1.需求
将学生成绩,按照各个成绩降序排序,各个科目成绩单独输出。
# 自定义partition 将下面数据分区处理:
人名 科目 成绩
张三 语文 10
李四 数学 30
王五 语文 20
赵6 英语 40
张三 数据 50
李四 语文 10
张三 英语 70
李四 英语 80
王五 英语 45
王五 数学 10
赵6 数学 10
赵6 语文 100
2.思路分析
# 自定义分区
1. 编写自定义分区类,继承Partitioner覆盖getPartition方法 注意:分区号从0开始算。
2. 给job注册分区类 【覆盖默认分区】 job.setPartitionerClass(自定义Partitioner.class); 3. 设置ReduceTask个数(开启分区) job.setNumReduceTasks(数字);//reduceTask数量要和分区数量一样。
3.Idea代码
DefinePartitionJob
package demo7;
import demo5.DescIntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
import java.io.IOException;
public class DefinePartitionJob {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("fs.defaultFS","hdfs://hadoop10:8020");
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(DefinePartitionJob.class);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
TextInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path("/mapreduce/demo10"));
TextOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,new Path("/mapreduce/demo10/out"));
job.setMapperClass(DefinePartitonMapper.class);
job.setReducerClass(DefinePartitonReducer.class);
//map输出的键与值类型
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(DescIntWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Subject.class);
//reducer输出的键与值类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Subject.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(DescIntWritable.class);
//设置reduceTask的个数
job.setNumReduceTasks(4);
//设置自定义分区
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartition.class);
boolean b = job.waitForCompletion(true);
System.out.println(b);
}
static class DefinePartitonMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, DescIntWritable,Subject> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] arr = value.toString().split("\t");
context.write(new DescIntWritable(Integer.parseInt(arr[2])),new Subject(arr[0],arr[1]));
}
}
static class DefinePartitonReducer extends Reducer<DescIntWritable,Subject,Subject,DescIntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(DescIntWritable key, Iterable<Subject> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Subject subject : values) {
context.write(subject, key);
}
}
}}
MyPartition
package demo7;
import demo5.DescIntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class MyPartition extends Partitioner<DescIntWritable,Subject> {
@Override
public int getPartition(DescIntWritable key, Subject value, int numPartitions) {
if ("语文".equals(value.getKemu())){
return 0;
}else if ("数学".equals(value.getKemu())) {
return 1;
}else if ("英语".equals(value.getKemu())) {
return 2;
}
return 3;
}
}
Subject
package demo7;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Subject implements Writable{
private String name;
private String kemu;
public Subject() {
}
public Subject(String name, String kemu) {
this.name = name;
this.kemu = kemu;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getKemu() {
return kemu;
}
public void setKemu(String kemu) {
this.kemu = kemu;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(name);
out.writeUTF(kemu);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.name = in.readUTF();
this.kemu = in.readUTF();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + " " +kemu;
}
}

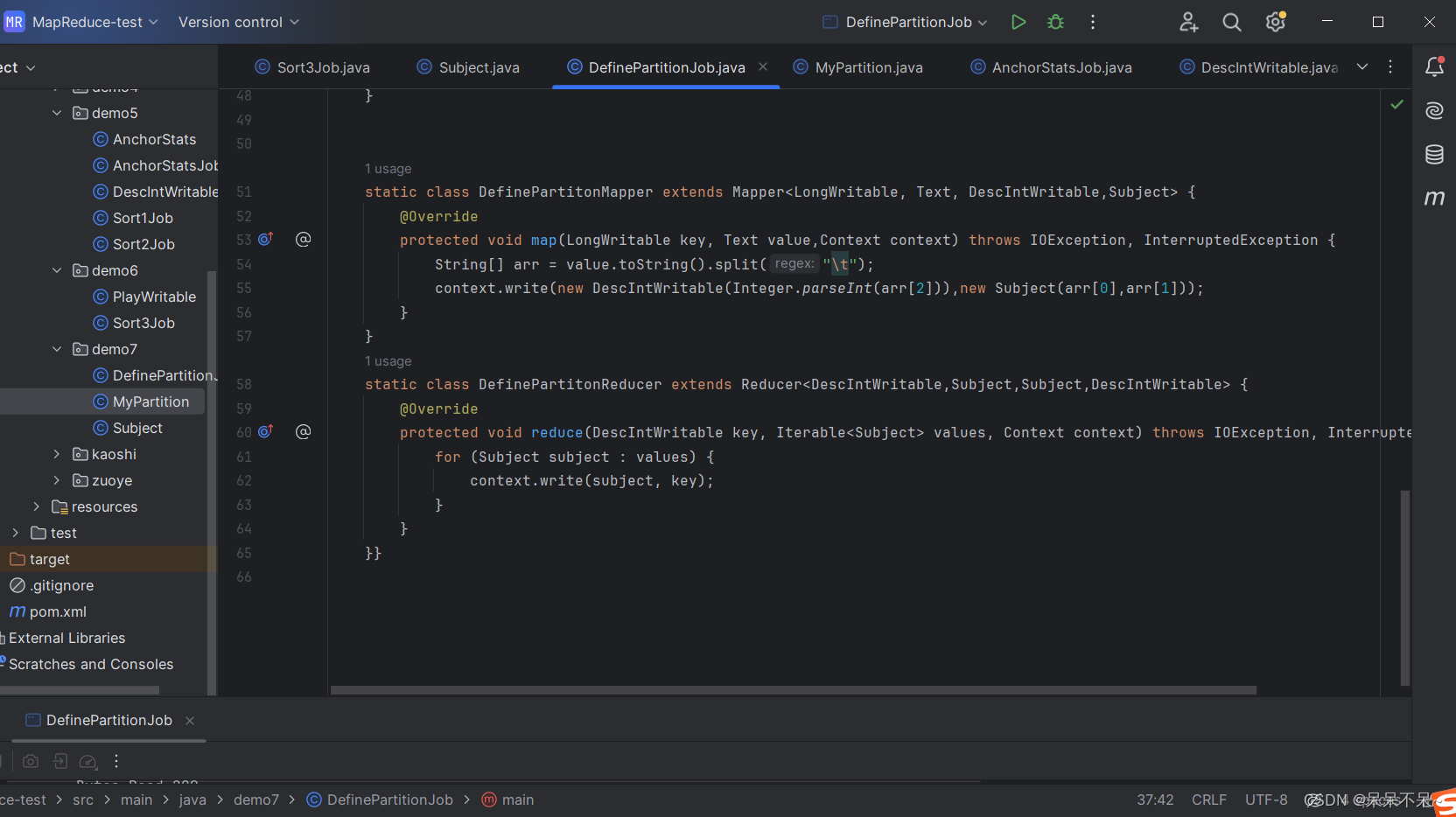

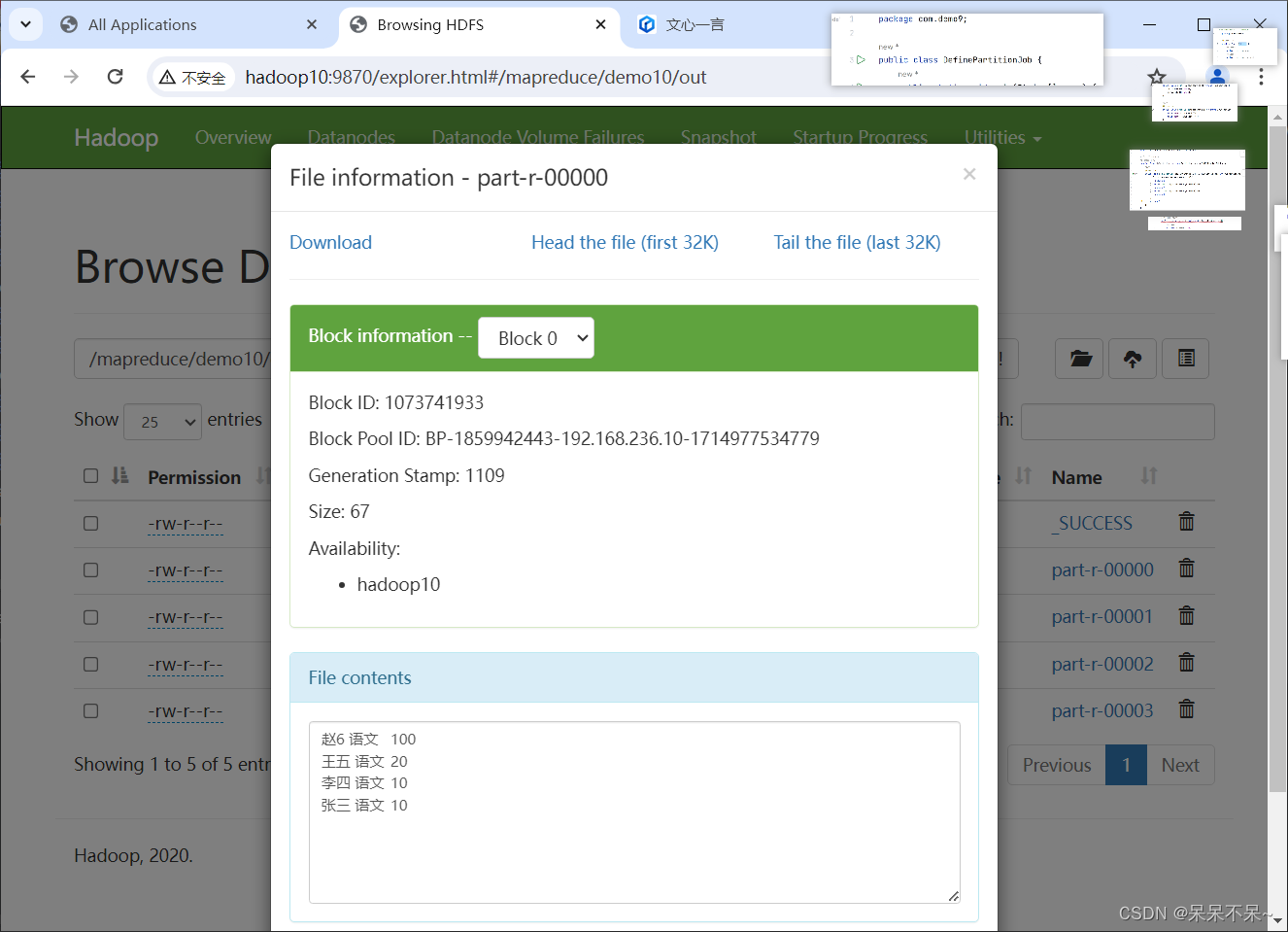
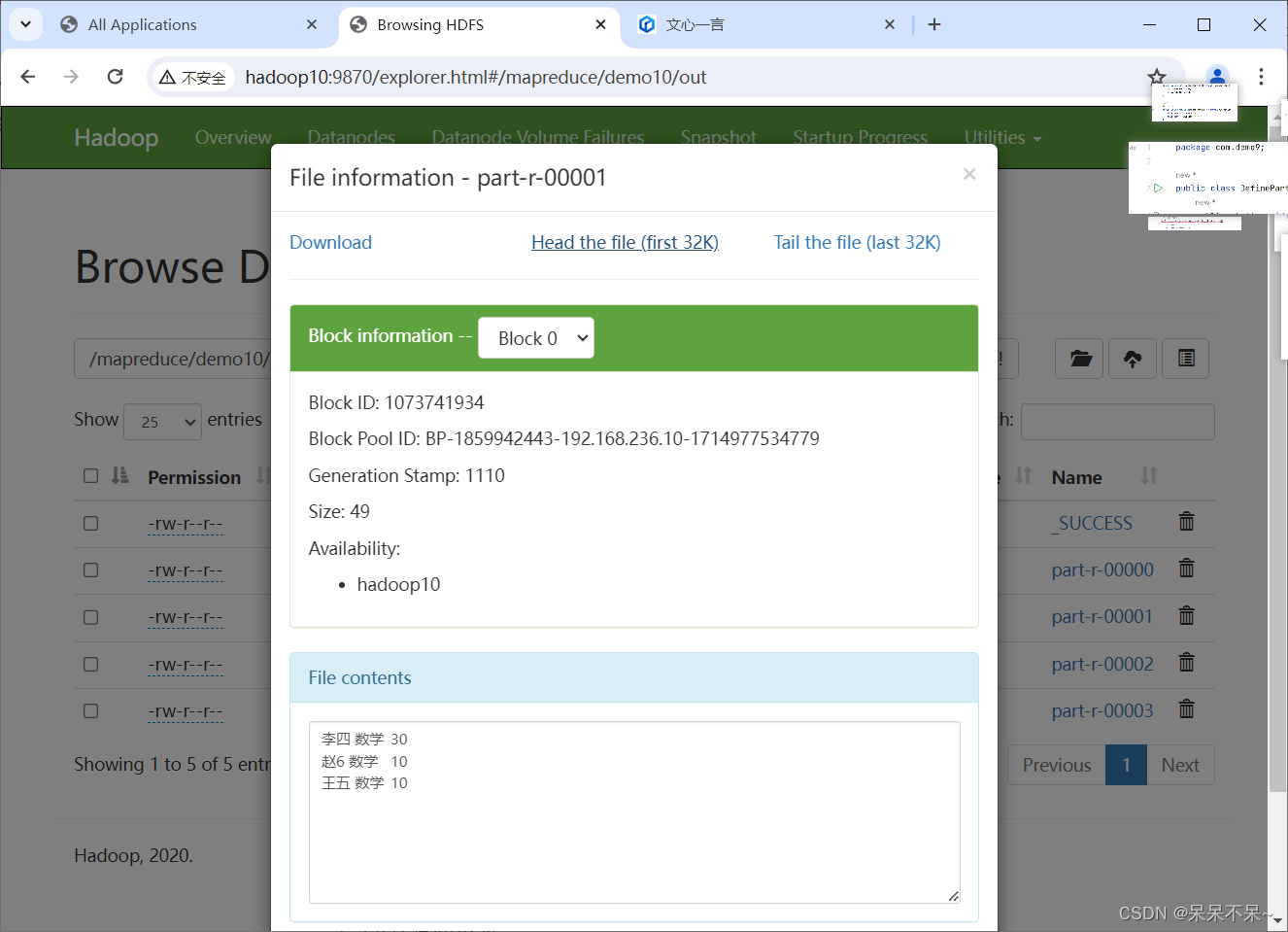
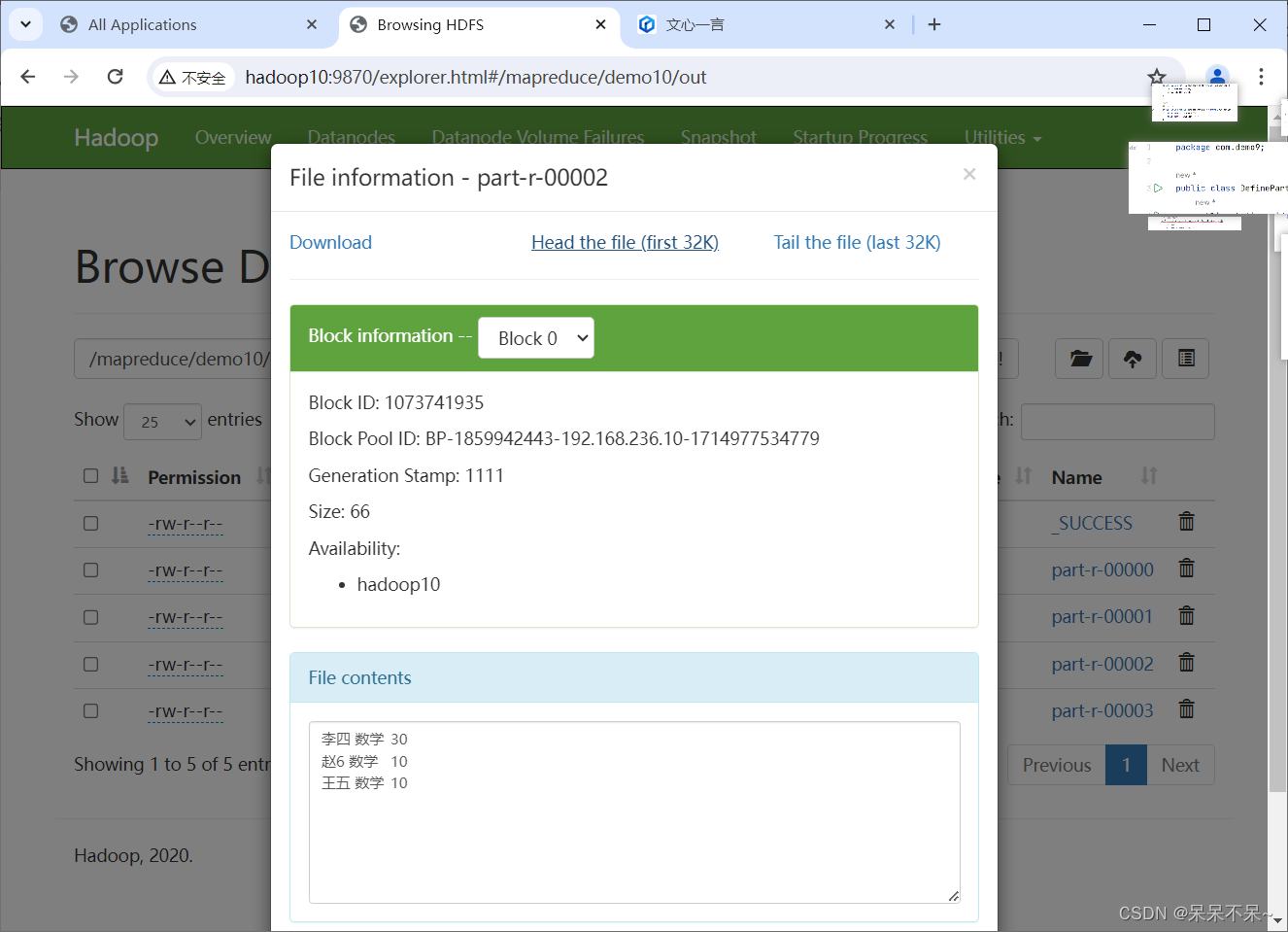
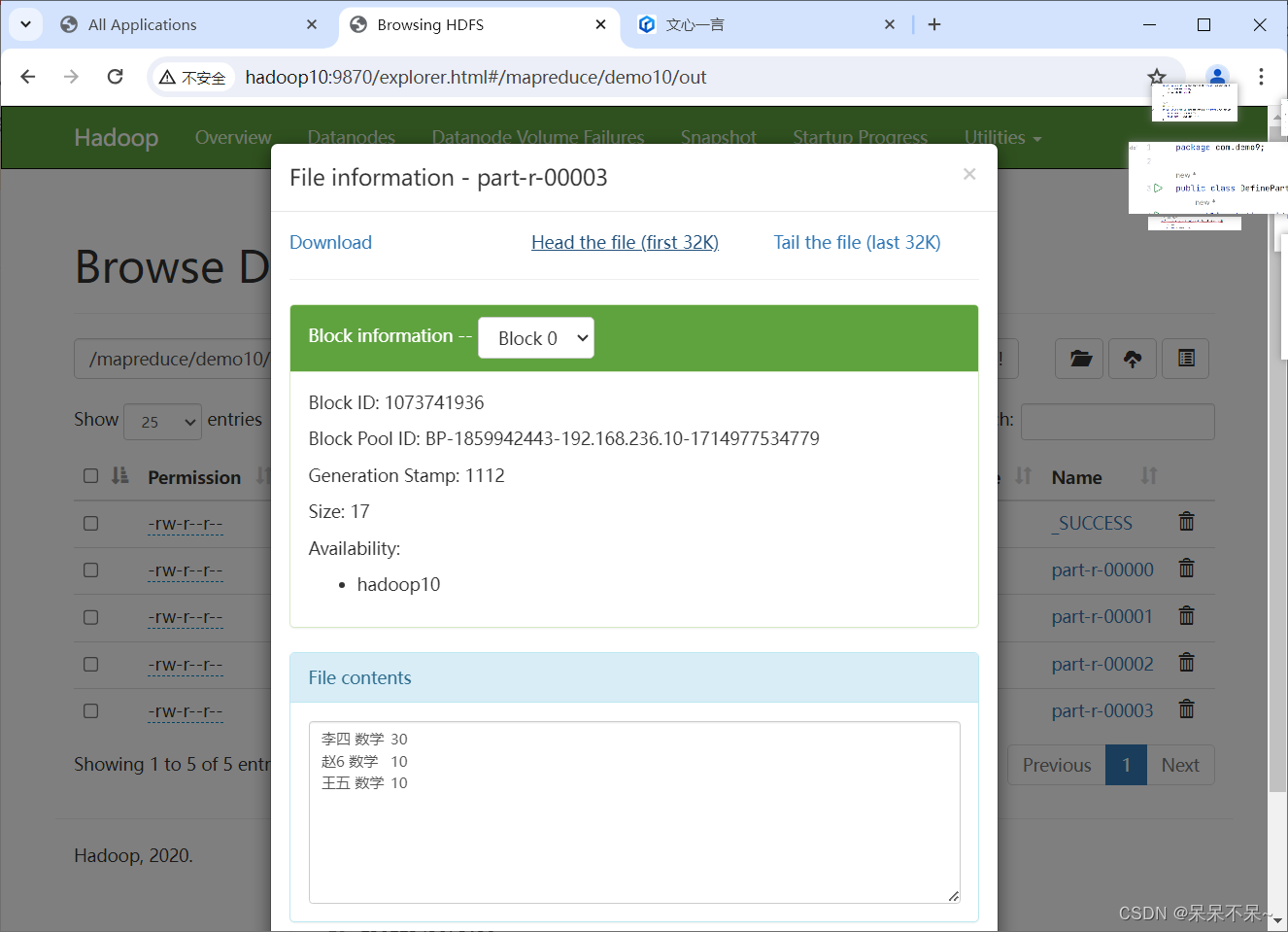
 4.在hdfs查看结果
4.在hdfs查看结果
不要去争辩,多提升自己~






















 217
217











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










