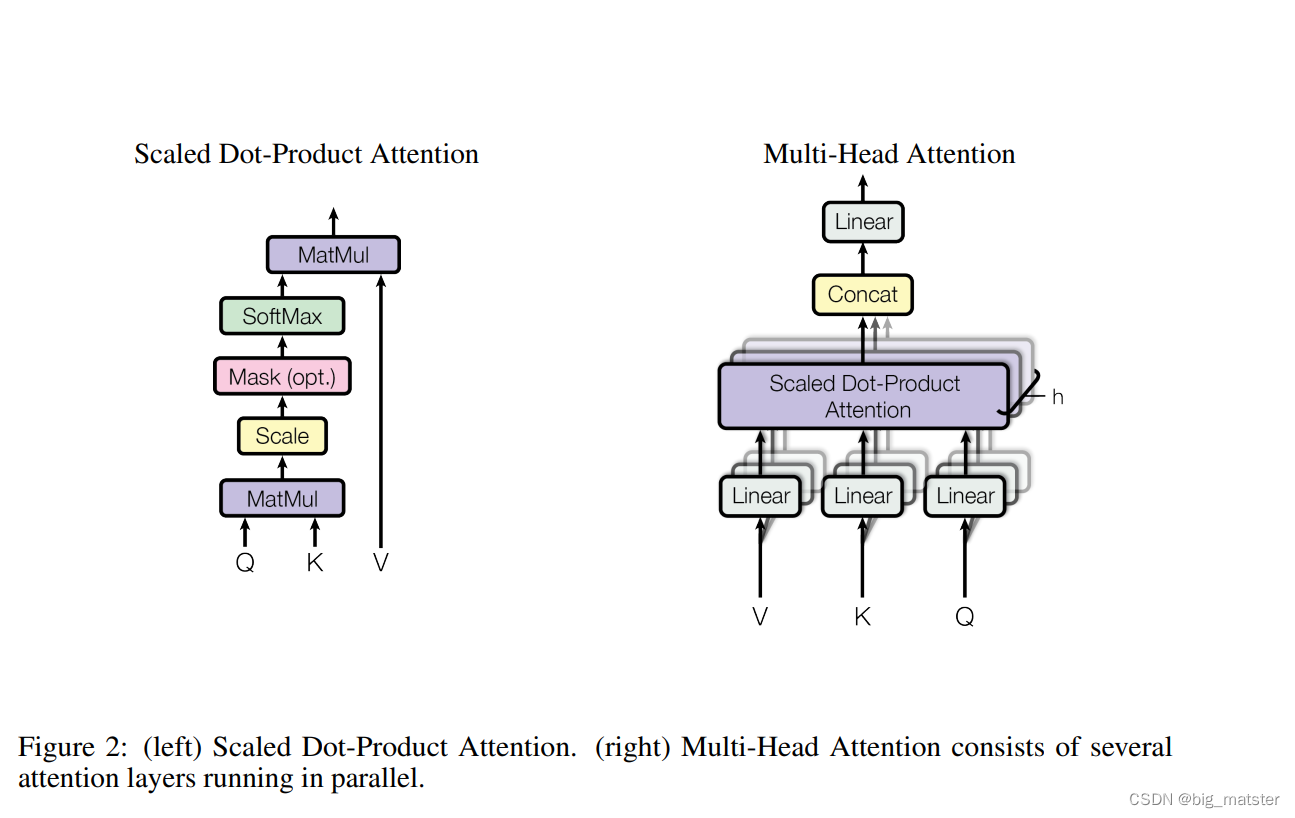
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
我们成为特别关注:Scaled Dot-Product Attention.
-
input: queries and keys of dimension d k d_k dk.
-
values of dimension d v d_v dv
-
我们计算the dot prodcuts of the query with all keys.
-
divide each by d k \sqrt{d_k} dk
-
apply the softmax function to obtain the weights on the values.
-
我们计算这个输出矩阵为 as :
A t t e n t i o n ( Q , K , V ) = s o f t m a x ( Q K T d k ) V Attention(Q,K,V) = softmax(\frac{QK^{T}}{\sqrt{d_k}})V Attention(Q,K,V)=softmax(dkQKT)V -
the scaling factor 比例因子: 1 d k \frac{1}{\sqrt{d_k}} dk1
add
- additive attention
- the compatibility function using a feed-forward network with a single hidden layer.
- dot-product 在实践中,是更快得和空间更加有效性的。
Multi-Head Attention
- a single attention function with d m o d e l d_{model} dmodel-dimensional keys,values,and quies.
- 产生输出值为 d v d_v dv-dimensional output values.
M u l t i H e a d ( Q , K , V ) = C o n c a t ( h e a d 1 , ⋯ , h e a d h ) W O MultiHead(Q,K,V) = Concat(head_1,\cdots,head_h)W^{O} MultiHead(Q,K,V)=Concat(head1,⋯,headh)WO
where h e a d i head_i headi = Attention(Q W i Q W^Q_i WiQ,K W i K W^K_i WiK,V W i V W^V_i WiV)

Applications of Attention in our Model
 = m a x ( 0 , x W 1 + b 1 ) W 2 + b 2 FFN(x) = max(0,xW_1 + b_1)W_2 + b_2 FFN(x)=max(0,xW1+b1)W2+b2
- the linear transformations are the same across different positions
- use different parameters from layer to layer.
- as two convlutions with kernel size 1.
- 输入和输出的维度是 d m o d e l = 512 d_{model} = 512 dmodel=512
- the inner-layer has dimensionality d f f d_{ff} dff = 2048
Embeddings and Softmax
- other sequence transduction models 序列转换模型
- use learned embedding to convert the input tokens and output tokens to vectors of dimension d m o d e l d_{model} dmodel
- the usual learned linear transformation and softmax function to convert the decoder output to predicted next-token probabilities
- share the weight matrix between the two embedding layers and the pre-softmax linear transformation.
Positional Encoding
- sine and cosine functions of different frequencies:
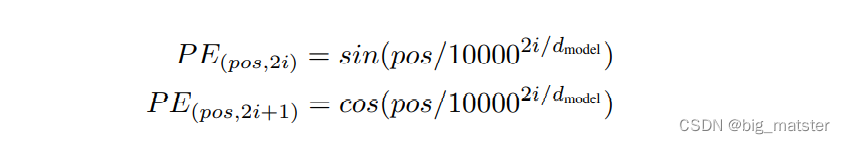
p o s pos pos is the position. i i i is the dimension.
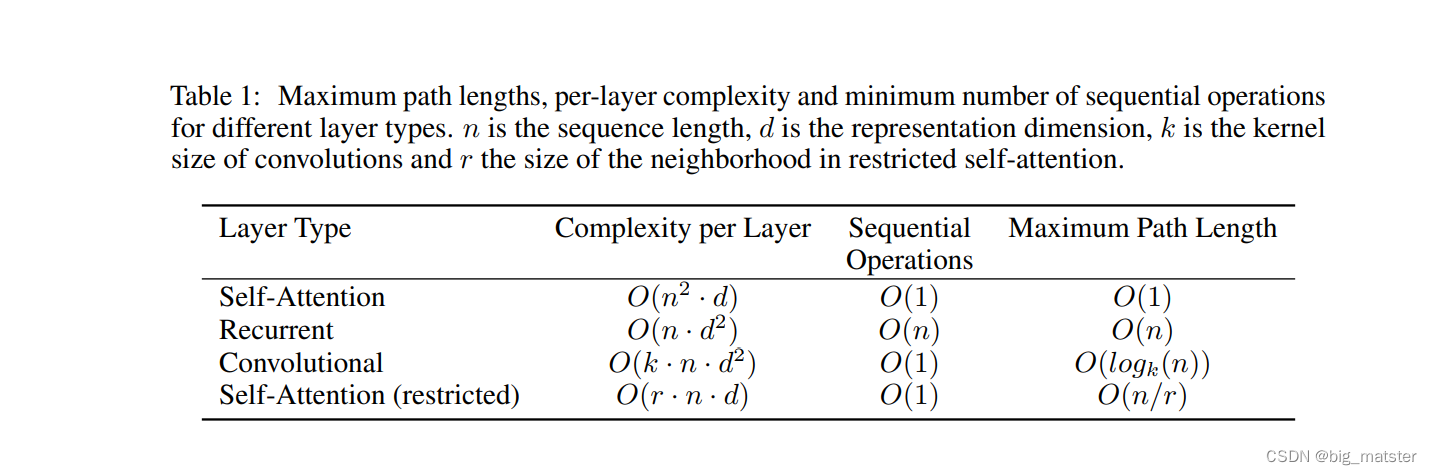
Why Self-Attention
- a recurrent layer requires O ( n ) O(n) O(n)sequential operations,
Training
Training Data and Batching
- the standard WMT 2014 English-German dataset
- 4.5 million sentence pairs.
- . Sentences were encoded using byte-pair encoding .
- approximate sequence length 最大化序列长度。
- source tokens 源词和target tokens 目标词。
Hardware and Schedule
- 训练模型:8 NVIDIA P100 GPUs
Optimizer
- the Adam optimizer

Regularization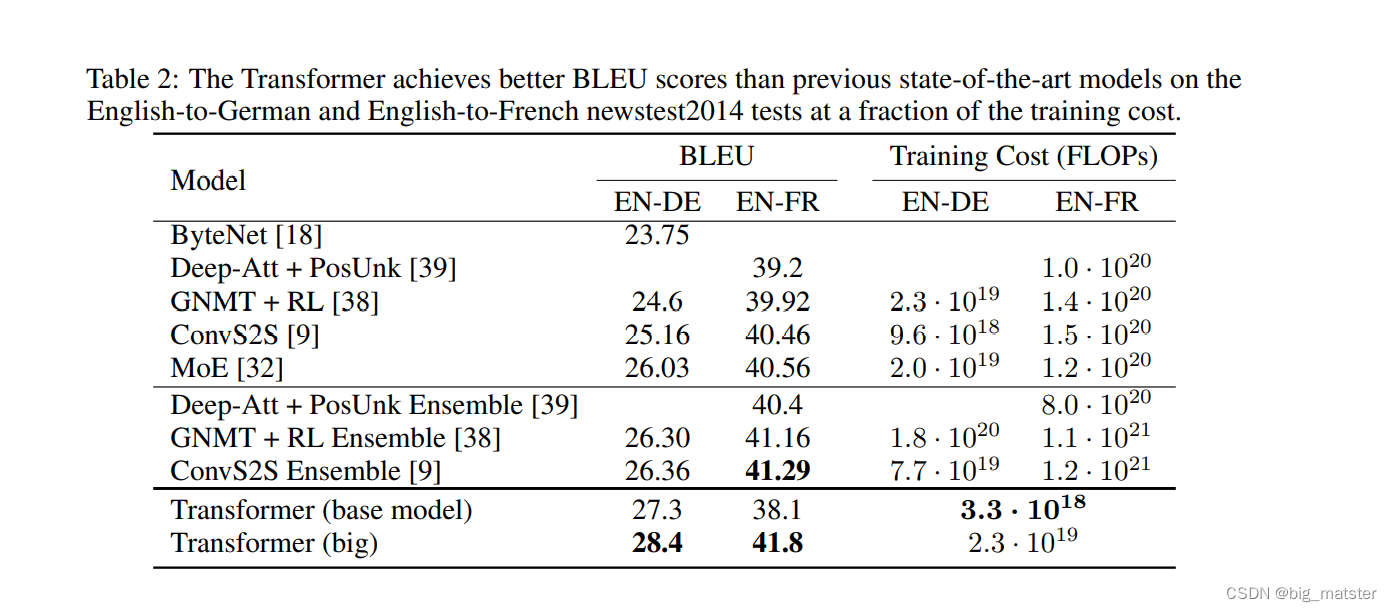
- Residual Dropout
- Label Smoothing
Results
Machine Translation
- On the WMT 2014 English-to-German translation task
- On the WMT 2014 English-to-French translation task
- the sustained single-precision floating-point capacity of each GPU
-
持续每个GPU的单精度浮点容量。
Model Variations
慢慢的将模型变体,啥的全部都将其搞定,研究透彻,研究彻底。慢慢的将这个研究透彻,研究的相当好都行啦的理由。
Transfomrer的输入
Transformer中单词的输入表示 x x x由单词Embedding和位置Embedding(Poxitional Encoding)相加得到。

单词Embedding
单词的Embedding有很多方式可以获取,例如可以采用Word2Vec、Glove等算法预训练得到,也可以在Transformer中训练得到。
位置Embedding
Transformer中除了单词的Embedding,还需要使用位置Embedding表示单词出现在句子中的位置。 因为Transformer不采用RNN的结构,而是使用全局信息,不能利用单词的顺序信息,而这部分信息对于NLP来说非常重要。所以,Transformer中使用位置Embedding保存单词在序列中的相对或绝对位置。
(位置Embedding 保存单词在序列中的相对或绝对位置)
位置Embedding用PE来表示,PE的维度与单词Embedding是一样的,PE可以通过训练得到,也可以使用某种公式计算得到,在Transformer中采用了后者,位置Embedding的计算公式如下:
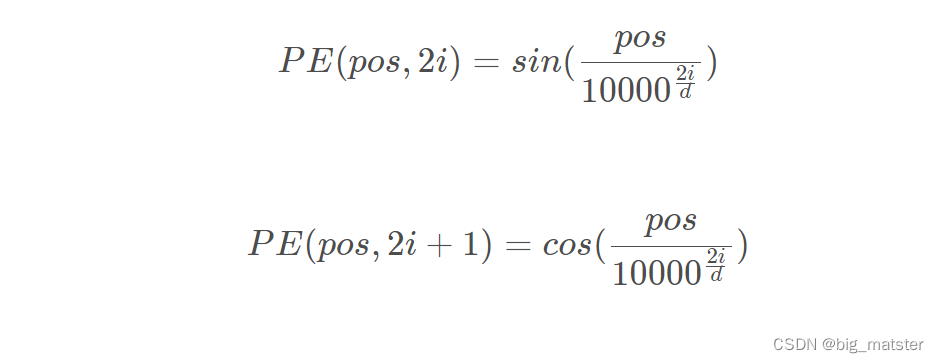
p
o
s
pos
pos 表示单词在句子中的位置。
d
d
d表示PE的维度。
自注意力机制

- Encoder block
- Decoder block
- Multi-Head Attention
- Add:表示残差链接:用于防止网格退化。
- Norm表示Layer Normalization: 用于对每一层的激活进行归一化。

总结
慢慢的将
t
r
a
n
s
f
o
r
m
e
r
transformer
transformer框架都给其搞透彻,将其研究彻底,研究透彻。
后面开始在开始研究代码,将代码运行一波,然后开始慢慢的将其搞定都行啦的回事与打算。慢慢的将代码给其研究彻底。研究透彻!























 4332
4332











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










