目录
线性界线:
 ————
————  (
( ),W:权重,b:偏差
),W:权重,b:偏差
y = label: 0 or 1
predection:

N维界线:
n维:
n - 1维超平面的方程:

predection:

感知器:
1、它是神经网络的基础构成组件。
2、

3、整个数据集中的每一个点都会把分类的结果提供给感知器(分类函数),并调整感知器。——这就是计算机在神经网络算法中,找寻最优感知器的原理。
4、
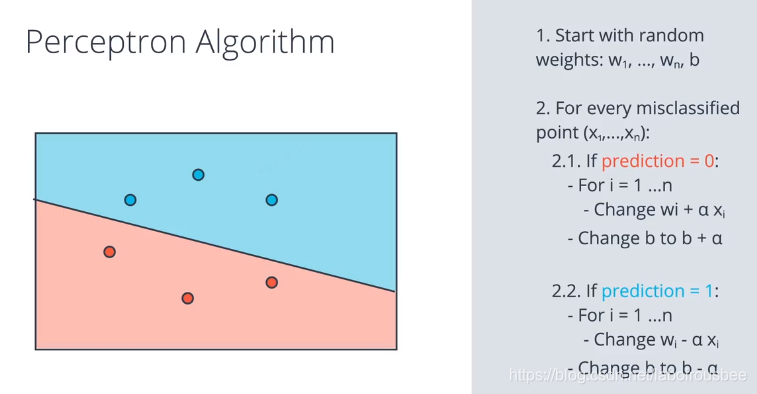
感知器算法实现:
import numpy as np
# Setting the random seed, feel free to change it and see different solutions.
np.random.seed(42)
def stepFunction(t):
if t >= 0:
return 1
return 0
def prediction(X, W, b):
return stepFunction((np.matmul(X,W)+b)[0])
# TODO: Fill in the code below to implement the perceptron trick.
# The function should receive as inputs the data X, the labels y,
# the weights W (as an array), and the bias b,
# update the weights and bias W, b, according to the perceptron algorithm,
# and return W and b.
def perceptronStep(X, y, W, b, learn_rate = 0.01):
# Fill in code
for i in range(len(X)):
y_hat = prediction(X[i], W, b)
if y[i] - y_hat == 1: #分类为负,标签为正
W[0] += X[i][0] * learn_rate
W[1] += X[i][1] * learn_rate
b += learn_rate
if y[i] - y_hat == -1:
W[0] -= X[i][0] * learn_rate
W[1] -= X[i][1] * learn_rate
b -= learn_rate
return W, b
# This function runs the perceptron algorithm repeatedly on the dataset,
# and returns a few of the boundary lines obtained in the iterations,
# for plotting purposes.
# Feel free to play with the learning rate and the num_epochs,
# and see your results plotted below.
def trainPerceptronAlgorithm(X, y, learn_rate = 0.01, num_epochs = 25):
x_min, x_max = min(X.T[0]), max(X.T[0])
y_min, y_max = min(X.T[1]), max(X.T[1])
W = np.array(np.random.rand(2,1))
b = np.random.rand(1)[0] + x_max
# These are the solution lines that get plotted below.
boundary_lines = []
for i in range(num_epochs):
# In each epoch, we apply the perceptron step.
W, b = perceptronStep(X, y, W, b, learn_rate)
boundary_lines.append((-W[0]/W[1], -b/W[1]))
return boundary_lines误差函数:
误差函数提供给我们的预测值与实际值之间的差异。误差函数不能是离散的,必须是连续的,必须是可微的。
Sigmoid函数:

Softmax公式:
![]()
One-Hot编码:

最大似然估计:
将各个点的概率相乘,红点是红色的概率,蓝点是蓝色的概率。采用某种方式将左边的概率增大到右边的概率的过程,叫做最大似然估计。

交叉熵:
对概率乘积取对数,然后再取反。概率和误差函数之间肯定有一定的联系,这种联系叫做交叉熵。交叉熵可以告诉我们两个向量是相似还是不同。


python编写交叉熵:
import numpy as np
def cross_entropy(Y, P):
Y = np.float_(Y)
P = np.float_(P)
result = -np.sum(Y * np.log(P) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - P))
return result多类别交叉熵:

Logistic 回归
对数几率回归算法。基本上是这样的:
- 获得数据
- 选择一个随机模型
- 计算误差
- 最小化误差,获得更好的模型
- 完成!


最小化误差:梯度下降法。
梯度下降法:

























 45万+
45万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










