System.Timers.Timer是多线程定时器,如果一个Timer没有处理完成,到达下一个时间点,新的Timer同样会被启动,所以在使用Timer时需要注意。
下面的实例显示了Timer的使用方法。
using System;
using System.Threading;
using System.Windows;
namespace TimerExp
{
public partial class MainWindow : Window
{
System.Timers.Timer timer;
public MainWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
if (timer == null)
{
timer = new System.Timers.Timer();
timer.Interval = 1000;
timer.Elapsed += timer_Elapsed;
}
}
void timer_Elapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
Thread.Sleep(3000);
string currentThreadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString();
this.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(new Action(() =>
{
this.Label_Result.Content += currentThreadId + ",";
}), null);
}
private void Button_Click_1(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
timer.Start();
}
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
下图是实例的运行结果。
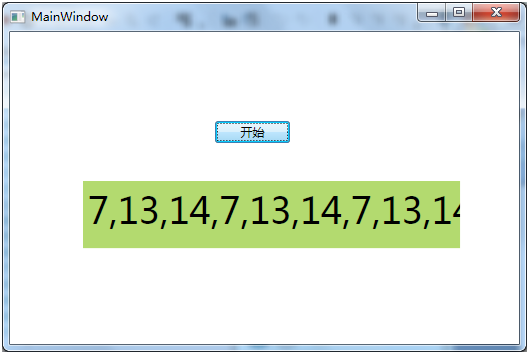
图中文本框显示的是运行定时器的当前线程ID。你会发现定时器会在不同的线程中运行。若将timer_Elapsed方法中让CPU休息3秒的代码去掉,你会发现这时定时器会在同一个线程中运行,为什么会这样呢?这是因为,实例中的Timer会每隔一秒钟执行一次timer_Elapsed方法,当前一次运行还没离开timer_Elapsed方法时,Timer便会在新的线程中运行timer_Elapsed方法,若前次运行已经离开timer_Elapsed方法,便会在同一个线程中继续运行timer_Elapsed方法。所以,Timer比较适合执行不太耗时的小任务,若在Timer中运行耗时任务,很容易出现由于超时导致的多线程重入问题,即多个线程同时进入timer_Elapsed方法。
为了应对多线程重入问题。可以加锁,也可以增加标志位。
下面的代码给出使用标志位的解决方案。
int inTimer = 0
void timer_Elapsed(object sender, System.Timers.ElapsedEventArgs e)
{
if (Interlocked.Exchange(ref inTimer, 1) == 0)
{
Thread.Sleep(3000)
string currentThreadId = Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString()
this.Dispatcher.BeginInvoke(new Action(() =>
{
this.Label_Result.Content += currentThreadId + ","
}), null)
Interlocked.Exchange(ref inTimer, 0)
}
}
若使用”inTimer = 0”给变量inTimer直接赋值,在多线程环境中,同样有问题。Interlocked.Exchange提供了一种轻量级的线程安全的给对象赋值的方法,所以使用Interlocked.Exchange给变量赋值。
























 3706
3706

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










