1.initializer_list是个好东西,但是把双刃剑,细节要吃透
test_initializer_list.h
#ifndef TEST_INITIALIZER_LIST_H_
#define TEST_INITIALIZER_LIST_H_
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
namespace test_initializer_list
{
class Wiget{
public:
Wiget(int i, int j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, int j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, double j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, double j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(std::initializer_list<std::string>){std::cout << "std::initializer_list<std::string>) is called.\n";}
Wiget(std::initializer_list<bool>){std::cout << "Wiget(std::initializer_list<bool>) is called.\n";}
};
auto myPrint(std::initializer_list<int>) -> void;
auto hybridTest() -> void;
// pass by value
void func0val(std::initializer_list<std::string> lis);
// pass by reference
void func0ref(std::initializer_list<std::string>& lis);
// pass by const reference
void func1(const std::initializer_list<std::string> &lis);
// pass by right val reference
void func2(std::initializer_list<std::string> &&lis);
auto valrefTest() -> void;
auto main() -> int;
}
#endif
test_initializer_list.cpp
#include "test_initializer_list.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <complex>
#include <algorithm> // std::max
namespace test_initializer_list
{
auto myPrint(std::initializer_list<int> il) -> void
{
for(auto it: il){
std::cout << it << ", ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
auto hybridTest() -> void
{
int arr[]{1,2,3,4,5};
for(auto it : arr)std::cout << it << ", ";std::cout << "sizeof arr is " << sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]) << std::endl;
std::vector<std::string> vec{"visual", "studio", "Ninja", "MinGW Makefiles", "Unix Makefiles"};
for(auto it : vec)std::cout << it << ", ";std::cout << std::endl;
std::initializer_list<int> il1{3,4,5,6,7,8,9};
std::initializer_list<int> il2({13,14,15,16,17,108});
for(auto it : il1)std::cout << it << ", ";std::cout << std::endl;
for(auto it : il2)std::cout << it << ", ";std::cout << std::endl;
std::initializer_list<int> il3;
std::cout << "sizeof il3: " << il3.size() << std::endl;
std::complex<double> cpx{42.0, 23.1};
std::cout << cpx.real() << "+" << cpx.imag() << "i" << std::endl;
std::vector<int> v1{1,2,3,45};
v1.insert(v1.begin()+2, {7,8,9});
for(auto it : v1) std::cout << it << ", "; std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << std::max({std::string("Ace"), std::string("Stacy"), std::string("Ball"), std::string("Turkey")}) << std::endl;
}
// pass by value
void func0val(std::initializer_list<std::string> lis){
std::cout << "func0val(): " << std::endl;
std::cout << "&lis = " << &lis << std::endl;
for(auto it = lis.begin(); it != lis.end(); ++it)
{
std::cout << *it << ", " << &(*it) << std::endl;
}
}
// pass by reference
void func0ref(std::initializer_list<std::string>& lis){
std::cout << "func0ref(): " << std::endl;
std::cout << "&lis = " << &lis << std::endl;
for(auto it = lis.begin(); it != lis.end(); ++it)
{
std::cout << *it << ", " << &(*it) << std::endl;
}
}
void func1(std::initializer_list<std::string> const& lis){
for(auto it = lis.begin(); it != lis.end(); ++it)
{
std::cout << *it << ", " << it << std::endl;
}
}
void func2(std::initializer_list<std::string> &&lis){
for(auto it = lis.begin(); it != lis.end(); ++it)
{
std::cout << *it << ", " << it << std::endl;
}
}
auto valrefTest() -> void
{
std::string s1("Hello");
std::string s2("Alice");
std::string s3("Hi");
std::string s4("CMake");
// std::cout << s1 << ", " << &s1 << std::endl;
// std::cout << s2 << ", " << &s2 << std::endl;
// std::cout << s3 << ", " << &s3 << std::endl;
// std::cout << s4 << ", " << &s4 << std::endl;
std::initializer_list<std::string> li{s1, s2, s3, s4};
for(auto it : li){ // range-based for,基于范围的for循环冒号“:”右侧必须是容器(提供begin/end方法)
std::cout << it << ", " << &it << std::endl;
/* 此处可能的输出:
Hello, 0x7ffd122ec840
Alice, 0x7ffd122ec840
Hi, 0x7ffd122ec840
CMake, 0x7ffd122ec840
对的,输出的四个地址相同,因为基于范围的for是把元素拷贝进it,
其实输出的都是it这个临时变量的地址,不是li的元素的地址
*/
}
std::cout << "+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++\n";
std::cout << "&li = " << &li << std::endl;
for(auto it = li.begin(); it != li.end(); ++it)
{
std::cout << *it << ", " << &(*it) << " vs " << it << std::endl;
/* 此处可能的输出:
Hello, 0x7ffd27680bf0
Alice, 0x7ffd27680c10
Hi, 0x7ffd27680c30
CMake, 0x7ffd27680c50
输出的是每个元素的地址
*/
}
func0val(li);
func0ref(li);
std::cout << "+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++\n";
std::cout << "A bunch of functions: " << std::endl;
func0val(li);
func0val({s1, s2, s3, s4}); // {s1, s2, s3, s4}会产生一个*没名字的*右值,右值的内容不可以被改动
func0ref(li);
// func0ref({s1, s2, s3, s4}); // [g++.exe (GCC) 11.2.0] error: cannot bind non-const lvalue reference of type 'std::initializer_list<std::__cxx11::basic_string<char> >&' to an rvalue of type 'std::initializer_list<std::__cxx11::basic_string<char> >'
func1(li);
func1({s1, s2, s3, s4});
// func2(li); // [g++.exe (GCC) 11.2.0] error: cannot bind rvalue reference of type 'std::initializer_list<std::__cxx11::basic_string<char> >&&' to lvalue of type 'std::initializer_list<std::__cxx11::basic_string<char> >'
func2({s1, s2, s3, s4});
std::cout << "*****************\n";
}
auto main() -> int
{
std::cout << "testing initializer_list..." << std::endl;
myPrint({-1, 1,2,3,90});
hybridTest();
valrefTest();
//Wiget awiget{1, 10.0}; // [ERROR & WARNING]编译器1."Visual Studio 15 2017 -A x64"的报错:
// error C2398: 元素“2”: 从“double”转换到“bool”需要收缩转换;
// warning C4305: “初始化”: 从“double”到“bool”截断
// [ERROR]编译器2. g++.exe (GCC) 11.2.0的报错:
// error: narrowing conversion of '1.0e+1' from 'double' to 'bool' [-Wnarrowing]
// [RIGHT]编译器3. g++ (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0可编译通过,可正常运行,运行结果为:Wiget(std::initializer_list<bool>) is called.
//Wiget bwiget{1, 10}; // [ERROR & WARNING]编译器1."Visual Studio 15 2017 -A x64"的报错[ERROR & WARNING]:
// error C2398: 元素“2”: 从“int”转换到“bool”需要收缩转换;
// warning C4305: “初始化”: 从“int”到“bool”截断
// [ERROR]编译器2. g++.exe (GCC) 11.2.0的报错:
// error: narrowing conversion of '1.0e+1' from 'double' to 'bool' [-Wnarrowing]
// [ERROR]编译器3. g++ (Ubuntu 7.5.0-3ubuntu1~18.04) 7.5.0的报错:
// error: narrowing conversion of ‘10’ from ‘int’ to ‘bool’ inside { } [-Wnarrowing]
Wiget cwiget{true, false}; // [RIGHT] Wiget(std::initializer_list<bool>) is called.
Wiget dwiget(1, 10.0); // [RIGHT] Wiget(int i, double j) is called.
Wiget ewiget(1, 10); // [RIGHT] Wiget(int i, int j) is called.
std::cout << "initializer_list test pass" << std::endl;
std::cout << "------------------------------" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
}
main.cpp
#include "test_initializer_list.h"
#include <iostream>
auto main() -> int
{
test_initializer_list::main();
}
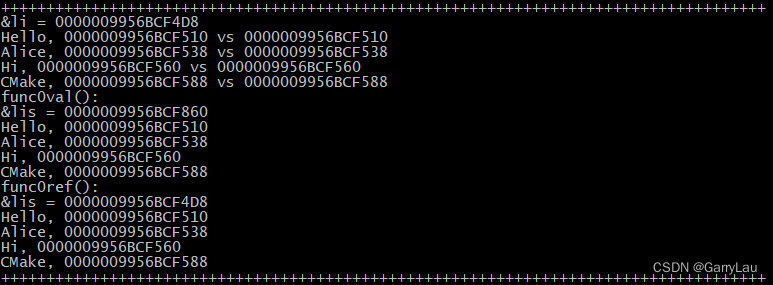
说到initializer_list偷别人的内存,参考上面两个std::cout << "+++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++++\n";之间的代码,该部分可能的输出是(每次运行地址是会变化的)。由于func0val()是pass by value因此func0val()内部的lis的地址和li不同,func0ref()是pass by reference因此func0ref()内部的lis的地址和li相同,这点没问题。但是li的内容即四个字符串的地址在func0val()和func0ref()中却是相同的,可见initializer_list自己是没有内存的,是使用入参(不管是传值还是引用)的内存。
initializer_list“偷”别人内存的原因可能跟它的实现有关,请看initializer_list的源代码。
从下面代码可知initializer_list只有两个成员iterator _M_array; size_type _M_len;,其中第一个是指针,第二个是元素个数。所以猜测第一个指针是指向”所偷“元素的首地址,而initializer_list自己是没有内存的。
附cxx-stl\gnu-libstdc++\4.9\include\initializer_list的源代码:
// std::initializer_list support -*- C++ -*-
// Copyright (C) 2008-2014 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
//
// This file is part of GCC.
//
// GCC is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
// it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
// the Free Software Foundation; either version 3, or (at your option)
// any later version.
//
// GCC is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU General Public License for more details.
//
// Under Section 7 of GPL version 3, you are granted additional
// permissions described in the GCC Runtime Library Exception, version
// 3.1, as published by the Free Software Foundation.
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License and
// a copy of the GCC Runtime Library Exception along with this program;
// see the files COPYING3 and COPYING.RUNTIME respectively. If not, see
// <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
/** @file initializer_list
* This is a Standard C++ Library header.
*/
#ifndef _INITIALIZER_LIST
#define _INITIALIZER_LIST
#pragma GCC system_header
#if __cplusplus < 201103L
# include <bits/c++0x_warning.h>
#else // C++0x
#pragma GCC visibility push(default)
#include <bits/c++config.h>
namespace std
{
/// initializer_list
template<class _E>
class initializer_list
{
public:
typedef _E value_type;
typedef const _E& reference;
typedef const _E& const_reference;
typedef size_t size_type;
typedef const _E* iterator;
typedef const _E* const_iterator;
private:
iterator _M_array;
size_type _M_len;
// The compiler can call a private constructor.
constexpr initializer_list(const_iterator __a, size_type __l)
: _M_array(__a), _M_len(__l) { }
public:
constexpr initializer_list() noexcept
: _M_array(0), _M_len(0) { }
// Number of elements.
constexpr size_type
size() const noexcept { return _M_len; }
// First element.
constexpr const_iterator
begin() const noexcept { return _M_array; }
// One past the last element.
constexpr const_iterator
end() const noexcept { return begin() + size(); }
};
/**
* @brief Return an iterator pointing to the first element of
* the initializer_list.
* @param __ils Initializer list.
*/
template<class _Tp>
constexpr const _Tp*
begin(initializer_list<_Tp> __ils) noexcept
{ return __ils.begin(); }
/**
* @brief Return an iterator pointing to one past the last element
* of the initializer_list.
* @param __ils Initializer list.
*/
template<class _Tp>
constexpr const _Tp*
end(initializer_list<_Tp> __ils) noexcept
{ return __ils.end(); }
}
#pragma GCC visibility pop
#endif // C++11
#endif // _INITIALIZER_LIST
2.narrowing conversion
示例1,不会默认执行double到int的转换:
namespace test_initializer_list2
{
class Wiget{
public:
Wiget(){std::cout << "Wiget default ctor is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, int j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, int j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, double j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, double j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(std::initializer_list<int>){std::cout << "Wiget(std::initializer_list<float>) is called.\n";}
};
auto main() -> void {
std::cout << "testing decltype..." << std::endl;
Wiget a{1, 10.0123456789}; // error: narrowing conversion of '1.0012345678899999e+1' from 'double' to 'int' [-Wnarrowing]
std::cout << "------------------------------" << std::endl;
}
}
示例2,不会默认执行double到bool的转换:
namespace test_initializer_list2
{
class Wiget{
public:
Wiget(){std::cout << "Wiget default ctor is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, int j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, int j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, double j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, double j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(std::initializer_list<bool>){std::cout << "std::initializer_list<bool>) is called.\n";}
};
auto main() -> void {
std::cout << "testing decltype..." << std::endl;
Wiget a{1, 10.0123456789}; // error: narrowing conversion of '1.0012345678899999e+1' from 'double' to 'bool' [-Wnarrowing]
std::cout << "------------------------------" << std::endl;
}
}
示例3,会默认执行double到float的转换:
namespace test_initializer_list2
{
class Wiget{
public:
Wiget(){std::cout << "Wiget default ctor is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, int j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, int j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, double j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, double j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(std::initializer_list<float>){std::cout << "std::initializer_list<float>) is called.\n";}
};
auto main() -> void {
std::cout << "testing decltype..." << std::endl;
Wiget a{1, 10.0123456789}; // right
std::cout << "------------------------------" << std::endl;
}
}
3. Item 7: Distinguish between () and {} when creating objects.
3.1 Empty() and Empty{}
#include <iostream>
namespace test_initializer_list2
{
class Wiget{
public:
Wiget(){std::cout << "Wiget default ctor is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, int j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, int j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(int i, double j){std::cout << "Wiget(int i, double j) is called.\n";}
Wiget(std::initializer_list<float>){std::cout << "std::initializer_list<float>) is called.\n";}
Wiget(const Wiget&){
std::cout << "Wiget copy ctor is called.\n";
}
operator float() const {
std::cout << "convert to float\n";
return 1.0;
}
};
auto main() -> void {
std::cout << "testing test_initializer_list2..." << std::endl;
Wiget a; // call Wiget()
// Wiget b(); // function declaration
Wiget c{}; // call Wiget()
Wiget d({}); // call Wiget(std::initializer_list<float>)
Wiget e{{}}; // call Wiget(std::initializer_list<float>)
std::cout << "===\n";
Wiget f(a); // call Wiget()
std::cout << "===\n";
Wiget g{a}; // call Wiget(std::initializer_list<float>)
std::cout << "------------------------------" << std::endl;
}
}
输出:
testing test_initializer_list2...
Wiget default ctor is called.
Wiget default ctor is called.
std::initializer_list<float>) is called.
std::initializer_list<float>) is called.
===
Wiget copy ctor is called.
===
convert to float
std::initializer_list<float>) is called.
------------------------------
3.2 Be Careful with vector、list、deque、forward_list
#include <iostream>
#include <utility> // std::forward
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <deque>
#include <forward_list>
namespace test_distinguish_parentheses_braces
{
template<typename T, // type of object to create
typename... Args> // types of arguments to use
void doSomeWorkParentheses(const T& obj, Args&&... args) {
T localObject(std::forward<Args>(args)...);
std::cout << "Parentheses, localObject size = " << localObject.size() << std::endl;
}
template<typename T, // type of object to create
typename... Args> // types of arguments to use
void doSomeWorkBraces(const T& obj, Args&&... args) {
T localObject{std::forward<Args>(args)...};
std::cout << "Braces, localObject size = " << localObject.size() << std::endl;
}
auto main() -> void {
std::cout << "testing test_distinguish_parentheses_braces..." << std::endl;
std::vector<int> vec;
std::list<int> lst;
std::deque<int> dq;
std::forward_list<int> flst;
doSomeWorkParentheses(vec, 10, 20);
doSomeWorkBraces(vec, 10, 20);
doSomeWorkParentheses(lst, 10, 20);
doSomeWorkBraces(lst, 10, 20);
doSomeWorkParentheses(dq, 10, 20);
doSomeWorkBraces(dq, 10, 20);
// std::forward_list<>无size()方法,可通过打印所有数据查看
// doSomeWorkParentheses(flst, 10, 20);
// doSomeWorkBraces(flst, 10, 20);
std::cout << "------------------------------" << std::endl;
}
}
输出结果:
testing test_distinguish_parentheses_braces...
Parentheses, localObject size = 10
Braces, localObject size = 2
Parentheses, localObject size = 10
Braces, localObject size = 2
Parentheses, localObject size = 10
Braces, localObject size = 2
------------------------------
3.3 初始化的三种方式{}()=
#include <iostream>
#include <atomic>
namespace test_distinguish_parentheses_braces
{
/* 2.可以使用{}、=,但不能使用()的情形 */
class Widget {
private:
int x{0}; // fine, x's default value is 0
int y = 0; // also fine
// int z(0); // error: expected identifier before numeric constant; error: expected ',' or '...' before numeric constant
};
auto main() -> void {
std::cout << "testing test_distinguish_parentheses_braces..." << std::endl;
/* 1.可以使用{}()=,初始化的三种方式 */
int x(0); // initializer is in parentheses
int y = 0; // initializer follows "="
int z{0}; // initializer is in braces, equals int z = {0};
/* 3.可以使用{}、(),但不能使用=的情形, but it depends */
std::atomic<int> ai{0};
std::atomic<int> bi(0);
//std::atomic<int> ci = 0; // 跟编译器、C++标准有关系
// MinGW Makefiles, 自C++17以来的标准可编译通过
// Visual Studio 15 2017自C++11以来的标准都可编译通过
// MinGW Makefiles,C++14的报错是: error: use of deleted function 'std::atomic<int>::atomic(const std::atomic<int>&)'
std::cout << "------------------------------" << std::endl;
}
}
注:*Effective Modern C++*的Item7, P51有以下描述:
A novel feature of braced initialization is that it prohibits implicit narrowing conver‐sions among built-in types. If the value of an expression in a braced initializer isn’t guaranteed to be expressible by the type of the object being initialized, the code won’t compile.
但实际编译器只会报Warnning,不是Error(也许跟编译器有关):
double a = 1.0, b = 2.0, c = 3.0;
int sum1{a + b + c}; // warning: narrowing conversion of '((a + b) + c)' from 'double' to 'int' [-Wnarrowing]
int sum2(a + b + c);
int sum3 = a + b + c;
Reference
[1]. Scott Meyers. Effective Modern C++. O’Reilly, November 2014: First Edition.






















 1755
1755











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








