dense sift即直接指定关键点位置和描述子采样区域,计算sift特征。一些介绍:http://www.vlfeat.org/api/dsift.html
主要过程是:
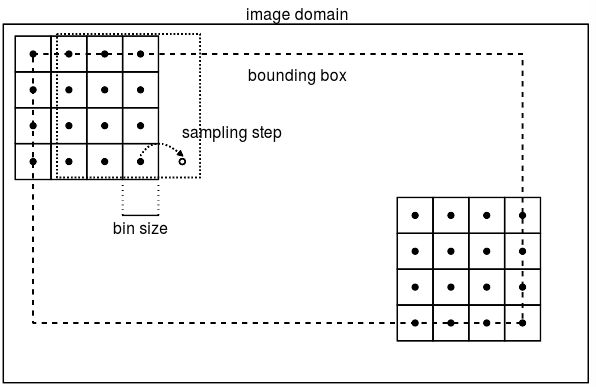
1,用一个patch在图像上以一定步长step滑动,代码中step=1,这个patch就是描述子采样区域,patch size是4bins*4bins,bin size可以自己指定,代码中是3pixels*3pixels。这里说的bin对应到《sift特征提取》中的第4步就是指子区域area。图中的bounding box是sift特征点的范围。
2,计算每个像素点的梯度(同sparse sift),统计每个bin内的像素点在8个方向上的梯度直方图,这样就生成了4*4*8维的sift特征。

代码来自SPM的包里面:
function [ SIFTFeatureVector, locationX, locationY ] = DenseSIFT( image, nPatchSize, nGridSpacing )
image = double( image );
image = mean( image, 3 );
image = image / max( image( : ) );
% parameters
nAngleNums = 8;
nBinNums = 4;
nSampleNums = nBinNums * nBinNums;
alpha = 9; %% parameter for attenuation of angles (must be odd)
if nargin < 5
sigmaGuassian = 1;
end
angleStep = 2 * pi / nAngleNums;
angles = 0 : angleStep : 2 * pi;
angles( nAngleNums + 1 ) = [ ]; % bin centers
[ nRow nCol ] = size( image );
[ gaussianX, gaussianY ] = genDeltaGaussian( sigmaGuassian );
imageVerticalEdges = filter2( gaussianX, image, 'same' ); % vertical edges
imageHorizontalEdges = filter2( gaussianY, image, 'same' ); % horizontal edges
imageGradientMagnitude = sqrt( imageVerticalEdges.^2 + imageHorizontalEdges.^2 ); % gradient magnitude
imageTheta = atan2( imageHorizontalEdges, imageVerticalEdges );
imageTheta( isnan( imageTheta ) ) = 0; % replace illegal result with 0
% descriptor locations
locationX = nPatchSize / 2 : nGridSpacing : nCol - nPatchSize / 2 + 1;
locationY = nPatchSize / 2 : nGridSpacing : nRow - nPatchSize / 2 + 1;
% make orientation images
imageOrientation = zeros( [ nRow, nCol, nAngleNums ], 'single' );
% for each histogram angle
imageCos = cos( imageTheta );
imageSin = sin( imageTheta );
for index = 1 : nAngleNums
% compute each orientation channel
tmp = ( imageCos * cos( angles( index ) ) + imageSin * sin( angles( index ) ) ).^ alpha;
tmp = tmp .* ( tmp > 0 );
% weight by magnitude
imageOrientation( :, :, index ) = tmp .* imageGradientMagnitude;
end
% Convolution formulation:
nHalfPatchSize = nPatchSize / 2;
nHalfPatchSizeMinusDotFive = nHalfPatchSize - 0.5;
sampleResolution = nPatchSize / nBinNums;
weightX = abs( ( 1 : nPatchSize ) - nHalfPatchSizeMinusDotFive ) / sampleResolution;
weightX = ( 1 - weightX ) .* ( weightX <= 1 );
for index = 1 : nAngleNums
imageOrientation( :, :, index ) = conv2( weightX, weightX', imageOrientation( :, :, index ), 'same' );
end
% Sample SIFT bins at valid locations (without boundary artifacts)
% find coordinates of sample points (bin centers)
[ samplePosX, samplePosY ] = meshgrid( linspace( 1, nPatchSize + 1, nBinNums + 1 ) );
samplePosX = samplePosX( 1 : nBinNums, 1 : nBinNums ); samplePosX = samplePosX( : ) - nPatchSize / 2;
samplePosY = samplePosY( 1 : nBinNums, 1 : nBinNums ); samplePosY = samplePosY( : ) - nPatchSize / 2;
SIFTFeatureVector = zeros( [ length( locationY ) length( locationX ) nAngleNums * nSampleNums ] , 'single' );
nOffset = 0;
for n = 1 : nBinNums * nBinNums
SIFTFeatureVector( :, :, nOffset + 1 : nOffset + nAngleNums ) = imageOrientation( locationY + samplePosY(n), locationX + samplePosX(n), : );
nOffset = nOffset + nAngleNums;
end
clear imageOrientation
% Outputs:
[ locationX, locationY ] = meshgrid( locationX, locationY );
[ nrows, ncols, cols ] = size( SIFTFeatureVector );
% normalize SIFT descriptors
SIFTFeatureVector = reshape( SIFTFeatureVector, [nrows * ncols nAngleNums * nSampleNums ] );
SIFTFeatureVector = SIFTNormalization( SIFTFeatureVector );
SIFTFeatureVector = reshape( SIFTFeatureVector, [ nrows ncols nAngleNums * nSampleNums] );
function [ GX, GY ] = genDeltaGaussian( sigma )
% laplacian of size sigma
G = genGaussian(sigma);
[ GX, GY ] = gradient( G );
GX = GX * 2 ./ sum( sum( abs( GX ) ) );
GY = GY * 2 ./ sum( sum( abs( GY ) ) );
function G = genGaussian( sigma )
if all( size( sigma ) == [ 1, 1 ] )
% isotropic gaussian
filterWindow = 4 * ceil( sigma ) + 1;
G = fspecial( 'gaussian', filterWindow, sigma );
else
% anisotropic gaussian
filterWindowX = 2 * ceil( sigma( 1 ) ) + 1;
filterWindowY = 2 * ceil( sigma( 2 ) ) + 1;
GaussianX = normpdf( -filterWindowX: filterWindowX, 0, sigma( 1 ) );
GaussianY = normpdf( -filterWindowY: filterWindowY, 0, sigma( 2 ) );
G = GaussianY' * GaussianX;
end
function SIFTFeatureVector = SIFTNormalization( SIFTFeatureVector )
% normalize SIFT descriptors (after Lowe)
% find indices of descriptors to be normalized (those whose norm is larger than 1)
tmp = sqrt( sum( SIFTFeatureVector.^2, 2 ) );
normalizeIndex = find( tmp > 1 );
SiftFeatureVectorNormed = SIFTFeatureVector( normalizeIndex, : );
SiftFeatureVectorNormed = SiftFeatureVectorNormed ./ repmat( tmp( normalizeIndex, : ), [ 1 size( SIFTFeatureVector, 2 ) ] );
% suppress large gradients
SiftFeatureVectorNormed( SiftFeatureVectorNormed > 0.2 ) = 0.2;
% finally, renormalize to unit length
tmp = sqrt( sum( SiftFeatureVectorNormed.^2, 2 ) );
SiftFeatureVectorNormed = SiftFeatureVectorNormed ./ repmat( tmp, [ 1 size( SIFTFeatureVector, 2 ) ] );
SIFTFeatureVector( normalizeIndex, : ) = SiftFeatureVectorNormed;






















 138
138

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








