1、栈的概念
栈是限制在一端进行插入或者删除操作的线性表(俗称堆栈)
允许进行操作的一端称为“栈顶”
另一固定端称为“栈底”
当栈中没有元素时称为“空栈”
特点:后进先出(LIFO)

栈的应用:解决非线性问题,通过一个栈把问题线性化。
2、顺序栈的创建
typedef int data_t;
//先定义一个结构体
typedef strcut{
data_t *data;
int maxlen;
int top;
}sqstack;
以32位的系统为例,指针为4个字节,int为4个字节,所以该结构体共为12字节。要存储100个数据时,空间明显不够,所以data要继续申请空间。
第一步,malloc给结构体申请一个空间
第二步,malloc给数据申请空间(放的是data_t类型的100个)
第三步,memset把内存清零(赋初值)
第四步,给结构体赋初值
第五步,返回s
sqstack * stack_create(int len){
sqstack *s;
s = (sqstack *)malloc(sizeof(sqstack));
if(s == NULL){
printf("s malloc failed!\n");
return NULL;
}
s->data = (data_t *)malloc(len * sizeof(data_t));
if(s == NULL){
printf("data malloc failed!\n");
free(s);
return NULL;
}
memset(s->data, 0, len*sizeof(data_t));
s->maxlen = len;
s->top = -1;
return s;
}
2.1、入栈
int stack_push(sqstack *s,data_t value){
if(s == NULL){
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
if(s->top == s->maxlen - 1){
printf("stcak is full\n");
return -1;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top] = value;
return 0;
}
2.2、出栈
一次出一个元素
data_t stack_pop(sqstack *s){
s->top--;
return(s->data[s->top+1]);
2.3、判断栈的空、满状态
/*
*@ret 1-empty
* */
int stack_empty(sqstack *s){
if(s == NULL){
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
return (s->top == -1 ? 1:0);
}
/*
*@ret 1-full
* */
int stack_full(sqstack *s){
if(s == NULL){
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
return (s->top == s->maxlen-1 ? 1:0 );
}
2.4、返回栈顶
data_t stack_top(sqstack *s){
return (s->data[s->top]);
}
2.5、清空栈
int stack_clear(sqstack *s){
if(s == NULL){
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
s->top = -1;
return 0;
}
2.6、释放栈
int stack_free(sqstack *s){
if(s == NULL){
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
if(s->data != NULL)
free(s->data);
free(s);
return 0;
}
2.7、主函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include "sqstack.h"
int main(int argc, const char *argv[]){
sqstack *s;
s = stack_create(100);
if(s == NULL)
return -1;
stack_push(s, 10);
stack_push(s, 20);
stack_push(s, 30);
stack_push(s, 40);
stack_push(s, 50);
while(!stack_empty(s)){
printf("pop: %d \n",stack_pop(s));
}
stack_free(s);
return 0;
}
3、链式栈
插入操作和删除操作均在链表头部进行,链表尾部就是栈底,栈顶指针就是头指针。
typedef int data_t;/*定义栈中数据元素数据类型*/
typedef struct node {
data_t data; /*数据域*/
struct node *next; /*链接指针域*/
}listnode, *linkstack; /*链栈类型定义*/
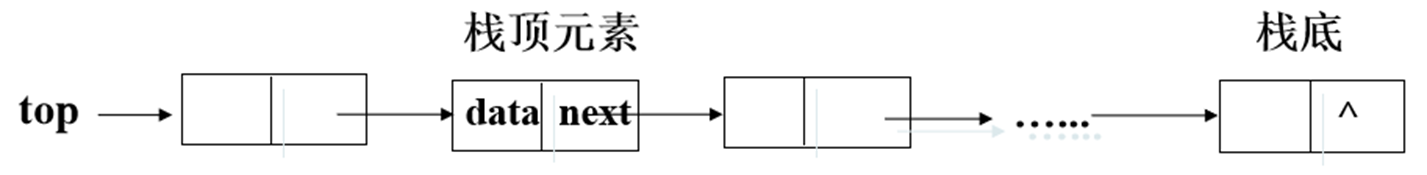
3.1、创建栈
linkstack stack_create() {
linkstack s;
s = (linkstack)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
if (s == NULL) {
printf("malloc failed\n");
return NULL;
}
s->data = 0;
s->next = NULL;
return s;
}
3.2、入栈
int stack_push(linkstack s, data_t value) {
linkstack p;
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
p = (linkstack)malloc(sizeof(listnode));
if (p == NULL) {
printf("malloc failed\n");
return -1;
}
p->data = value;
//p->next = NULL;
p->next = s->next;
s->next = p;
return 0;
}
3.3、出栈

data_t stack_pop(linkstack s) {
linkstack p;
data_t t;
p = s->next;
s->next = p->next;
t = p->data;
free(p);
p =NULL;
return t;
}
3.4、空栈判断
int stack_empty(linkstack s) {
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return -1;
}
return (s->next == NULL ? 1 : 0);
}
3.5、栈顶
data_t stack_top(linkstack s) {
return (s->next->data);
}
3.6、释放栈
linkstack stack_free(linkstack s) {
linkstack p;
if (s == NULL) {
printf("s is NULL\n");
return NULL;
}
while (s != NULL) {
p = s;
s = s->next;
printf("free:%d\n", p->data);
free(p);
}
return NULL;
}
3.7、主函数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "linkstack.h"
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
linkstack s;
s = stack_create();
if (s == NULL)
return -1;
stack_push(s, 10);
stack_push(s, 20);
stack_push(s, 30);
stack_push(s, 40);
#if 0
while (!stack_empty(s)) {
printf("pop:%d\n", stack_pop(s));
}
#endif
s = stack_free(s);
return 0;
}






















 257
257











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








