计算建模是HIT大三秋季计院计算机科学方向的专业核心课,内容cover了随机过程、优化、信号处理等topic
这里是笔者对课余参考的一些补充材料的collection,主要是一些概念
个人向的意思是,本文不对内容的严谨性与正确性负责
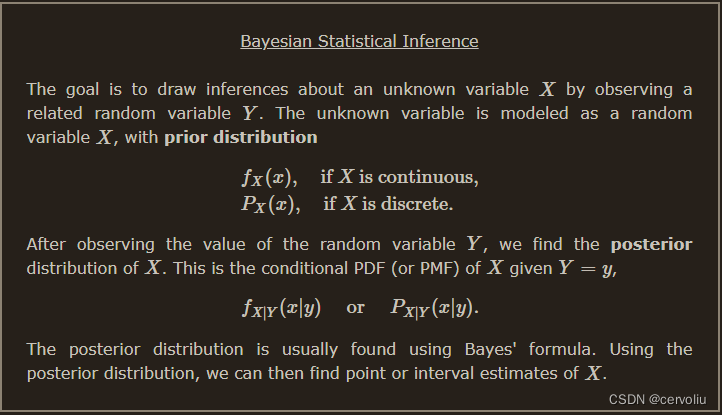
Bayesian Inference
MLE & MAP : 略



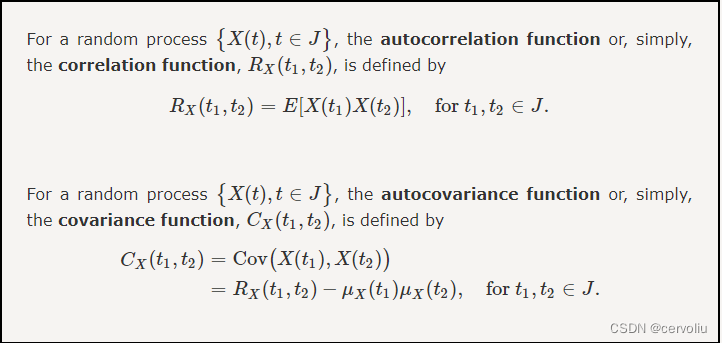
Stochastic Processes
A random process(stochastic process) is a collection of random variables usually indexed by time.
A random process is a random function of time.




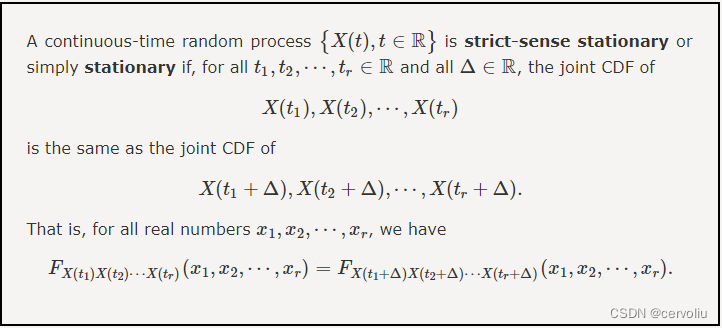
Stationary

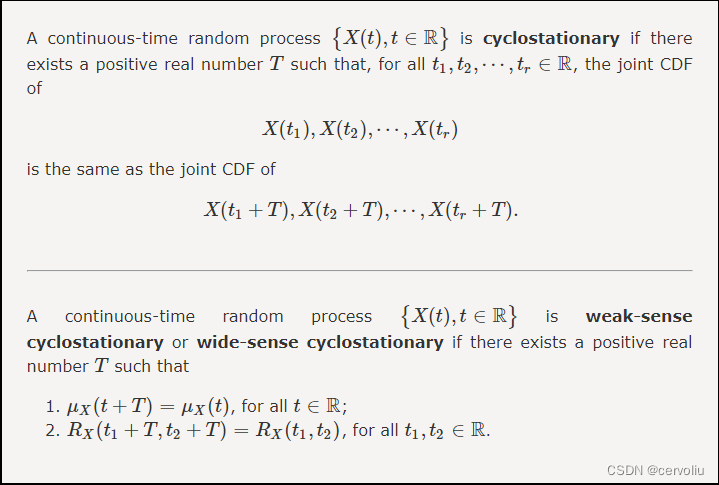
Similar definitions (Strict-sense stationary / WSS) apply for discrete-time random process.
WSS is more commonly observed and used.

Gaussian Process

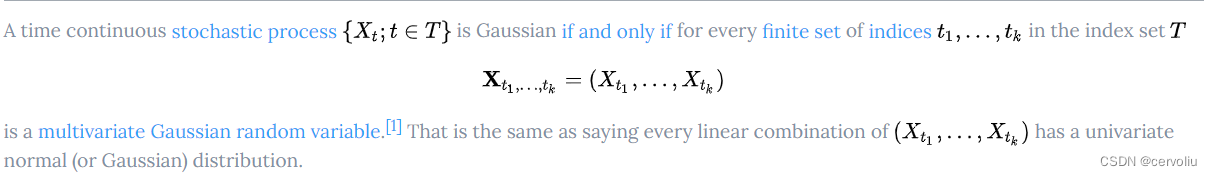
Gaussian processes can be seen as an infinite-dimensional generalization of multivariate normal distributions.
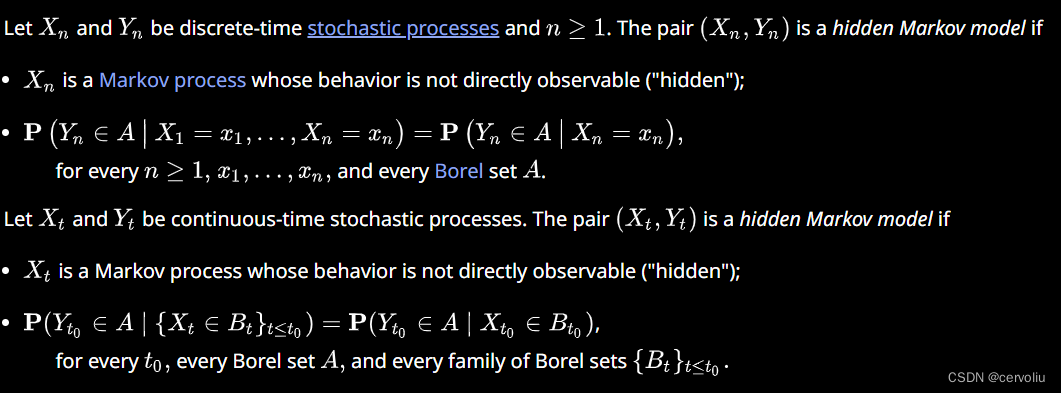
HMM
Definition
Probabilities Calculation
- given model M = ( A , B , π ) M=(A,B,\pi) M=(A,B,π) (where A A A is the transition matrix, B B B is the emission matrix, π \pi π is the initial value vector) and observation sequence Y Y Y
forward & backward DP:
- α t ( i ) = P ( Y 1 , Y 2 , … , Y t , X t = q i ∣ M ) \alpha_t(i)=P(Y_1,Y_2,\dots,Y_t,X_t=q_i | M) αt(i)=P(Y1,Y2,…,Yt,Xt=qi∣M)
- β t ( i ) = P ( Y t , Y t + 1 , … , Y T ∣ X t = q i , M ) \beta_t(i)=P(Y_t, Y_{t+1}, \dots, Y_T | X_t=q_i, M) βt(i)=P(Yt,Yt+1,…,YT∣Xt=qi,M)
Model Learning
- EM algorithm
Decoding
- Viterbi algorithm (DP)
Random Simulation
假设已有一个均匀分布的随机数,如何由它得到任意连续分布的随机数?
设我们想要的服从某种特定连续分布的随机数为
X
X
X,它的CDF为
P
X
(
x
)
=
P
[
X
≤
x
]
P_{X}(x)=P[X\leq x]
PX(x)=P[X≤x]
令
U
=
P
X
(
X
)
U=P_{X}(X)
U=PX(X),可以证明
U
U
U服从
[
0
,
1
]
[0,1]
[0,1]上的均匀分布
考虑
P
[
U
≤
y
]
=
P
[
P
X
(
X
)
≤
y
]
P[U\leq y]=P[P_{X}(X)\leq y]
P[U≤y]=P[PX(X)≤y]
设
P
[
P
X
(
x
0
)
=
y
]
P[P_{X}(x_{0})= y]
P[PX(x0)=y],由
P
X
P_{X}
PX的单调性知,
P
[
P
X
(
X
)
≤
y
]
=
P
[
X
≤
x
0
]
=
P
X
(
x
0
)
=
y
P[P_{X}(X)\leq y]=P[X\leq x_0]=P_{X}(x_0)=y
P[PX(X)≤y]=P[X≤x0]=PX(x0)=y
即
P
[
U
≤
y
]
=
y
P[U\leq y]=y
P[U≤y]=y,即
U
∼
U
[
0
,
1
]
U\sim U[0,1]
U∼U[0,1]
那么只需要把
U
=
P
X
(
X
)
U=P_{X}(X)
U=PX(X)取反函数即可得到
X
=
P
X
−
1
(
U
)
X=P_{X}^{-1}(U)
X=PX−1(U)
Reference
Introduction to Probabilities, Statistics and Random Processes
Wikipedia






















 3038
3038











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








