和HDU2894一样,先求出一条回路,然后按照要求输出相应的边,
Ouroboros Snake
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 864 | Accepted: 410 |
Description
Ouroboros is a mythical snake from ancient Egypt. It has its tail in its mouth and continously devours itself.
The Ouroboros numbers are binary numbers of 2^n bits that have the property of "generating" the whole set of numbers from 0 to 2^n - 1. The generation works as follows: given an Ouroboros number, we place its 2^n bits wrapped in a circle. Then, we can take 2^n groups of n bits starting each time with the next bit in the circle. Such circles are called Ouroboros circles for the number n. We will work only with the smallest
Ouroboros number for each n.
Example: for n = 2, there are only four Ouroboros numbers. These are 0011;0110;1100; and 1001. In this case, the smallest one is 0011. Here is the Ouroboros circle for 0011:
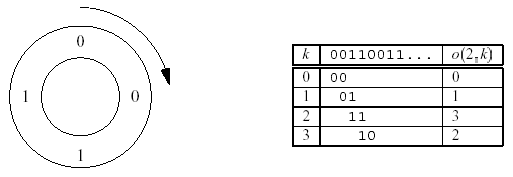
The table describes the function o(n;k) which calculates the k-th number in the Ouroboros circle of the smallest Ouroboros number of size n. This function is what your program should compute.
The Ouroboros numbers are binary numbers of 2^n bits that have the property of "generating" the whole set of numbers from 0 to 2^n - 1. The generation works as follows: given an Ouroboros number, we place its 2^n bits wrapped in a circle. Then, we can take 2^n groups of n bits starting each time with the next bit in the circle. Such circles are called Ouroboros circles for the number n. We will work only with the smallest
Ouroboros number for each n.
Example: for n = 2, there are only four Ouroboros numbers. These are 0011;0110;1100; and 1001. In this case, the smallest one is 0011. Here is the Ouroboros circle for 0011:

The table describes the function o(n;k) which calculates the k-th number in the Ouroboros circle of the smallest Ouroboros number of size n. This function is what your program should compute.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. For each test case, there will be a line containing two integers n and k (1<=n<=15; 0<=k<2^n). The end of the input file is indicated by a line containing two zeros. Don抰 process that line.
Output
For each test case, output o(n;k) on a line by itself.
Sample Input
2 0 2 1 2 2 2 3 0 0
Sample Output
0 1 3 2
//转动鼓轮模型
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 2<<16
struct node
{
int v,id,next;
}edge[MAXN];
int path[MAXN],top;
bool vis[MAXN];
int head[MAXN],en;
int n,k;
void add(int u,int v,int id)
{
edge[en].v=v;
edge[en].id=id;
edge[en].next=head[u];
head[u]=en++;
}
void dfs(int u)
{
for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=edge[i].next)
if(!vis[edge[i].id])
{
vis[edge[i].id]=1;
dfs(edge[i].v);
path[top++]=edge[i].id;
}
}
int main()
{
while(~scanf("%d%d",&n,&k))
{
if(n==0 && k==0)
break;
int cnt;
cnt=1<<n;
int len=1<<(n-1);
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)),en=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
int id=i<<1|1;
int v=id%len;
add(i,v,id);
id=i<<1;
v=id%len;
add(i,v,id);
//字典序最小
}
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)),top=0;
dfs(0);
top=top-k-1;
printf("%d\n",path[top]);
}
return 0;
}
























 463
463

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








