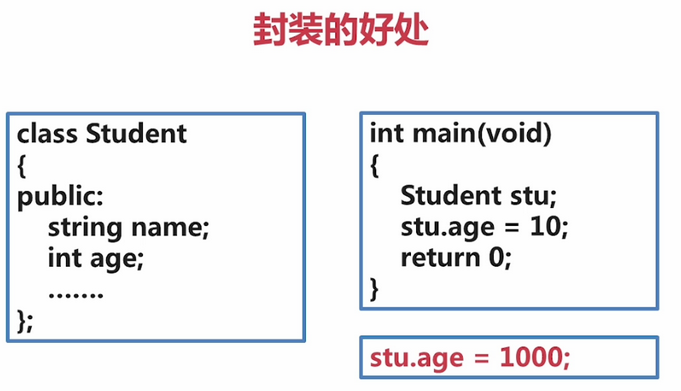
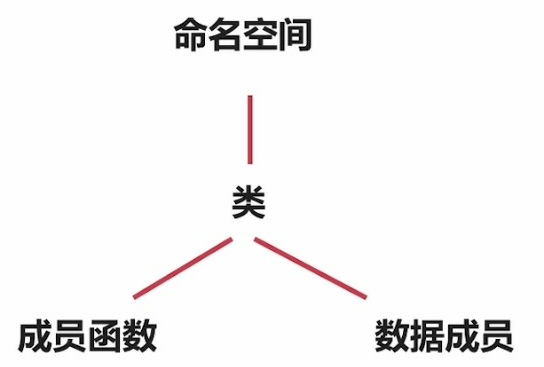
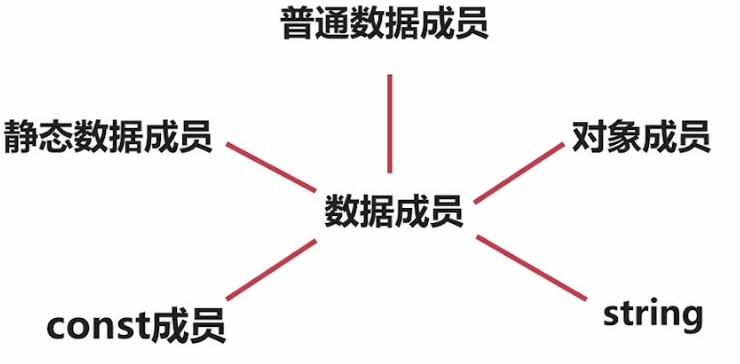
1.数据封装
数据封装可以保护和限定数据。比如stu.age = 1000, 年龄不可能为1000
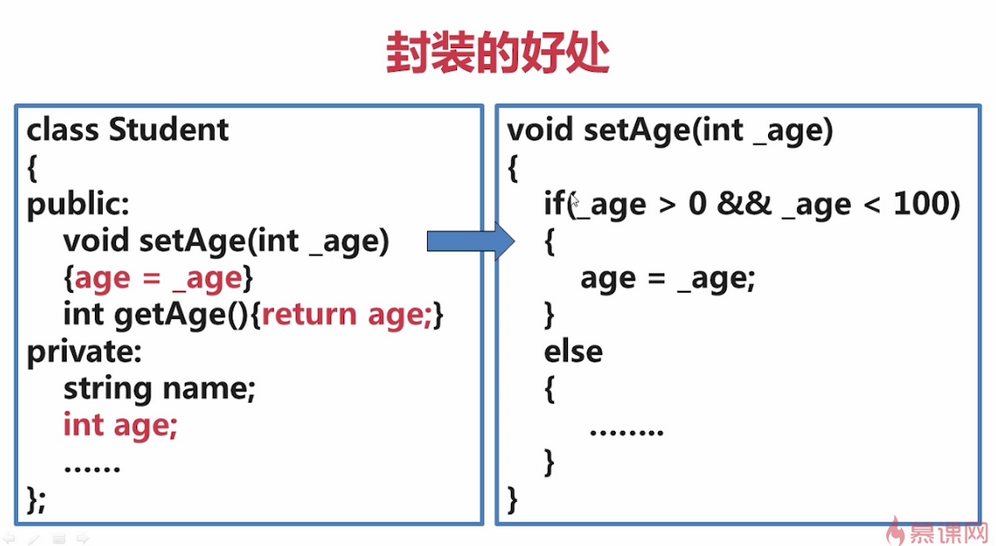
下图code可进行年龄限制。
********************************************************************
/*数据的封装
/*定义一Student类,包含
/*1.姓名:name
/*2.性别:gender
/*3.学分(只读):score
/*4.学习:study
/************************************************************
/*数据的封装
/*定义一Student类,包含
/*1.姓名:name
/*2.性别:gender
/*3.学分(只读):score
/*4.学习:study
****************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
void setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
void setGender(string _gender)
{
m_strGender = _gender;
}
string getGender()
{
return m_strGender;
}
void initScore()
{
m_iScore = 0;
/*
// m_iScore = 0;
若不初始化m_iScore则:
xiaoming , girl , -858993452
*/
}
void study(int _score)
{
m_iScore += _score;
}
int getScore()
{
return m_iScore;
}
private:
string m_strName;
string m_strGender;
int m_iScore;
};
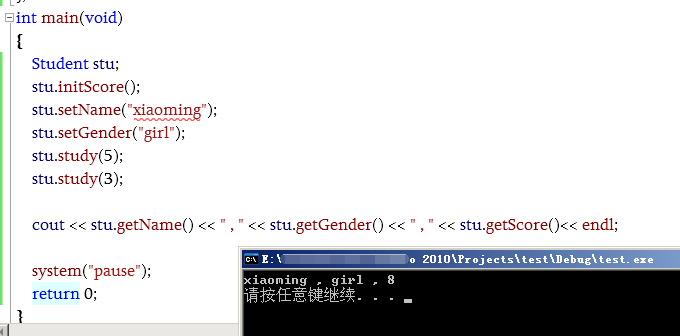
int main(void)
{
Student stu;
stu.initScore();
stu.setName("xiaoming");
stu.setGender("girl");
stu.study(5);
stu.study(3);
cout << stu.getName() << " , " << stu.getGender() << " , " << stu.getScore()<< endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
****************************************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
**************************************************************************************************
/************************************************************
定义一个Student类,包含名字一个数据成员,使用get和set函数封装名字这个数据成员。
在main函数中通过new实例化对象,并打印其相关函数。
----------------------------------
* 定义类:Student
* 数据成员:m_strName
* 数据成员的封装函数:setName()、getName()
****************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Student
{
public:
void setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
private:
string m_strName;
};
int main(void)
{
Student *stup = new Student();
stup->setName("michael");
cout << stup->getName() << endl;
delete stup;
stup = NULL;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

**************************************************************************************************
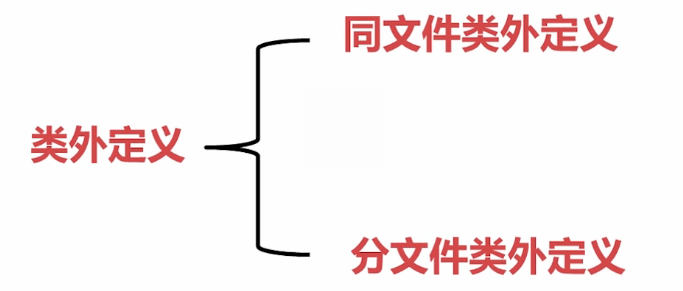
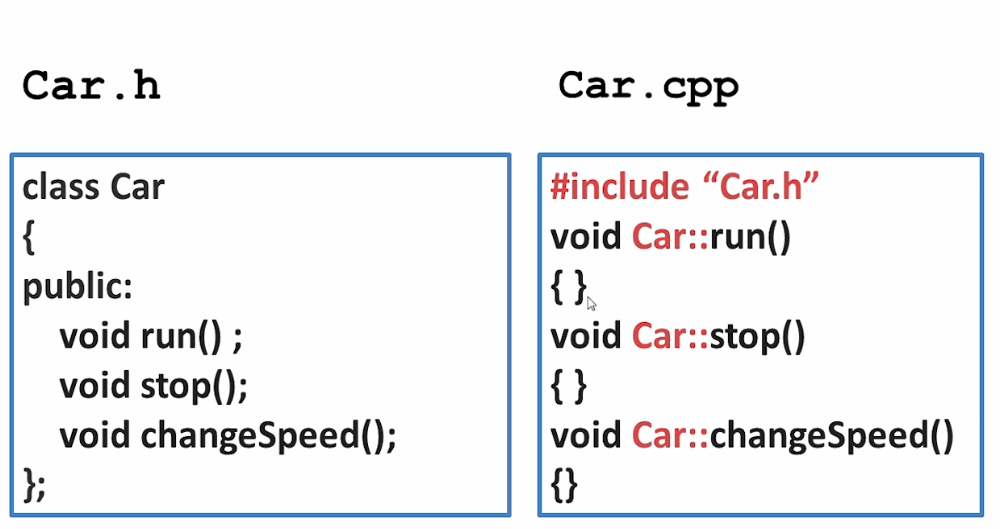
2.类外定义
**************************************************************************************************
同文件类外定义
**************************************************************************************************
分文件类外定义
**************************************************************************************************
Teacher类,同文件类外定义
/************************************************************
定义一个Teacher类,同文件类外定义和分文件类内定义
数据成员:
名字
年龄
性别
成员函数:
数据成员的封装函数
授课tech
****************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
void setName(string _name);
string getName();
void setGender(string _gender);
string getGender();
void setAge(int _age);
int getAge();
void teach();
private:
string m_strName;
string m_strGender;
int m_iAge;
};
void Teacher::setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
void Teacher::setGender(string _gender)
{
m_strGender = _gender;
}
string Teacher::getGender()
{
return m_strGender;
}
void Teacher::setAge(int _age)
{
m_iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::getAge()
{
return m_iAge;
}
void Teacher::teach()
{
cout << "上课......" << endl;
}
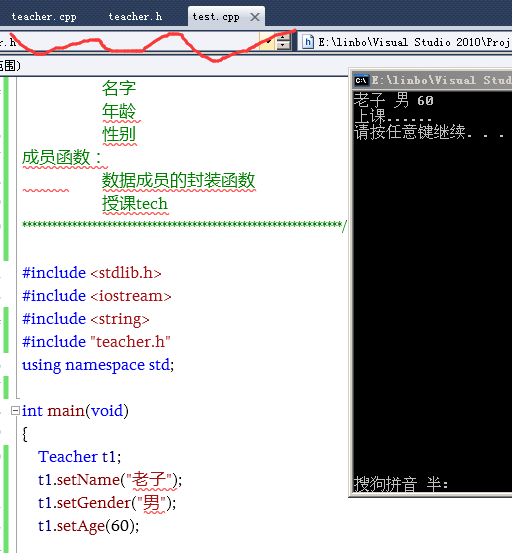
int main(void)
{
Teacher t1;
t1.setName("老子");
t1.setGender("男");
t1.setAge(60);
cout << t1.getName() << " " << t1.getGender() << " " << t1.getAge() << endl;
t1.teach();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
***********************************************************
Teacher类,分文件类外定义
teacher.h
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
void setName(string _name);
string getName();
void setGender(string _gender);
string getGender();
void setAge(int _age);
int getAge();
void teach();
private:
string m_strName;
string m_strGender;
int m_iAge;
};teacher.cpp
#include "teacher.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void Teacher::setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
void Teacher::setGender(string _gender)
{
m_strGender = _gender;
}
string Teacher::getGender()
{
return m_strGender;
}
void Teacher::setAge(int _age)
{
m_iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::getAge()
{
return m_iAge;
}
void Teacher::teach()
{
cout << "上课......" << endl;
}
test.cpp
/************************************************************
定义一个Teacher类,同文件类外定义和分文件类内定义
数据成员:
名字
年龄
性别
成员函数:
数据成员的封装函数
授课tech
****************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "teacher.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
Teacher t1;
t1.setName("老子");
t1.setGender("男");
t1.setAge(60);
cout << t1.getName() << " " << t1.getGender() << " " << t1.getAge() << endl;
t1.teach();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
********************************************************************
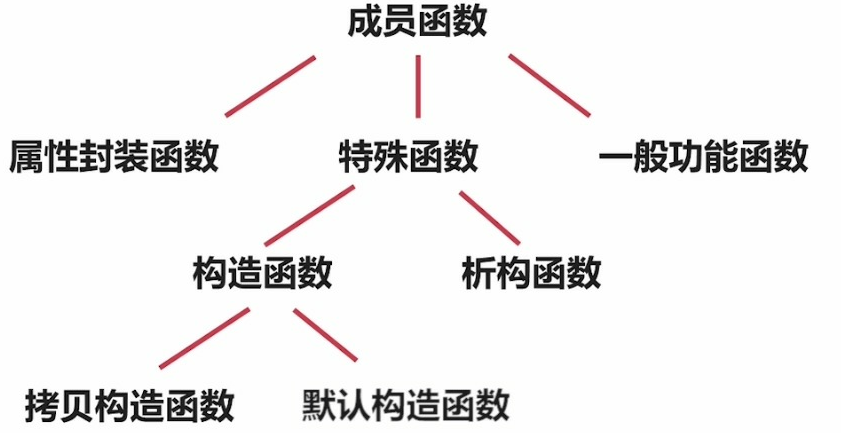
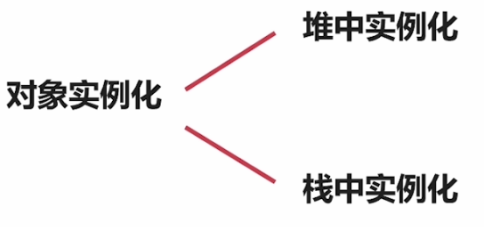
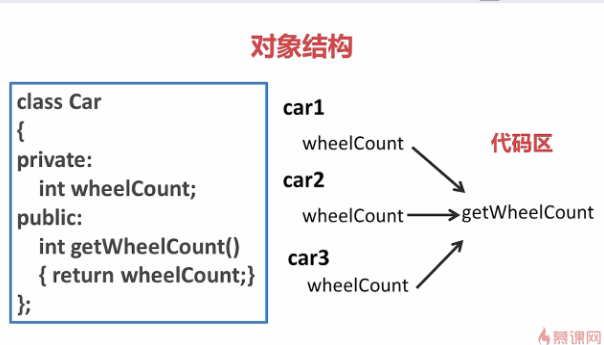
3.构造函数
举例说明,如下图。实例化了car1,car2,car3每个对象会在栈上开辟空间存储各自的数据。而逻辑代码只有一份。
对象初始化
讨论有且只有一次的
续
******************************************************************
****************************************************************
************************************************************
定义一个Teacher类
有参构造函数
无参构造函数
数据成员:
名字
年龄
成员函数:
数据成员的封装函数
************************************************************
teacher.h
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
Teacher();//无参构造函数
Teacher(string name, int age);//有参构造函数
void setName(string _name);
string getName();
void setGender(string _gender);
int getAge();
void setAge(int _age);
private:
string m_strName;
int m_iAge;
};
#include "teacher.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Teacher::Teacher()
{
m_strName = "jam";
m_iAge = 15;
cout << "Teacher()" << endl;
}
Teacher::Teacher(string name, int age)
{
m_strName = name;
m_iAge = age;
cout << "Teacher(string name, int age)" << endl;
}
void Teacher::setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
void Teacher::setAge(int _age)
{
m_iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::getAge()
{
return m_iAge;
}test.cpp
/************************************************************
定义一个Teacher类
有参构造函数
无参构造函数
数据成员:
名字
年龄
成员函数:
数据成员的封装函数
****************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "teacher.h"
using namespace std;
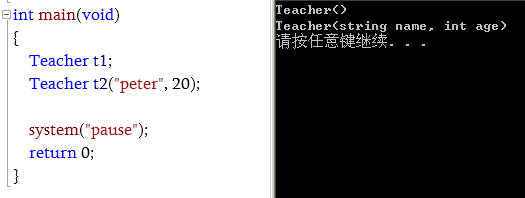
int main(void)
{
Teacher t1;
Teacher t2("peter", 20);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
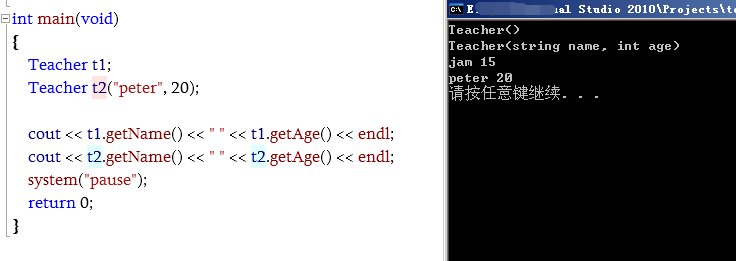
************************************************************int main(void)
{
Teacher t1;
Teacher t2("peter", 20);
cout << t1.getName() << " " << t1.getAge() << endl;
cout << t2.getName() << " " << t2.getAge() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
*****************************************************************************************
/******************************teacher.h*****************************/
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Teacher
{
public:
Teacher();//无参构造函数
Teacher(string name, int age = 9);//有参构造函数
void setName(string _name);
string getName();
void setGender(string _gender);
int getAge();
void setAge(int _age);
private:
string m_strName;
int m_iAge;
};
/******************************teacher.cpp*****************************/
#include "teacher.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Teacher::Teacher()
{
m_strName = "jam";
m_iAge = 15;
cout << "Teacher()" << endl;
}
Teacher::Teacher(string name, int age )
{
m_strName = name;
m_iAge = age;
cout << "Teacher(string name, int age)" << endl;
}
void Teacher::setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
void Teacher::setAge(int _age)
{
m_iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::getAge()
{
return m_iAge;
}
/******************************test.cpp*****************************/
/************************************************************
定义一个Teacher类
有参构造函数
无参构造函数
数据成员:
名字
年龄
成员函数:
数据成员的封装函数
****************************************************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "teacher.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
Teacher t1;
Teacher t2("peter", 20);
Teacher t3("jame");
cout << t1.getName() << " " << t1.getAge() << endl;
cout << t2.getName() << " " << t2.getAge() << endl;
cout << t3.getName() << " " << t3.getAge() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
******************************************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
构造函数初始化列表
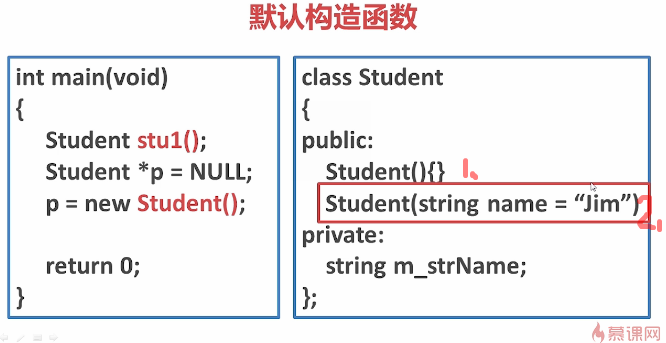
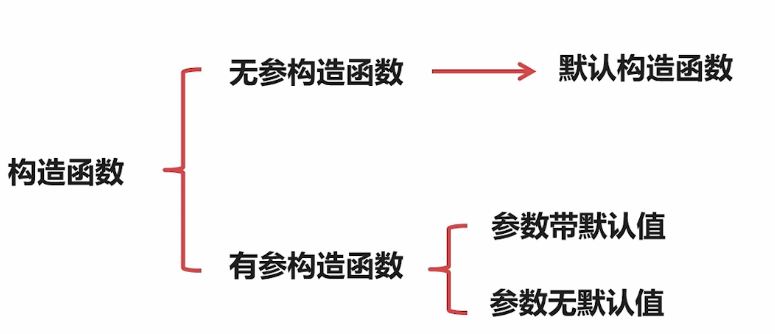
在实例化对象时不需要传递参数的构造函数称为默认构造函数。
如下图中的1,2都是默认构造函数
*****************************************************************************************
左边const修饰的会报error。右边通过初始化列表则ok
/************************teacher.h***************************/
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/******************************
Teacher 类
自定义有参默认构造函数
使用初始化列表初始化数据
数据
名字
年龄
成员函数
数据成员的封装
拓展
定义可以带最多学生的个数,此为常量
*******************************/
class Teacher
{
public:
Teacher(string name = "jam", int age = 6, int m = 100);//有参构造函数
void setName(string _name);
string getName();
int getAge();
void setAge(int _age);
int getMax();
private:
string m_strName;
int m_iAge;
const int m_iMax;
};
/************************teacher.cpp***************************/
#include "teacher.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
Teacher::Teacher(string name, int age, int max ):m_strName(name),m_iAge(age),m_iMax(max)
{
cout << "Teacher(string name, int age)" << endl;
}
void Teacher::setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
void Teacher::setAge(int _age)
{
m_iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::getAge()
{
return m_iAge;
}
int Teacher::getMax()
{
return m_iMax;
}
/************************test.cpp***************************/
/******************************
Teacher 类
自定义有参默认构造函数
使用初始化列表初始化数据
数据
名字
年龄
成员函数
数据成员的封装
拓展
定义可以带最多学生的个数,此为常量
*******************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "teacher.h"
using namespace std;
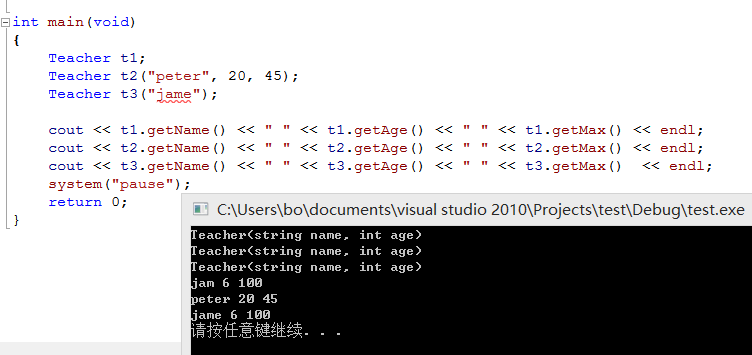
int main(void)
{
Teacher t1;
Teacher t2("peter", 20, 45);
Teacher t3("jame");
cout << t1.getName() << " " << t1.getAge() << " " << t1.getMax() << endl;
cout << t2.getName() << " " << t2.getAge() << " " << t2.getMax() << endl;
cout << t3.getName() << " " << t3.getAge() << " " << t3.getMax() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
拷贝构造函数
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
*****************************************************************************************
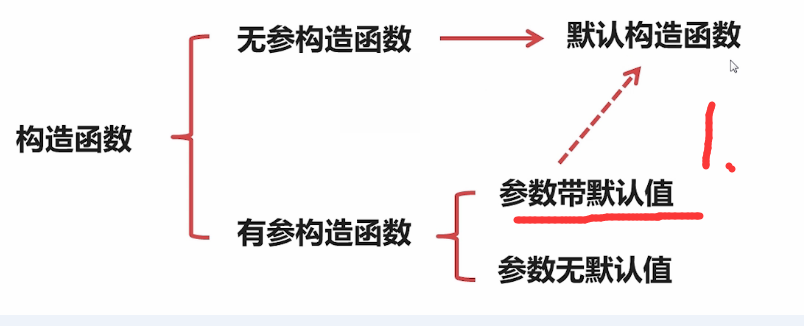
如果 所有参数都带有默认值,那么它就是一个默认构造函数。下图中1所示
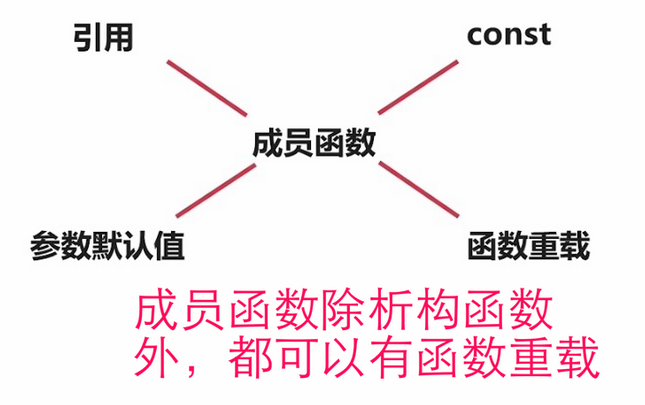
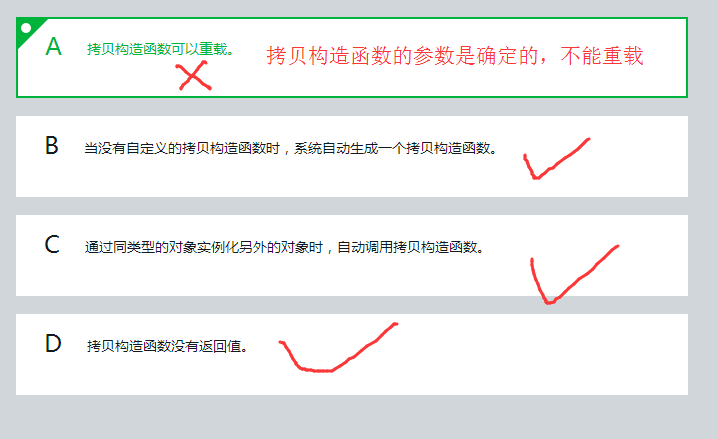
系统会自动生成一些函数,生产的函数包括默认的 “普通构造函数”,“拷贝构造函数”。如果我们自定义了 “普通构造函数”,“拷贝构造函数”。系统不会生产默认的 “普通构造函数”,“拷贝构造函数”。
*****************************************************************************************
拷贝构造函数代码code演示
拷贝构造函数 Teacher(constTeacher &tea) //变量tea可以写也可不写。
/************************teacher.h***************************/
#include <string>
using namespace std;
/******************************
Teacher 类
自定义有参默认构造函数
使用初始化列表初始化数据
数据
名字
年龄
成员函数
数据成员的封装
拓展
定义可以带最多学生的个数,此为常量
*******************************/
class Teacher
{
public:
Teacher(string name = "jam", int age = 6);//有参构造函数
Teacher(const Teacher &tea);//变量tea可以写也可不写。 拷贝构造函数
void setName(string _name);
string getName();
int getAge();
void setAge(int _age);
int getMax();
private:
string m_strName;
int m_iAge;
};
/************************teacher.cpp***************************/
#include "teacher.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//构造函数 和 : 初始化列表
Teacher::Teacher(string name, int age):m_strName(name),m_iAge(age)
{
cout << "Teacher(string name, int age)" << endl;
}
Teacher::Teacher(const Teacher&tea) //拷贝构造函数
{
cout << "Teacher(const Teacher&tea)" << endl;
}
void Teacher::setName(string _name)
{
m_strName = _name;
}
string Teacher::getName()
{
return m_strName;
}
void Teacher::setAge(int _age)
{
m_iAge = _age;
}
int Teacher::getAge()
{
return m_iAge;
}
/************************test.cpp***************************/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "teacher.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
Teacher t1;
Teacher t2 = t1;
Teacher t3(t1);
//cout << t1.getName() << " " << t1.getAge() << endl;
//cout << t2.getName() << " " << t2.getAge() << endl;
//cout << t3.getName() << " " << t3.getAge() << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
*****************************************************************************************
看以看到,t1是调用普通构造函数。t2,t3是调用拷贝构造函数
*****************************************************************************************
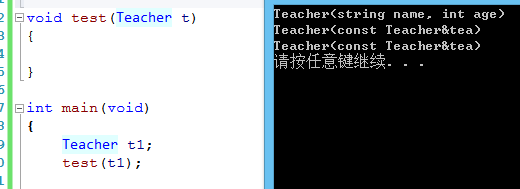
如果是一函数调用拷贝构造函数。
*****************************************************************************************

















































 1495
1495

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








