Phase correlation
In image processing, phase correlation is a method of image registration,
and uses a fast frequency-domain approach to estimate
the relativetranslative offset between two similar images.
Contents[hide] |
Example[edit]
The following image demonstrates the usage of phase correlation to determine relative translative movement
between two images corrupted by independent Gaussian noise. The image was translated by (30,33) pixels.
Accordingly, one can clearly see a peak in the phase-correlation representation at approximately (30,33).
Method[edit]
Given two input images 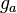 and
and 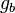 :
:
Apply a window function (e.g., a Hamming window) on both images to reduce edge effects.
Then, calculate the discrete 2D Fourier transform of both images.
Calculate the cross-power spectrum by taking the complex conjugate of the second result,
multiplying the Fourier transforms together elementwise, and normalizing this product elementwise.
Where  is the Hadamard product (entry-wise product).
is the Hadamard product (entry-wise product).
Obtain the normalized cross-correlation by applying the inverse Fourier transform.
Determine the location of the peak in  .
.
-
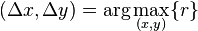
-
- 通常,非整数点峰值位置的值利用插值法来估计。
Commonly, interpolation methods are used to estimate the peak location to non-integer values,
despite the fact that the data are discrete.
Because the Fourier representation of the data has already been computed,
it is especially convenient to use the Fourier shift theorem with real-valued shifts for this purpose.
It is also possible to infer the peak location from phase characteristics in Fourier space
without the inverse transformation, as noted by Stone [1]
Rationale[edit]
The method is based on the Fourier shift theorem.
Let the two images 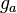 and
and 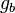 be circularly-shifted versions of each other:
be circularly-shifted versions of each other:
(where the images are  in size).
in size).
Then, the discrete Fourier transforms of the images will be shifted relatively in phase:
One can then calculate the normalized cross-power spectrum to factor out the phase difference:
-
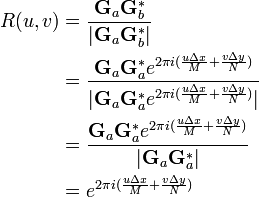
-
虚指数的幅度通常为1,
 的相位通常为0。
的相位通常为0。
since the magnitude of an imaginary exponential always is one, and the phase of  always is zero.
always is zero.
The inverse Fourier transform of a complex exponential is a Kronecker delta, i.e. a single peak:
This result could have been obtained by calculating the cross correlation directly.
The advantage of this method is
that the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse can be performed using the fast Fourier transform,
which is much faster than correlation for large images.
Benefits[edit]
Unlike many spatial-domain algorithms, the phase correlation method is resilient to noise, occlusions,
and other defects typical of medical or satellite images.[citation needed]
首先对图像进行对数极坐标变换,可以将该方法扩展到旋转和尺度变换。
The method can be extended to determine rotation and scaling differences between two images
by first converting the images to log-polar coordinates. Due to properties of the Fourier transform,
the rotation and scaling parameters can be determined in a manner invariant to translation.[2][3]
Limitations[edit]
In practice, it is more likely that 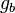 will be a simple linear shift of
will be a simple linear shift of 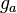 ,
,
rather than a circular shift as required by the explanation above.
In such cases,  will not be a simple delta function, which will reduce the performance of the method.
will not be a simple delta function, which will reduce the performance of the method.
In such cases, a window function (such as a Gaussian or Tukey window)
should be employed during the Fourier transform to reduce edge effects,
or the images should be zero padded so that the edge effects can be ignored.
If the images consist of a flat background, with all detail situated away from the edges,
then a linear shift will be equivalent to a circular shift,
and the above derivation will hold exactly. The peak can be sharpened by using edge or vector correlation. [4]
For periodic images (such as a chessboard), phase correlation may yield ambiguous results
with several peaks in the resulting output.
Applications[edit]
Phase correlation is the preferred method for television standards conversion,
as it leaves the fewest artifacts.
References[edit]
- ^ Harold S. Stone, "A Fast Direct Fourier-Based Algorithm for Subpixel Registration of Images", IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, V. 39, No. 10, Oct. 2001, pp.2235-2242.
- ^ E. De Castro and C. Morandi "Registration of Translated and Rotated Images Using Finite Fourier Transforms", IEEE Transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, Sept. 1987
- ^ B. S Reddy and B. N. Chatterji, “An FFT-based technique for translation, rotation, and scale-invariant image registration”, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 5, no. 8 (1996): 1266–1271.
- ^ http://www.jprr.org/index.php/jprr/article/viewFile/355/148









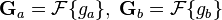


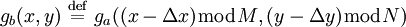
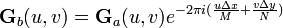

















 338
338

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








