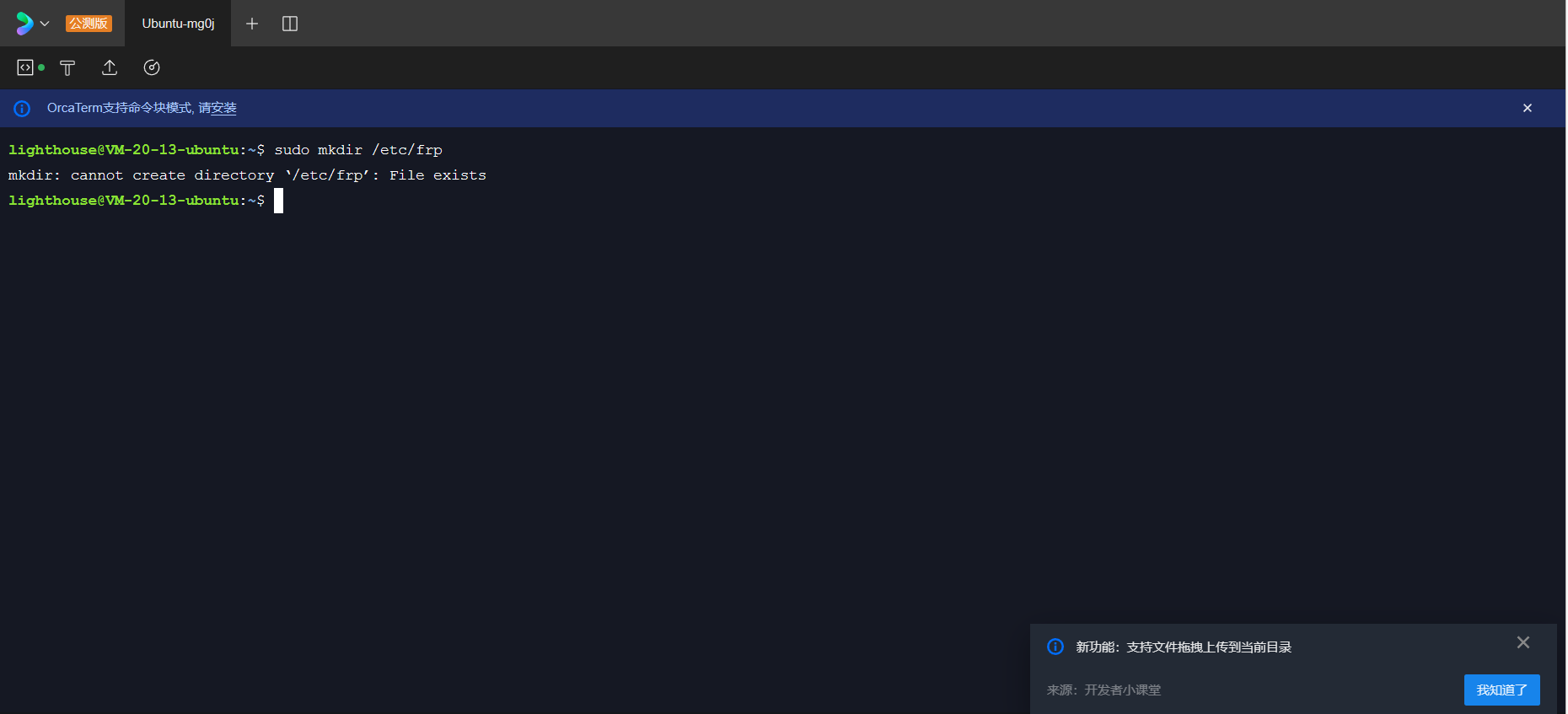
首先进入自己的云服务器终端
# 创建存放目录
sudo mkdir /etc/frp
# 创建frps.ini文件
sudo nano /etc/frp/frps.ini
代码块
[common]
# 监听端口
bind_port = 7000
# 面板端口
dashboard_port = 7500
# 登录面板账号设置
dashboard_user = admin
dashboard_pwd = spoto1234
# 设置http及https协议下代理端口(非重要)
vhost_http_port = 7080
vhost_https_port = 7081
# 身份验证
token = 12345678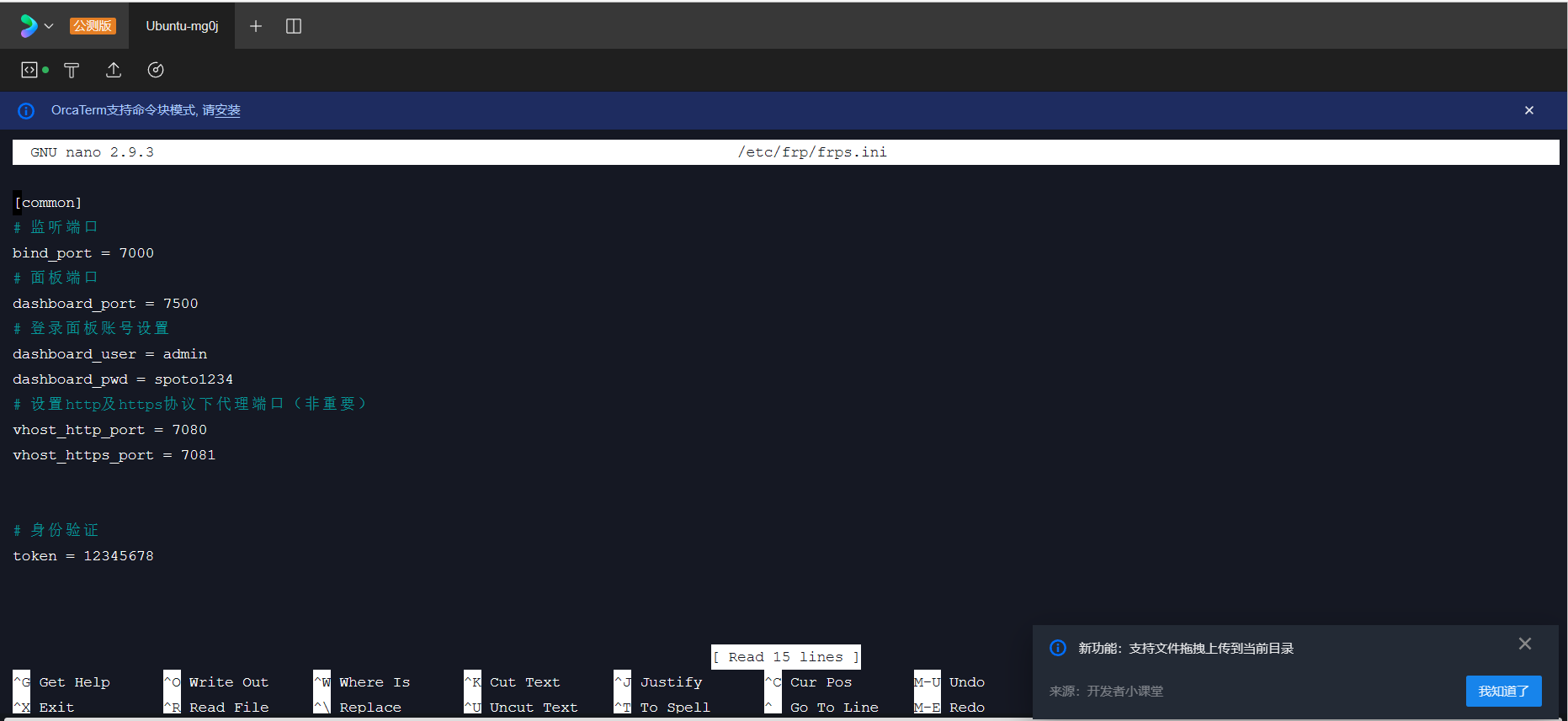
输入完成后按CTRL+X后按Y回车保存退出
在终端输入下面代码创建frp容器
sudo docker run --restart=always --network host -d -v /etc/frp/frps.ini:/etc/frp/frps.ini --name frps snowdreamtech/frps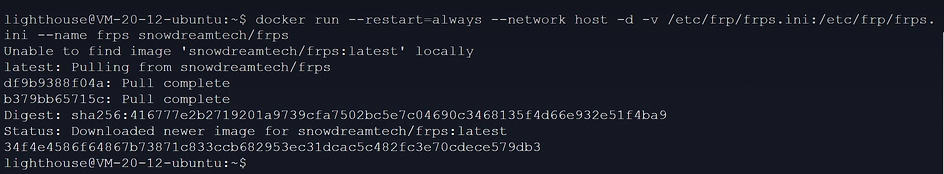
打开云服务器的7000,7080,7081,7500端口,如果安装了宝塔面板也要在宝塔面板带开这些端口
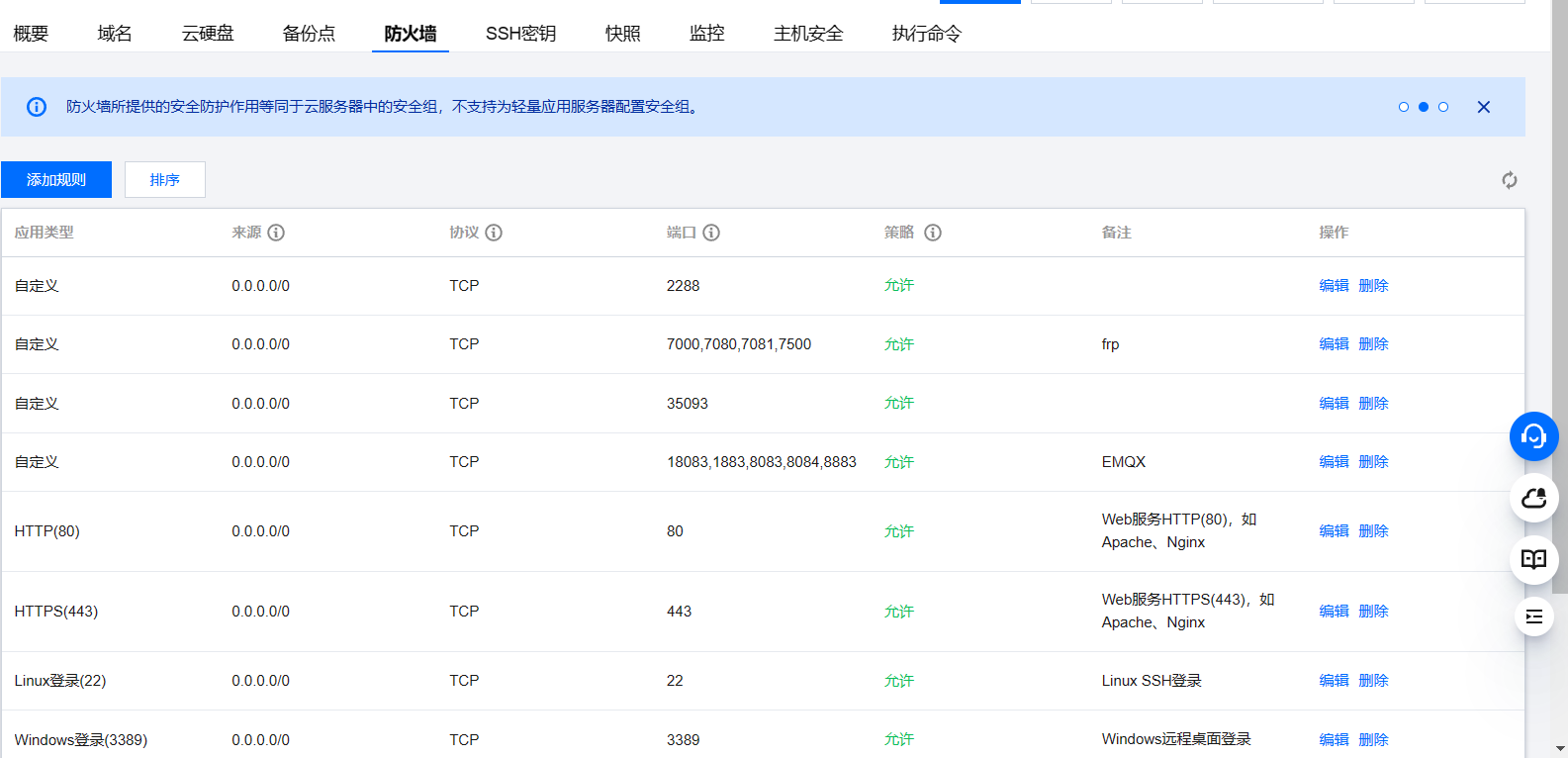
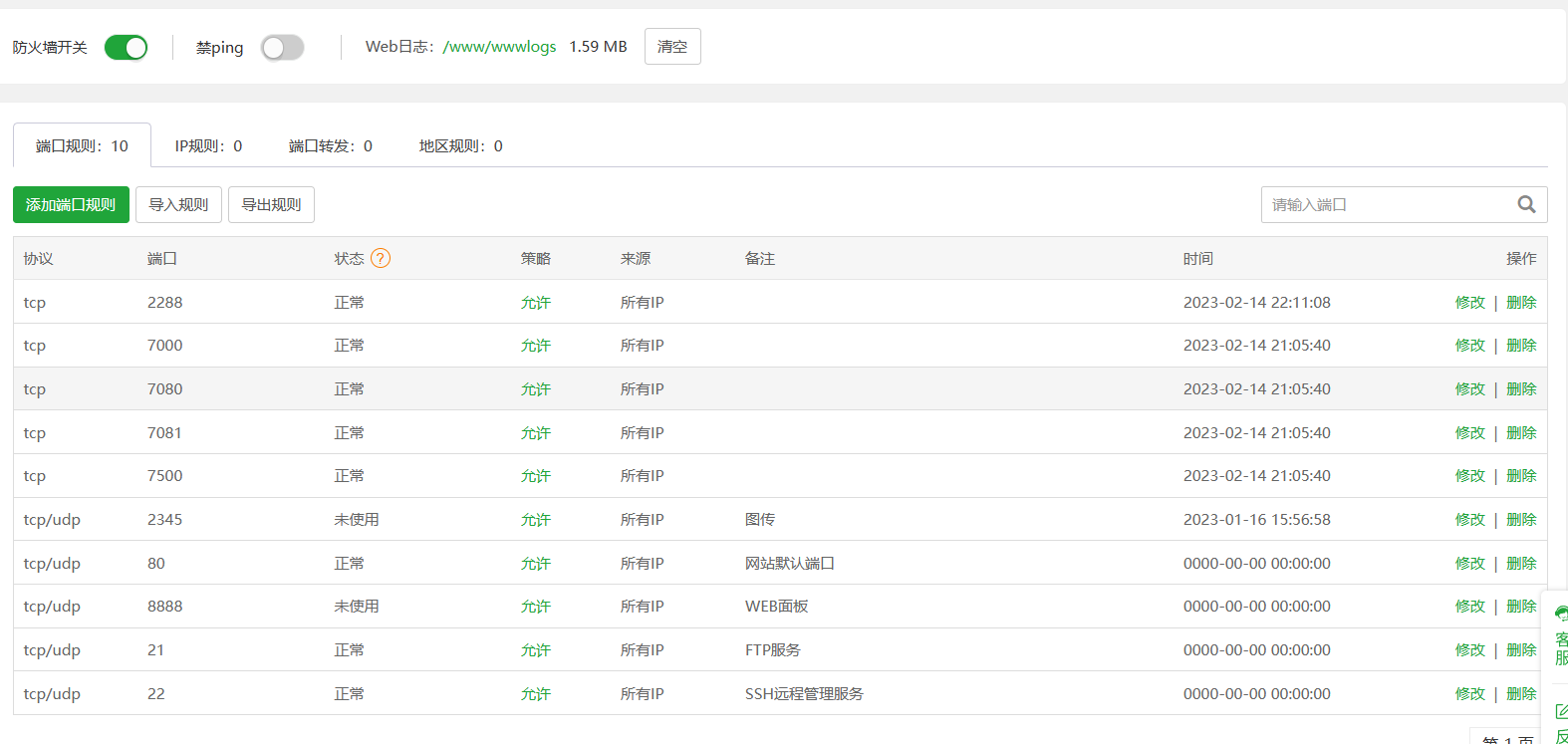
在浏览器中打开(自己服务器的公网IP:7500)进入frp管理页面
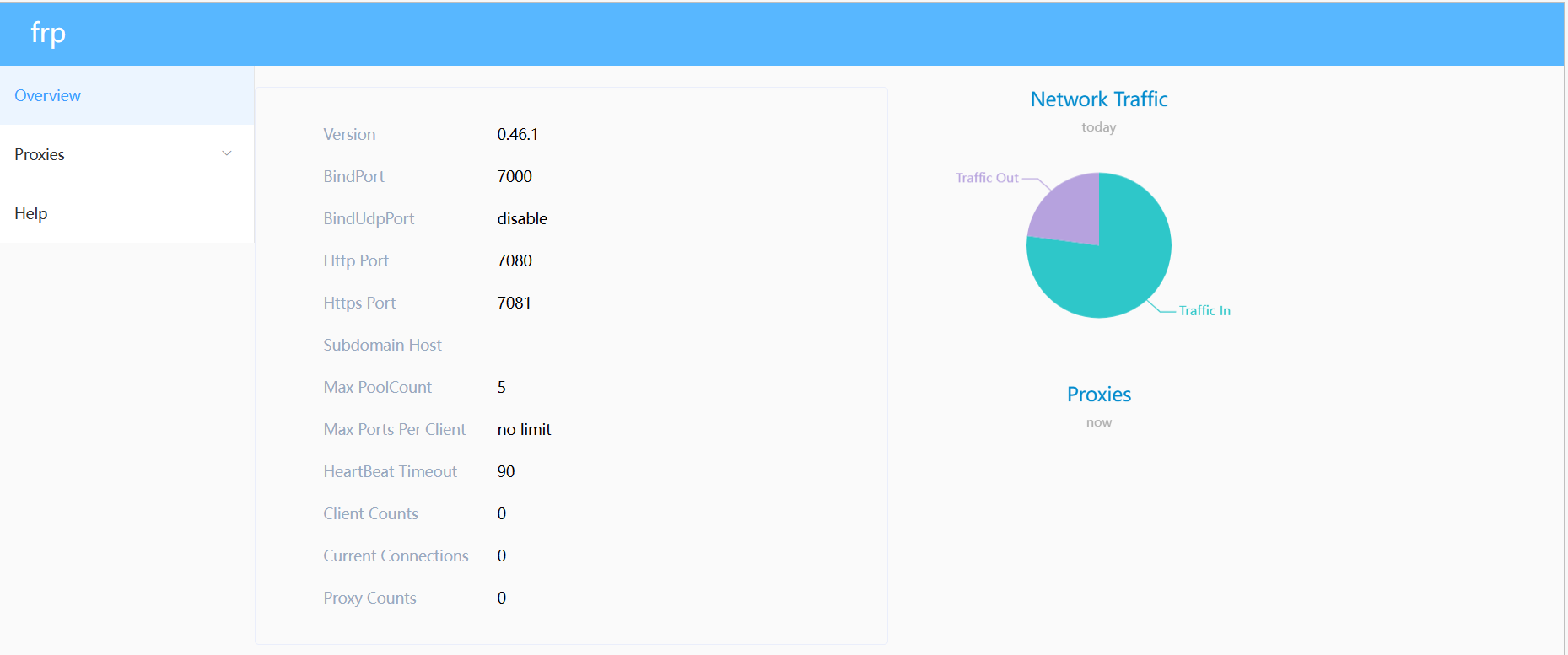
自此云服务器端的frp部署完成
win10pc端的frp客户端部署
解压压缩包至你想要的路径
打开frp.ini输入下面代码后保存退出
注意:server_addr处填写自己的公网IP,local_ip处填写自己穿透对象的内网IP
[common]
# server_addr为FRPS服务器IP地址
server_addr = xxx.xxx.xxx
# server_port为服务端监听端口,bind_port
server_port = 7000
# 身份验证
token = 12345678
[ssh]
type = tcp
local_ip = 192.168.101.23
local_port = 80
remote_port = 2288
# [ssh] 为服务名称,下方此处设置为,访问frp服务段的2288端口时,等同于通过中转服务器访问127.0.0.1的22端口。
# type 为连接的类型,此处为tcp
# local_ip 为中转客户端实际访问的IP
# local_port 为目标端口
# remote_port 为远程端口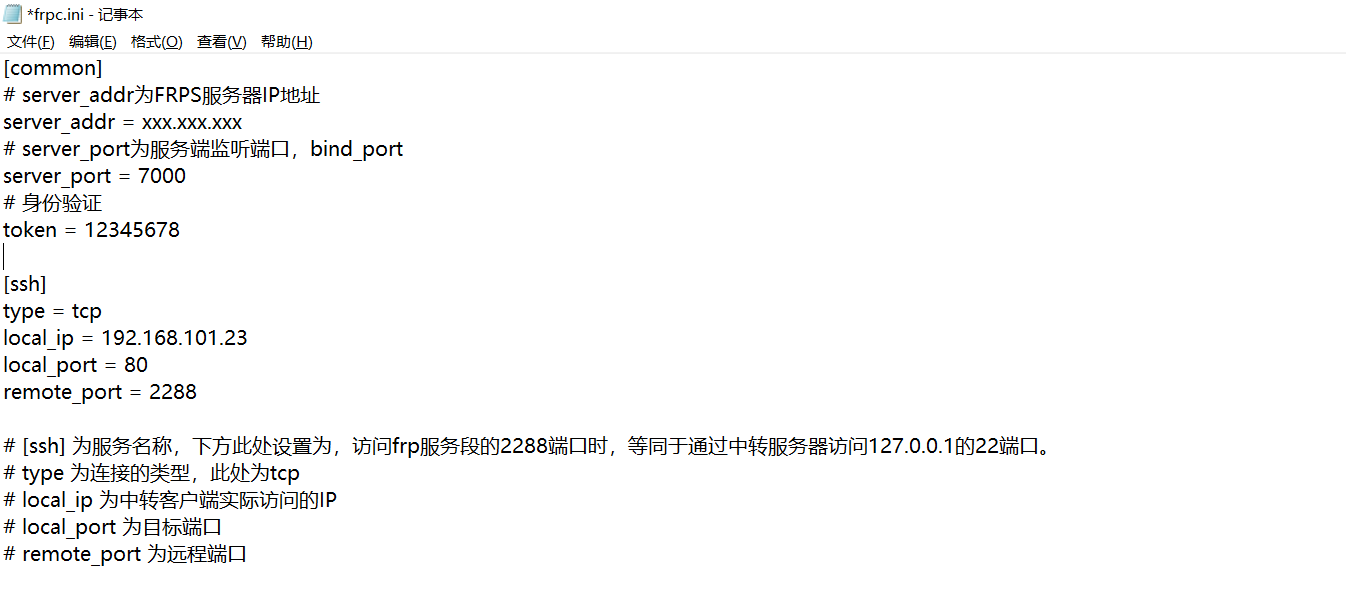
在cmd中启动frpc.exe客户端
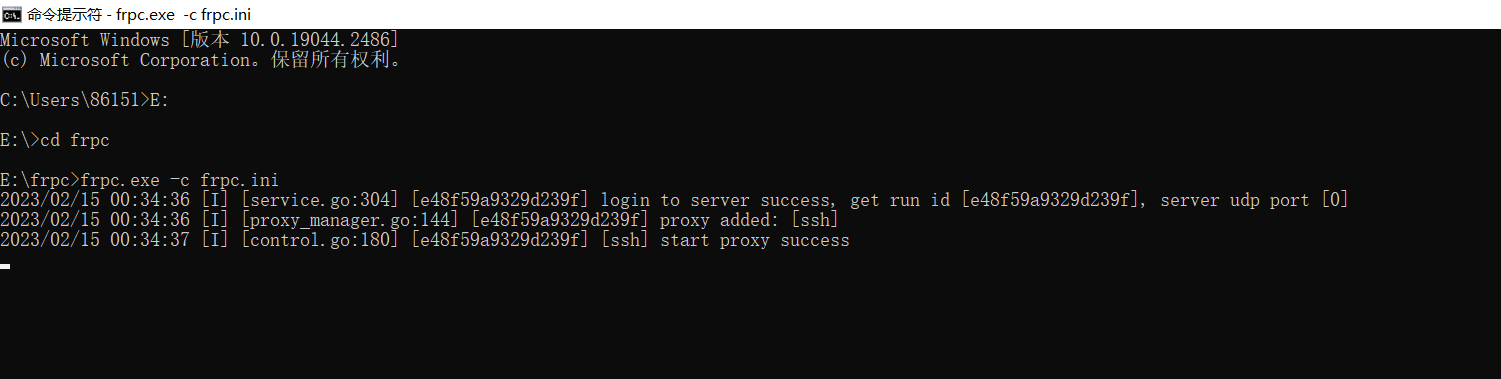
若想停止frp服务退出cmd即可
在浏览器中输入(自己的云服务器公网IP:2288(跟frpc.ini中的remote_port一致就行))就能打开局域网的服务器网站
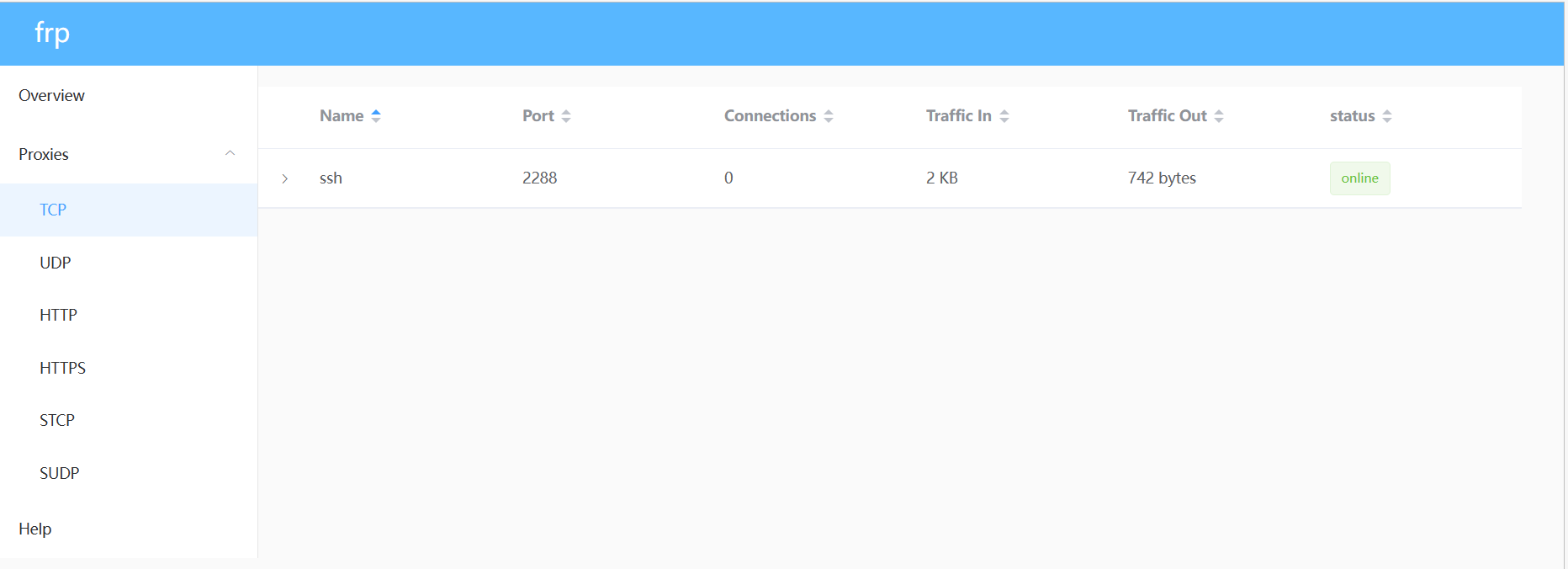
例子:云服务器端显示已连接
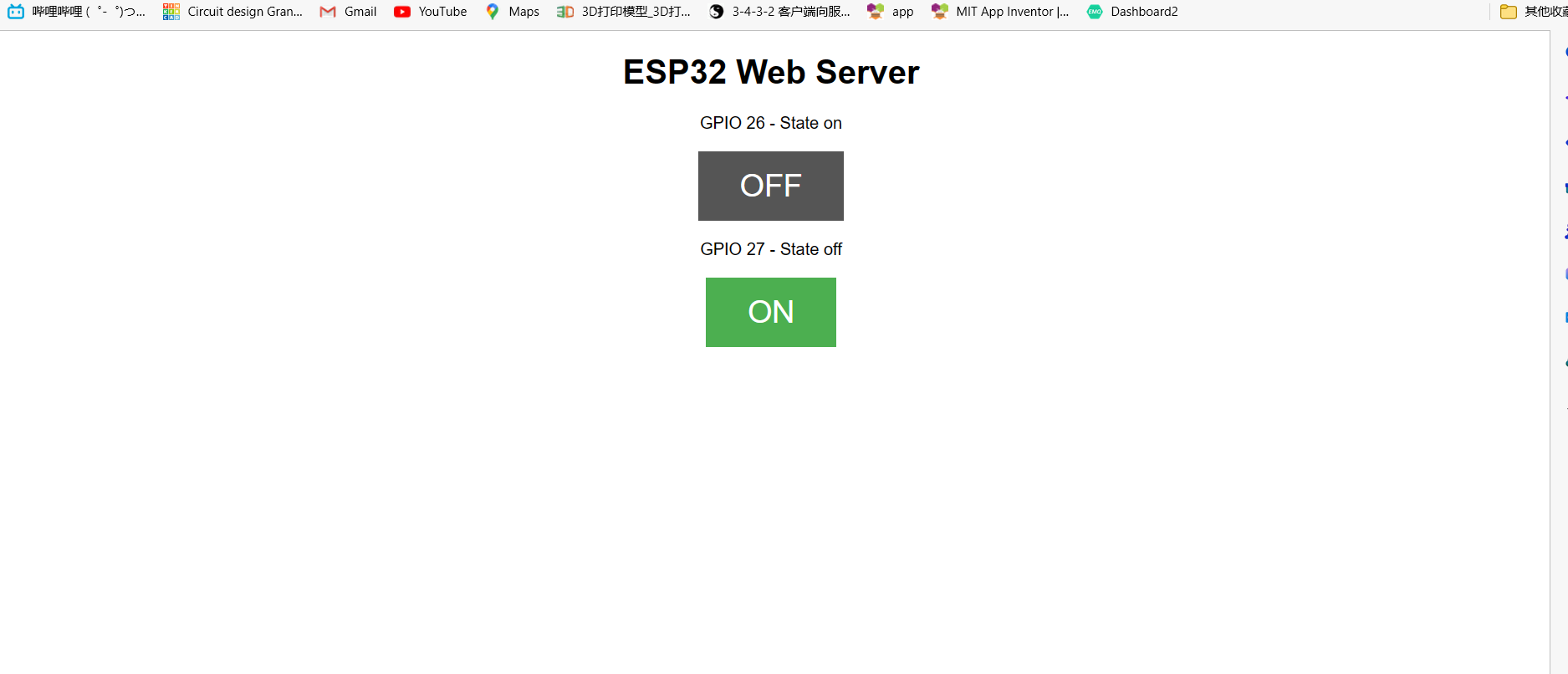
输入公网IP和2288端口后成功跳转到自己内网里部署的esp32服务端
附上esp32服务器端代码(arduino架构)
#include <WiFi.h>
// Replace with your network credentials
const char* ssid = "ChinaUnicom-EALJ24";
const char* password = "abc123456";
// Set web server port number to 80
WiFiServer server(80);
// Variable to store the HTTP request
String header;
// Auxiliar variables to store the current output state
String output26State = "off";
String output27State = "off";
// Assign output variables to GPIO pins
const int output26 = 26;
const int output27 = 27;
// Current time
unsigned long currentTime = millis();
// Previous time
unsigned long previousTime = 0;
// Define timeout time in milliseconds (example: 2000ms = 2s)
const long timeoutTime = 2000;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(115200);
// Initialize the output variables as outputs
pinMode(output26, OUTPUT);
pinMode(output27, OUTPUT);
// Set outputs to LOW
digitalWrite(output26, LOW);
digitalWrite(output27, LOW);
// Connect to Wi-Fi network with SSID and password
Serial.print("Connecting to ");
Serial.println(ssid);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
while (WiFi.status() != WL_CONNECTED) {
delay(500);
Serial.print(".");
}
// Print local IP address and start web server
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("WiFi connected.");
Serial.println("IP address: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.localIP());
server.begin();
}
void loop(){
WiFiClient client = server.available(); // Listen for incoming clients
if (client) { // If a new client connects,
currentTime = millis();
previousTime = currentTime;
Serial.println("New Client."); // print a message out in the serial port
String currentLine = ""; // make a String to hold incoming data from the client
while (client.connected() && currentTime - previousTime <= timeoutTime) { // loop while the client's connected
currentTime = millis();
if (client.available()) { // if there's bytes to read from the client,
char c = client.read(); // read a byte, then
Serial.write(c); // print it out the serial monitor
header += c;
if (c == '\n') { // if the byte is a newline character
// if the current line is blank, you got two newline characters in a row.
// that's the end of the client HTTP request, so send a response:
if (currentLine.length() == 0) {
// HTTP headers always start with a response code (e.g. HTTP/1.1 200 OK)
// and a content-type so the client knows what's coming, then a blank line:
client.println("HTTP/1.1 200 OK");
client.println("Content-type:text/html");
client.println("Connection: close");
client.println();
// turns the GPIOs on and off
if (header.indexOf("GET /26/on") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 26 on");
output26State = "on";
digitalWrite(output26, HIGH);
} else if (header.indexOf("GET /26/off") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 26 off");
output26State = "off";
digitalWrite(output26, LOW);
} else if (header.indexOf("GET /27/on") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 27 on");
output27State = "on";
digitalWrite(output27, HIGH);
} else if (header.indexOf("GET /27/off") >= 0) {
Serial.println("GPIO 27 off");
output27State = "off";
digitalWrite(output27, LOW);
}
// Display the HTML web page
client.println("<!DOCTYPE html><html>");
client.println("<head><meta name=\"viewport\" content=\"width=device-width, initial-scale=1\">");
client.println("<link rel=\"icon\" href=\"data:,\">");
// CSS to style the on/off buttons
// Feel free to change the background-color and font-size attributes to fit your preferences
client.println("<style>html { font-family: Helvetica; display: inline-block; margin: 0px auto; text-align: center;}");
client.println(".button { background-color: #4CAF50; border: none; color: white; padding: 16px 40px;");
client.println("text-decoration: none; font-size: 30px; margin: 2px; cursor: pointer;}");
client.println(".button2 {background-color: #555555;}</style></head>");
// Web Page Heading
client.println("<body><h1>ESP32 Web Server</h1>");
// Display current state, and ON/OFF buttons for GPIO 26
client.println("<p>GPIO 26 - State " + output26State + "</p>");
// If the output26State is off, it displays the ON button
if (output26State=="off") {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/26/on\"><button class=\"button\">ON</button></a></p>");
} else {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/26/off\"><button class=\"button button2\">OFF</button></a></p>");
}
// Display current state, and ON/OFF buttons for GPIO 27
client.println("<p>GPIO 27 - State " + output27State + "</p>");
// If the output27State is off, it displays the ON button
if (output27State=="off") {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/27/on\"><button class=\"button\">ON</button></a></p>");
} else {
client.println("<p><a href=\"/27/off\"><button class=\"button button2\">OFF</button></a></p>");
}
client.println("</body></html>");
// The HTTP response ends with another blank line
client.println();
// Break out of the while loop
break;
} else { // if you got a newline, then clear currentLine
currentLine = "";
}
} else if (c != '\r') { // if you got anything else but a carriage return character,
currentLine += c; // add it to the end of the currentLine
}
}
}
// Clear the header variable
header = "";
// Close the connection
client.stop();
Serial.println("Client disconnected.");
Serial.println("");
}
}
参考链接:自建内网穿透服务器: 通过FRP,Zerotier等几种通过自己服务器实现内网穿透的教程 (gitee.com)
本文是作者自学过程的总结,其中借鉴了多个B站大佬的教程




















 433
433











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








