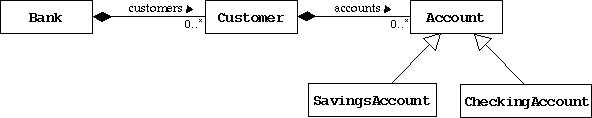
1.Use Collections to Represent Multiplicity
Objective
In this exercise you will replace the arrays code that you used to implement multiplicity in the relationships between bank and customer, and customer and their accounts.
Directions
This exercise is based on the exercise Create Your Own Exception.So copy all the previous Banking project files of that project, then make necessary modifications.
Modify the Bank Class
Modify the Bank class to use an ArrayList to implement the multiplicty on the customers association. Don't forget to import the necessary java.util classes.
- Modify the declaration for the customers attribute to be of type List and drop the numberOfCustomers attribute.
- Modify the Bank constructor to initialize the customers attribute to be a new ArrayList object.
- Modify the addCustomer method to use the add method.
- Modify the getCustomer method to use the get method.
- Modify the getNumOfCustomers method to use the size method.
Modify the Customer Class
Modify the Customer class to use an ArrayList to implement the multiplicty on the accounts association. Perform the same modifications as above.
Compile and Run the Main Program
You need to borrow the preset code of the Create Your Own Exception Project, make necessary modifications if needed. Compile and run the Main program and you should see the same output as before.
Optional: Modify the CustomerReport Class
Modify the CustomerReport class to use an ArrayList to implement the multiplicty on the accounts association. Perform the same modifications as above.
- In the Bank class, add a method called getCustomers that returns an Iterator on the customers list.
- In the Customer class, add a method called getAccounts that returns an Iterator on the accounts list.
- Modify the CustomerReport class to use a pair of nested while loops that iterate over the customer's iterator and the account's iterator; instead of using the nested forloops. You can also try to use the enhanced for loops.
import java.text.NumberFormat;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank bank = Bank.getBank();
Customer customer;
int curCustomer = 0;
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = s.nextInt();
s.nextLine();
while (t-- > 0) {
String f = s.next();
String l = s.next();
s.nextLine();
bank.addCustomer(f, l);
customer = bank.getCustomer(curCustomer++);
int numAccount = s.nextInt();
s.nextLine();
while (numAccount-- > 0) {
String[] type = s.nextLine().split(" ");
double balance;
double interesOrProtect;
if (type[0].trim().toUpperCase().equals("C")) {
balance = Double.parseDouble(type[1]);
if (type.length == 3) {
interesOrProtect = Double.parseDouble(type[2]);
customer.addAccount(new CheckingAccount(balance,
interesOrProtect));
} else {
customer.addAccount(new CheckingAccount(balance));
}
} else if (type[0].trim().toUpperCase().equals("S")) {
balance = Double.parseDouble(type[1]);
interesOrProtect = Double.parseDouble(type[2]);
customer.addAccount(new SavingsAccount(balance,
interesOrProtect));
}
}
}
int nOPs = s.nextInt();
s.nextLine();
while (nOPs-- > 0) {
String[] sOP = s.nextLine().split(" ");
char op = sOP[0].charAt(0);
int customerIndex = Integer.parseInt(sOP[1]);
int accountIndex = Integer.parseInt(sOP[2]);
double amount = Double.parseDouble(sOP[3]);
switch (op) {
case 'w':
case 'W':
customer = bank.getCustomer(customerIndex);
try{
customer.getAccount(accountIndex).withdraw(amount);
}
catch (OverdraftException ode){
System.out.println( customer + " withdraw " + amount + ", " + ode.getMessage() + ": " + ode.getDeficit());
}
break;
case 'd':
case 'D':
customer = bank.getCustomer(customerIndex);
customer.getAccount(accountIndex).deposit(amount);
break;
}
}
CustomerReport cr = new CustomerReport();
cr.generateReport();
}
}
class Account {
protected double balance;
public Account(double init_balance) {
this.balance = init_balance;
}
public String getBalance() {
return String.format("%.1f",balance);
}
public boolean deposit(double amt) {
balance = balance + amt;
return true;
}
public void withdraw(double amt) throws OverdraftException {
if (balance >= amt) {
balance = balance - amt;
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("Insufficient funds", amt - balance);
}
}
}
class Bank{
private static Bank bankInstance;
private Bank(){};
public static Bank getBank(){
if(bankInstance==null){
bankInstance = new Bank();
}
return bankInstance;
}
ArrayList<Customer> List=new ArrayList<>();
public void addCustomer(String s, String l) {
Customer customer = new Customer(s, l);
this.List.add(customer);
}
public int getNumOfCustomers() {
return List.size();
}
public Customer getCustomer(int index) {
return List.get(index);
}
}
class CheckingAccount extends Account {
private Double protectedBy;
public CheckingAccount(double balance) {
super(balance);
this.protectedBy = 0.0;
}
public CheckingAccount(double balance, Double protect) {
super(balance);
this.protectedBy = protect;
}
public void withdraw(double amt) throws OverdraftException {
if (balance >= amt) {
balance -= amt;
} else {
if (protectedBy > 0) {
if (balance + protectedBy >= amt) {
protectedBy -= (amt - balance);
balance = 0.0;
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("Insufficient funds", amt - balance - protectedBy);
}
} else {
throw new OverdraftException("No overdraft protection", amt - balance);
}
}
}
}
class Customer {
private int acct;
ArrayList<Account> list=new ArrayList<>();
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Customer(String f, String l) {
this.firstName = f;
this.lastName = l;
acct = 0;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void addAccount(Account n) {
list.add(n);
acct++;
}
public Account getAccount(int x) {
return list.get(x);
}
public int getNumOfAccounts() {
return acct;
}
public String toString() {
return "["+firstName + " " +lastName +"]";
}
}
class OverdraftException extends Exception{
private double deficit;
public double getDeficit(){
return this.deficit;
}
public OverdraftException(String message,double deficit){
super(message);
this.deficit=deficit;
}
}
class SavingsAccount extends Account {
private double interestRate;
public SavingsAccount(double balance, double interest_rate) {
super(balance);
this.interestRate = interest_rate;
}
}
class CustomerReport {
public void generateReport() {
NumberFormat currency_format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance();
Bank bank =Bank.getBank();
Customer customer;
System.out.println("CUSTOMERS REPORT");
System.out.println("================");
for ( int cust_idx = 0; cust_idx < bank.getNumOfCustomers(); cust_idx++ ) {
customer = bank.getCustomer(cust_idx);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Customer: "+"["
+ customer.getFirstName() +" "
+ customer.getLastName()+"]");
for ( int acct_idx = 0; acct_idx < customer.getNumOfAccounts(); acct_idx++ ) {
Account account = customer.getAccount(acct_idx);
String account_type = "";
if ( account instanceof SavingsAccount ) {
account_type = "Savings Account";
} else if ( account instanceof CheckingAccount ) {
account_type = "Checking Account";
} else {
account_type = "Unknown Account Type";
}
System.out.println(" " + account_type + ": current balance is "
+"$"+ account.getBalance());
}
}
}
}2.Sort Customers
Objective
This exercise is based on the previous exercise of Use Collections to Represent Multiplicity. you will sort the list of bank customers by their names. This will require you to have the Customer class implement the Comparable interface.
Directions
Start by copying all the previous project files into your working directory.
- Add the sortCustomers method to the Bank class.
- Modify the Customer class to implement the Comparable interface. You will need to specify the compareTo method. Make this method compare the two customers in a lexigraphical order with the last name taking precedence over the first name. For example, "Joe Smith" should come before "Samuel Smith".
- Modify the CustomerReport class to call the sortCustomers method before generating the report.
- Compile and run the Main program. You should see the expected result accordingly
import java.text.NumberFormat; import java.util.*; import java.util.List; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Bank bank = Bank.getBank(); Customer customer; int curCustomer = 0; Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int t = s.nextInt(); s.nextLine(); while (t-- > 0) { String f = s.next(); String l = s.next(); s.nextLine(); bank.addCustomer(f, l); customer = bank.getCustomer(curCustomer++); int numAccount = s.nextInt(); s.nextLine(); while (numAccount-- > 0) { String[] type = s.nextLine().split(" "); double balance; double interesOrProtect; if (type[0].trim().toUpperCase().equals("C")) { balance = Double.parseDouble(type[1]); if (type.length == 3) { interesOrProtect = Double.parseDouble(type[2]); customer.addAccount(new CheckingAccount(balance, interesOrProtect)); } else { customer.addAccount(new CheckingAccount(balance)); } } else if (type[0].trim().toUpperCase().equals("S")) { balance = Double.parseDouble(type[1]); interesOrProtect = Double.parseDouble(type[2]); customer.addAccount(new SavingsAccount(balance, interesOrProtect)); } } } int nOPs = s.nextInt(); s.nextLine(); while (nOPs-- > 0) { String[] sOP = s.nextLine().split(" "); char op = sOP[0].charAt(0); int customerIndex = Integer.parseInt(sOP[1]); int accountIndex = Integer.parseInt(sOP[2]); double amount = Double.parseDouble(sOP[3]); switch (op) { case 'w': case 'W': customer = bank.getCustomer(customerIndex); try{ customer.getAccount(accountIndex).withdraw(amount); } catch (OverdraftException ode){ System.out.println( customer + " withdraw " + amount + ", " + ode.getMessage() + ": " + ode.getDeficit()); } break; case 'd': case 'D': customer = bank.getCustomer(customerIndex); customer.getAccount(accountIndex).deposit(amount); break; } } CustomerReport cr = new CustomerReport(); cr.generateReport(); } } class Account { protected double balance; public Account(double init_balance) { this.balance = init_balance; } public String getBalance() { return String.format("%.1f",balance); } public boolean deposit(double amt) { balance = balance + amt; return true; } public void withdraw(double amt) throws OverdraftException { if (balance >= amt) { balance = balance - amt; } else { throw new OverdraftException("Insufficient funds", amt - balance); } } } class Bank{ private static Bank bankInstance; private Bank(){}; public List<Customer> sortCustomer(){ Collections.sort(this.list); return this.list; } public static Bank getBank(){ if(bankInstance==null){ bankInstance = new Bank(); } return bankInstance; } ArrayList<Customer> list=new ArrayList<>(); public void addCustomer(String s, String l) { Customer customer = new Customer(s, l); this.list.add(customer); } public int getNumOfCustomers() { return list.size(); } public Customer getCustomer(int index) { return list.get(index); } } class CheckingAccount extends Account { private Double protectedBy; public CheckingAccount(double balance) { super(balance); this.protectedBy = 0.0; } public CheckingAccount(double balance, Double protect) { super(balance); this.protectedBy = protect; } public void withdraw(double amt) throws OverdraftException { if (balance >= amt) { balance -= amt; } else { if (protectedBy > 0) { if (balance + protectedBy >= amt) { protectedBy -= (amt - balance); balance = 0.0; } else { throw new OverdraftException("Insufficient funds", amt - balance - protectedBy); } } else { throw new OverdraftException("No overdraft protection", amt - balance); } } } } class Customer implements Comparable<Customer> { private int acct; ArrayList<Account> list=new ArrayList<>(); private String firstName; private String lastName; public Customer(String f, String l) { this.firstName = f; this.lastName = l; acct = 0; } @Override public int compareTo(Customer o) { if(this.lastName.equals(o.getLastName())){ return this.firstName.compareTo(o.getFirstName()); } else{ return this.lastName.compareTo(o.getLastName()); } } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void addAccount(Account n) { list.add(n); acct++; } public Account getAccount(int x) { return list.get(x); } public int getNumOfAccounts() { return acct; } public String toString() { return "["+firstName + " " +lastName +"]"; } } class OverdraftException extends Exception{ private double deficit; public double getDeficit(){ return this.deficit; } public OverdraftException(String message,double deficit){ super(message); this.deficit=deficit; } } class SavingsAccount extends Account { private double interestRate; public SavingsAccount(double balance, double interest_rate) { super(balance); this.interestRate = interest_rate; } } class CustomerReport { public void generateReport() { NumberFormat currency_format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(); Bank bank =Bank.getBank(); Customer customer; System.out.println("CUSTOMERS REPORT"); System.out.println("================"); bank.sortCustomer(); for ( int cust_idx = 0; cust_idx < bank.getNumOfCustomers(); cust_idx++ ) { customer = bank.getCustomer(cust_idx); System.out.println(); System.out.println("Customer: "+"[" + customer.getFirstName() +" " + customer.getLastName()+"]"); for ( int acct_idx = 0; acct_idx < customer.getNumOfAccounts(); acct_idx++ ) { Account account = customer.getAccount(acct_idx); String account_type = ""; if ( account instanceof SavingsAccount ) { account_type = "Savings Account"; } else if ( account instanceof CheckingAccount ) { account_type = "Checking Account"; } else { account_type = "Unknown Account Type"; } System.out.println(" " + account_type + ": current balance is " + "$"+account.getBalance()); } } } }3.Sort Customers(alternate)
Objective
In this exercise you will sort the list of bank customers as you have done in the previous exercise. But this time you are required to sort the customers in various way: by their names, balance of their checking accounts or saving accounts. You need to create comparing classes implementing the Comparator interface and apply the comparation using the class instance.
Directions
Copy the previous Banking project files. Of course, the Customer class does not need to implment the Comparable interface this time.
- Add the sortCustomers method to the Bank class. This time, you need to pass a Comparator object as a parameter to the method so that it will sort the customers according to the comparator(). Hint, you may need to use the Collections.sort method to sort the list. Refer to JDK API documents please. Do not forget to pass the Type parameter when using the generics.
- Create your own NameComp, SavingComp and CheckingComp classes that implement the Comparator interface. You will need to specify the compare method. Make this method compare the two customers in a lexigraphical order with the last name taking precedence over the first name for the NameComp class. For example, "Joe Smith" should come before "Samuel Smith".
Do the similar thing with the SavingComp and CheckingComp classes as NameComp class.
- Modify the CustomerReport class to call the sortCustomers method before generating the report.
- Write your own Main program, sort the customers by Name, Savings and Ckecking, and generate report accordingly.
import java.text.NumberFormat; import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Bank bank = Bank.getBank(); Customer customer; int curCustomer = 0; Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in); int t = s.nextInt(); s.nextLine(); while (t-- > 0) { String f = s.next(); String l = s.next(); s.nextLine(); bank.addCustomer(f, l); customer = bank.getCustomer(curCustomer++); int numAccount = s.nextInt(); s.nextLine(); while (numAccount-- > 0) { String[] type = s.nextLine().split(" "); double balance; double interesOrProtect; if (type[0].trim().toUpperCase().equals("C")) { balance = Double.parseDouble(type[1]); if (type.length == 3) { interesOrProtect = Double.parseDouble(type[2]); customer.addAccount(new CheckingAccount(balance, interesOrProtect)); } else { customer.addAccount(new CheckingAccount(balance)); } } else if (type[0].trim().toUpperCase().equals("S")) { balance = Double.parseDouble(type[1]); interesOrProtect = Double.parseDouble(type[2]); customer.addAccount(new SavingsAccount(balance, interesOrProtect)); } } } int nOPs = s.nextInt(); s.nextLine(); while (nOPs-- > 0) { String[] sOP = s.nextLine().split(" "); char op = sOP[0].charAt(0); int customerIndex = Integer.parseInt(sOP[1]); int accountIndex = Integer.parseInt(sOP[2]); double amount = Double.parseDouble(sOP[3]); switch (op) { case 'w': case 'W': customer = bank.getCustomer(customerIndex); try{ customer.getAccount(accountIndex).withdraw(amount); } catch (OverdraftException ode){ System.out.println( customer + " withdraw " + amount + ", " + ode.getMessage() + ": " + ode.getDeficit()); } break; case 'd': case 'D': customer = bank.getCustomer(customerIndex); customer.getAccount(accountIndex).deposit(amount); break; } } CustomerReport cr = new CustomerReport(); cr.generateReport(); } } class OverdraftException extends Exception{ private Double deficit; public Double getDeficit(){ return deficit; } public OverdraftException(String message , Double defici){ super(message); deficit=defici; } } class Account{ protected double balance; public Double getBalance(){ return balance; } public boolean deposit( Double amt){ balance = balance + amt; return true; } public void withdraw( Double amt ) throws OverdraftException{ if (balance - amt >=0) balance =balance - amt; else { throw new OverdraftException("Insufficient funds", amt - balance) ; } } public Account(Double init_balance ){ balance = init_balance; } } class SavingsAccount extends Account{ private double interestRate ; public SavingsAccount ( Double balance , Double interest_rate){ super(balance); interest_rate = interestRate; } } class CheckingAccount extends Account{ private Double overdraftProtection; public CheckingAccount( Double balance ){ super(balance); } public CheckingAccount(Double balance, Double protect){ super(balance); this.overdraftProtection =protect; } public double getOverdraftProtection() { return overdraftProtection; } public void setOverdraftProtection(double overdraftProtection) { this.overdraftProtection = overdraftProtection; } public void withdraw(Double amt)throws OverdraftException{ if (amt <= balance){ balance -= amt; }else{ if (overdraftProtection ==null) { throw new OverdraftException("No overdraft protection", amt - balance) ; }else if (balance+overdraftProtection <= amt){ if(amt - balance - overdraftProtection!=0) {throw new OverdraftException("Insufficient funds", amt - balance - overdraftProtection) ;} else {balance = 0.0; } }else { overdraftProtection -= (amt -balance) ; balance = 0.0; } } } } class Customer { private String firstName; private String lastName; private SavingsAccount savingsAccount; private CheckingAccount checkingAccount; private List<Account> accounts; public Customer(String f, String l ){ firstName =f; lastName = l; accounts = new ArrayList<Account>(); } public String toString(){ return "["+firstName+" "+lastName+"]" ; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void addAccount( Account acct){ accounts.add(acct); } public int getNumOfAccounts(){ return accounts.size(); } public Account getAccount(int index) { return accounts.get(index); } } class CustomerReport { Bank bank = Bank.getBank() ; Customer customer ; public void generateReport(){ String[] str={"User Name","Savings Account Balance","Checking Account Balance"}; for(String a: str ){ bank.sortCustomers(a); NumberFormat currency_format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance() ; System.out.println("CUSTOMERS REPORT according to "+a+":"); System.out.println("============================================="); for (int cust_idx = 0 ; cust_idx < bank.getNumOfCustomers() ; cust_idx++){ customer = bank.getCustomer(cust_idx) ; System.out.println(); System.out.println("Customer: [" + customer.getFirstName() + " " + customer.getLastName()+"]"); for (int acct_idx = 0; acct_idx < customer.getNumOfAccounts(); acct_idx++){ Account account = customer.getAccount(acct_idx) ; String account_type = "" ; if (account instanceof SavingsAccount){ account_type = "Savings Account" ; } if (account instanceof CheckingAccount){ account_type = "Checking Account" ; } System.out.println(" "+account_type + ": current balance is $" + account.getBalance()); } } } } } class Bank { private List<Customer> customers; private static Bank bank= new Bank(); public static Bank getBank(){ return bank ; } public Bank() { customers = new ArrayList<Customer>(); } public void addCustomer(String f,String l) { Customer aa = new Customer(f,l); customers.add(aa); } public int getNumOfCustomers() { return customers.size(); } public Customer getCustomer(int index) { return customers.get(index); } public void sortCustomers( String message){ if(message.equals("User Name")){ Collections.sort(customers,new NameComp()); } else if(message.equals("Savings Account Balance")){ Collections.sort(customers,new SavingComp()); } else{ Collections.sort(customers,new CheckingComp()); } } } class NameComp implements Comparator<Customer>{ @Override public int compare(Customer o1,Customer o2){ int result = 0; result = o1.getLastName().compareTo(o2.getLastName()); if(result == 0){ result = o1.getFirstName().compareTo(o2.getFirstName()); } return result; } } class SavingComp implements Comparator<Customer>{ @Override public int compare(Customer o1, Customer o2) { double x = -1; double y = -1; for(int i=0; i<o1.getNumOfAccounts();i++){ if(o1.getAccount(i) instanceof SavingsAccount){ x = o1.getAccount(i).balance; } } for(int i=0;i<o2.getNumOfAccounts();i++){ if(o2.getAccount(i) instanceof SavingsAccount){ y = o2.getAccount(i).balance; } } if(x < y) return -1; else if(x > y) return 1; else return 0; } } class CheckingComp implements Comparator<Customer>{ public int compare(Customer o1, Customer o2) { double x = -1; double y = -1; for(int i=0; i<o1.getNumOfAccounts();i++){ if(o1.getAccount(i) instanceof CheckingAccount){ x = o1.getAccount(i).balance; } } for(int i=0;i<o2.getNumOfAccounts();i++){ if(o2.getAccount(i) instanceof CheckingAccount){ y = o2.getAccount(i).balance; } } if(x < y) return -1; else if(x > y) return 1; else return 0; } }4.The Collatz Sequence
成绩: 5 / 折扣: 0.8
The famous Collatz sequence is generated by a method decribed as follows. Given a positive integer N, if it is odd, then replace it with 3*N+1. For even number N, use N/2 instead. You can get a sequence of number by this method. It is conjectured that the algorithm above will terminate at 1 for any integral input value. Despite the simplicity of the algorithm, it is unknown whether this conjecture is true. It has been verified, however, for all integers n such that 0 < n < 1,000,000 (and, in fact, for many more numbers than this.)
Input
The first line contains a single integer T tells that there are T cases in the problem. Then for each case, there is an integers N.
Output
For each number N, output the sequence generated in a line, using coma as its separator.
Sample Input
2
22
33
Sample Output
22,11,34,17,52,26,13,40,20,10,5,16,8,4,2,1
33,100,50,25,76,38,19,58,29,88,44,22,11,34,17,52,26,13,40,20,10,5,16,8,4,2,1
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = s.nextInt();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
int a = s.nextInt();
while(a != 1){
System.out.print(a + ",");
if(a % 2 == 0) a = a/2;
else a = a*3 + 1;
}
System.out.println("1");
}
s.close();
}
}5.Collatz Sequence Again
As you have seen in the previous practice, the Collatz sequence is generated by a method decribed as follows. Given a positive integer N, if it is odd, then replace it with 3*N+1. For even number N, use N/2 instead. You can get a sequence of number by this method. It is conjectured that the algorithm above will terminate at 1 for any integral input value. Despite the simplicity of the algorithm, it is unknown whether this conjecture is true. It has been verified, however, for all integers n such that 0 < n < 1,000,000 (and, in fact, for many more numbers than this.)
Input
The first line contains a single integer T tells that there are T cases in the problem. Then for each case, there are two integers i and j.
Output
For each pair of input integers i and j you should output i, j, and the maximum sequence length for integers between and including i and j. These three numbers should be separated by at least one space with all three numbers on one line and with one line of output for each line of input. The integers i and j must appear in the output in the same order in which they appeared in the input and should be followed by the maximum cycle length (on the same line).
Sample Input
4
1 10
100 200
201 210
900 1000
Sample Output
1 10 20
100 200 125
201 210 89
900 1000 174
这个问题每一组数据都硬算的话会超时,所以可做一个数组记录前面几组数据已经算出来的结果,需要就去调用
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner s = new Scanner(System.in);
long n = s.nextInt();
int[] record = new int[1000000];
record[1] = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
long a = s.nextLong();
long b = s.nextLong();
int count = 0;
for(long j = Math.min(a,b); j < Math.max(a,b); j++){
long m = j;
int count2 = 0;
while(m > j || record[(int)m] == 0){
if(m % 2 == 0) m = m/2;
else m = m*3 + 1;
count2++;
}
count2 += record[(int)m];
record[(int)j] = count2;
if(count2 > count) count = count2;
}
System.out.println(a + " " + b + " " + count);
}
s.close();
}
}























 346
346











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










