总结
本系列是机器学习课程的系列课程,主要介绍基于python实现神经网络。
参考
本门课程的目标
完成一个特定行业的算法应用全过程:
懂业务+会选择合适的算法+数据处理+算法训练+算法调优+算法融合
+算法评估+持续调优+工程化接口实现
机器学习定义
关于机器学习的定义,Tom Michael Mitchell的这段话被广泛引用:
对于某类任务T和性能度量P,如果一个计算机程序在T上其性能P随着经验E而自我完善,那么我们称这个计算机程序从经验E中学习。
从零构建神经网络
手写数据集MNIST介绍
mnist_dataset
MNIST数据集是一个包含大量手写数字的集合。 在图像处理领域中,它是一个非常受欢迎的数据集。 经常被用于评估机器学习算法的性能。 MNIST是改进的标准与技术研究所数据库的简称。 MNIST 包含了一个由 70,000 个 28 x 28 的手写数字图像组成的集合,涵盖了从0到9的数字。
本文通过神经网络基于MNIST数据集进行手写识别。
代码读取数据集MNIST
导入库
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot
读取mnist_train_100.csv
# open the CSV file and read its contents into a list
data_file = open("mnist_dataset/mnist_train_100.csv", 'r')
data_list = data_file.readlines()
data_file.close()
查看数据集的长度
# check the number of data records (examples)
len(data_list)
# 输出为 100
查看一条数据,这个数据是手写数字的像素值
# show a dataset record
# the first number is the label, the rest are pixel colour values (greyscale 0-255)
data_list[1]
输出为:

需要注意的是,这个字符串的第一个字为真实label,比如
data_list[50]
输出为:
这个输出看不懂,因为这是一个很长的字符串,我们对其进行按照逗号进行分割,然后输出为28*28的,就能看出来了
# take the data from a record, rearrange it into a 28*28 array and plot it as an image
all_values = data_list[50].split(',')
num=0
for i in all_values[1:]:
num = num +1
print("%-3s"%(i),end=' ')
if num==28:
num = 0
print('',end='\n')
输出为:
通过用图片的方式查看
# take the data from a record, rearrange it into a 28*28 array and plot it as an image
all_values = data_list[50].split(',')
image_array = numpy.asfarray(all_values[1:]).reshape((28,28))
matplotlib.pyplot.imshow(image_array, cmap='Greys', interpolation='None')
输出为:
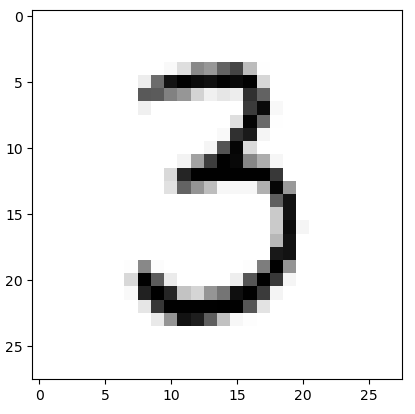
这个像素值为0-255,对其进行归一化操作
# scale input to range 0.01 to 1.00
scaled_input = (numpy.asfarray(all_values[1:]) / 255.0 * 0.99) + 0.01
# print(scaled_input)
scaled_input
输出为:
构建一个包含十个输出的标签
#output nodes is 10 (example)
onodes = 10
targets = numpy.zeros(onodes) + 0.01
targets[int(all_values[0])] = 0.99
# print(targets)
targets
输出为:

神经网络实现
导入库
import numpy
# scipy.special for the sigmoid function expit()
import scipy.special
# library for plotting arrays
import matplotlib.pyplot
神经网络实现
# neural network class definition
# 神经网络类定义
class neuralNetwork:
# initialise the neural network
# 初始化神经网络
def __init__(self, inputnodes, hiddennodes, outputnodes, learningrate):
# set number of nodes in each input, hidden, output layer
# 设置每个输入、隐藏、输出层的节点数
self.inodes = inputnodes
self.hnodes = hiddennodes
self.onodes = outputnodes
# link weight matrices, wih and who
# weights inside the arrays are w_i_j, where link is from node i to node j in the next layer
# w11 w21
# w12 w22 etc
# 链接权重矩阵,wih和who
# 数组内的权重w_i_j,链接从节点i到下一层的节点j
# w11 w21
# w12 w22 等等
self.wih = numpy.random.normal(0.0, pow(self.inodes, -0.5), (self.hnodes, self.inodes))
self.who = numpy.random.normal(0.0, pow(self.hnodes, -0.5), (self.onodes, self.hnodes))
# learning rate 学习率
self.lr = learningrate
# activation function is the sigmoid function
# 激活函数是sigmoid函数
self.activation_function = lambda x: scipy.special.expit(x)
pass
# train the neural network
# 训练神经网络
def train(self, inputs_list, targets_list):
# convert inputs list to 2d array
# 将输入列表转换为2d数组
inputs = numpy.array(inputs_list, ndmin=2).T
targets = numpy.array(targets_list, ndmin=2).T
# calculate signals into hidden layer
# 计算输入到隐藏层的信号
hidden_inputs = numpy.dot(self.wih, inputs)
# calculate the signals emerging from hidden layer
# 计算从隐藏层输出的信号
hidden_outputs = self.activation_function(hidden_inputs)
# calculate signals into final output layer
# 计算最终输出层的信号
final_inputs = numpy.dot(self.who, hidden_outputs)
# calculate the signals emerging from final output layer
# 计算从最终输出层输出的信号
final_outputs = self.activation_function(final_inputs)
# output layer error is the (target - actual)
# 输出层误差是(目标 - 实际)
output_errors = targets - final_outputs
# hidden layer error is the output_errors, split by weights, recombined at hidden nodes
# 隐藏层误差是输出层误差,按权重分解,在隐藏节点重新组合
hidden_errors = numpy.dot(self.who.T, output_errors)
# update the weights for the links between the hidden and output layers
# 更新隐藏层和输出层之间的权重
self.who += self.lr * numpy.dot((output_errors * final_outputs * (1.0 - final_outputs)), numpy.transpose(hidden_outputs))
# update the weights for the links between the input and hidden layers
# 更新输入层和隐藏层之间的权重
self.wih += self.lr * numpy.dot((hidden_errors * hidden_outputs * (1.0 - hidden_outputs)), numpy.transpose(inputs))
pass
# query the neural network
# 查询神经网络
def query(self, inputs_list):
# convert inputs list to 2d array
# 将输入列表转换为2d数组
inputs = numpy.array(inputs_list, ndmin=2).T
# calculate signals into hidden layer
# 计算输入到隐藏层的信号
hidden_inputs = numpy.dot(self.wih, inputs)
# calculate the signals emerging from hidden layer
# 计算从隐藏层输出的信号
hidden_outputs = self.activation_function(hidden_inputs)
# calculate signals into final output layer
# 计算最终输出层的信号
final_inputs = numpy.dot(self.who, hidden_outputs)
# calculate the signals emerging from final output layer
# 计算从最终输出层输出的信号
final_outputs = self.activation_function(final_inputs)
return final_outputs
定义参数,并初始化神经网络
# number of input, hidden and output nodes
input_nodes = 784
hidden_nodes = 200
output_nodes = 10
# learning rate
learning_rate = 0.1
# create instance of neural network
n = neuralNetwork(input_nodes,hidden_nodes,output_nodes, learning_rate)
n # <__main__.neuralNetwork at 0x2778590e5e0>
查看数据集
# load the mnist training data CSV file into a list
training_data_file = open("mnist_dataset/mnist_train.csv", 'r')
training_data_list = training_data_file.readlines()
training_data_file.close()
len(training_data_list) # 60001
# 其中第1行为列名 ,后面需要去掉,只保留后60000条
开始训练,该步骤需要等待一会,才能训练完成
# train the neural network
# 训练神经网络
# epochs is the number of times the training data set is used for training
# epochs次数,循环训练5次
epochs = 5
for e in range(epochs):
# go through all records in the training data set
# 每次取60000条数据,剔除列名
for record in training_data_list[1:]:
# split the record by the ',' commas
# 用逗号分割
all_values = record.split(',')
# scale and shift the inputs
# 对图像的像素值进行归一化操作
inputs = (numpy.asfarray(all_values[1:]) / 255.0 * 0.99) + 0.01
# create the target output values (all 0.01, except the desired label which is 0.99)
# 创建一个包含十个输出的向量,初始值为0.01
targets = numpy.zeros(output_nodes) + 0.01
# all_values[0] is the target label for this record
# 对 label的 位置设置为0.99
targets[int(all_values[0])] = 0.99
# 开始训练
n.train(inputs, targets)
pass
pass
查看训练后的权重
n.who.shape # (10, 200)
n.who
输出为:

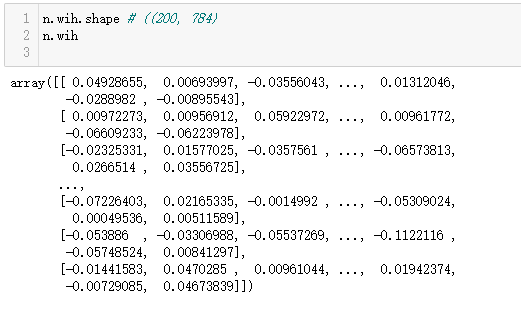
n.wih.shape # ((200, 784)
n.wih
输出为:
查看测试集
# load the mnist test data CSV file into a list
test_data_file = open("mnist_dataset/mnist_test.csv", 'r')
test_data_list = test_data_file.readlines()
test_data_file.close()
len(test_data_list) # 10001
# 其中第1行为列名 ,后面需要去掉,只保留后10000条
预测测试集
# test the neural network
# 测试网络
# scorecard for how well the network performs, initially empty
# 计算网络性能,初始为空
scorecard = []
# go through all the records in the test data set
# 传入所有的测试集
for record in test_data_list[1:]:
# split the record by the ',' commas
# 使用逗号分割
all_values = record.split(',')
# correct answer is first value
# 获取当前的测试集的label
correct_label = int(all_values[0])
# scale and shift the inputs
# 归一化操作
inputs = (numpy.asfarray(all_values[1:]) / 255.0 * 0.99) + 0.01
# query the network
# 对测试集进行预测
outputs = n.query(inputs)
# the index of the highest value corresponds to the label
# 获取输出中最大的概率的位置
label = numpy.argmax(outputs)
# append correct or incorrect to list
# 按照预测的正确与否分别填入1和0
if (label == correct_label):
# network's answer matches correct answer, add 1 to scorecard
# 答案匹配正确,输入1
scorecard.append(1)
else:
# network's answer doesn't match correct answer, add 0 to scorecard
# 答案不匹配,输入0
scorecard.append(0)
pass
pass
计算网络性能
# calculate the performance score, the fraction of correct answers
scorecard_array = numpy.asarray(scorecard)
print ("performance = ", scorecard_array.sum() / scorecard_array.size)
# performance = 0.9725
输出为:
performance = 0.9725
基于神经网络实现鸢尾花数据集
# 使用sklearn分割数据
#导入数据集模块
from sklearn import datasets
#分别加载iris和digits数据集
iris_dataset = datasets.load_iris() #鸢尾花数据集
print(iris_dataset.keys())
# dict_keys(['data', 'target', 'frame', 'target_names', 'DESCR', 'feature_names', 'filename', 'data_module'])
iris_dataset.data[0]
# array([5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2])
#output nodes is 10 (example)
onodes = 3
targets = numpy.zeros(onodes) + 0.01
targets
targets[int(iris_dataset.target[0])] = 0.99
# print(targets)
targets
# 0.99 0.01 0.01
# number of input, hidden and output nodes
input_nodes = 4
hidden_nodes = 20
output_nodes = 3
# learning rate
learning_rate = 0.1
# create instance of neural network
n = neuralNetwork(input_nodes,hidden_nodes,output_nodes, learning_rate)
n # <__main__.neuralNetwork at 0x2778590e5e0>
# 鸢尾花分类
# 3.2 1.67 0.8 0.54 0
# train the neural network
# 训练神经网络
# epochs is the number of times the training data set is used for training
# epochs次数,循环训练5次
epochs = 100
for e in range(epochs):
# go through all records in the training data set
# 每次取60000条数据,剔除列名
print("\n epochs------->",e)
num = 0
data_list = len(iris_dataset.data[:])
nc = 0
for record,label in zip(iris_dataset.data[:],iris_dataset.target[:]):
# split the record by the ',' commas
# 用逗号分割
# scale and shift the inputs
# 对图像的像素值进行归一化操作
inputs = numpy.asfarray(record)
# create the target output values (all 0.01, except the desired label which is 0.99)
# 创建一个包含十个输出的向量,初始值为0.01
targets = numpy.zeros(output_nodes) + 0.01
# all_values[0] is the target label for this record
# 对 label的 位置设置为0.99
targets[int(label)] = 0.99
# 开始训练
n.train(inputs, targets)
num +=1
nc = nc+1
if num %10==0:
print("\r epochs {} 当前进度为 {}".format(e,num/data_list),end="")
pass
pass
inputs= numpy.asfarray([5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2])
outputs = n.query(inputs)
# the index of the highest value corresponds to the label
# 获取输出中最大的概率的位置
label = numpy.argmax(outputs)
label






















 806
806











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










