Integer :
源码分析,进行理解
简单介绍Integer:
Integer 类在对象中包装了一个基本类型 int 的值。Integer 类对象包含一个 int 类型的字段。此外,该类提供了多个方法,能在 int 类型和 String 类型之间互相转换,还提供了处理 int 类型时非常有用的其他一些常量和方法。
源码分析:
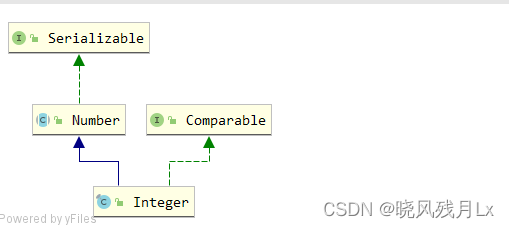
1.继承和接口实现图
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer>
2.成员变量
// @Native是Java元注解,表明不是Java代码实现,但可以被本地代码调用。
// staic final 修饰变量,表示一旦赋值就不能修改,可以通过类名可以访问。
// 修饰方法,表示不可以覆盖,可以通过类名直接访问
@Native public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;
@Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
// 表示原始类型int的类实例。
public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");
//用来以二进制补码形式表示 int 值的比特位数。
@Native public static final int SIZE = 32;
//int的字节数 bytes = 4
public static final int BYTES = SIZE / Byte.SIZE;
final static char[] digits = {
'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' ,
'6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,
'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' ,
'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' ,
'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' ,
'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z'
};
final static char [] DigitTens = {
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
'1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1',
'2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2',
'3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3',
'4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4',
'5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5',
'6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6',
'7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7',
'8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8',
'9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9',
} ;
final static char [] DigitOnes = {
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
} ;
final static int [] sizeTable = { 9, 99, 999, 9999, 99999, 999999, 9999999,
99999999, 999999999, Integer.MAX_VALUE };
/*
digits数组用于表示所有可能出现的字符,因为int支持从2进制到36进制,所以这里需要有36个字符才能表示所有不同进制的数字
DigitTens和DigitOnes两个数组也很好理解,它们主要用于获取0到99之间某个数的十位和个位,比如36,通过DigitTens数组直接取出来十位为3,而通过DigitOnes数组取出来个位为6。
sizeTable数组主要用在判断一个int型数字对应字符串的长度。避免了使用除法或求余等操作,以提高效率。
*/
// 私有成员变量
// Integer对象中保存int值的
private final int value;
// 和序列化有关,是为了兼容不同版本的,在JDK中,可以利用JDK的bin目录下的serialver.exe工具产
// 生这个serialVersionUID,根据serialVersionUID值来判断是否兼容来反序列化。
@Native private static final long serialVersionUID = 1360826667806852920L;3. 构造方法
// 以 int 型变量作为参数创建 Integer 对象
public Integer(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
// 以 String 型变量作为参数创建 Integer 对象
public Integer(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
this.value = parseInt(s, 10); // 传入字符串和进制数
}4.IntegerCache
// Integer的内部类(作用是缓存 -128 到 high 的Integer对象)
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
// 在"java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high"中获取
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127); // 获取的数和127比大小 一般不调整数值都是127
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1); // 防止数值设置过大
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1]; // 缓存的数有多少个
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++); // 将这些数放在cache数组中
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127; // assert断言检测 成功就可继续运行
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
5.方法
5.1 parseInt方法(将String类型转换为int类型)
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
/*
* WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
* the valueOf method.
*/
if (s == null) { // 字符串等于null,抛出异常
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) { // 进制不能小于2进制
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) { // 进制不能大于36进制
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
int result = 0; //result为最终传回结果
boolean negative = false; // 判断正负 false为正 true为负
int i = 0; // 循环变量
int len = s.length(); // 获得字符串长度
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 界限-2147483647 默认取最大整数的取反值
int multmin; // 在解析最后一位数字之前的最大范围
int digit; // 所解析的每一位数字
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0); // 返回第0个索引的字符
if (firstChar < '0') { // ASCII码比较
if (firstChar == '-') { // 如果第一个字符是“-”
negative = true; // 为负数
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 界限赋最小值
} else if (firstChar != '+') // 如果第一个字符不是“+”
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
// 抛出异常信息"For input string: \"" + s + "\""
if (len == 1) // 首字符为'+'但是传入字符串长度为1,抛出数字格式异常
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
// 抛出异常信息,结束运行
i++; // 当第一位有符号时, 循环遍历数组时从第二位开始遍历 将i++
}
multmin = limit / radix; // multmin = -214748364 负数跟整数的limit是不同的
while (i < len) { // 开始遍历
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++),radix);// 获取字符转换为相应进制的整数
if (digit < 0) { // 当小于0,抛出数字格式化异常
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
// 因为是负值存储, 所以当result小于multmin时说明越界了
// 如果当前数值已经超过了 multmin, 那么说明在添加当前数值之前就已经越界了
// 直接抛出异常. 提前判断一次的原因, 是因为防止下一步越界
if (result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
// 在更新 result 值之前, 先比较 result 和 multmin
// 如果已经越界了, 那么再进行这一步操作就会越界
result *= radix;
// 判断加了当前位的值是否越界
if (result < limit + digit) { // 越界抛出
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result -= digit; // 使用负数存储 这一步不会溢出
}
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
// 根据negative的值判断返回值是否取反
return negative ? result : -result;
}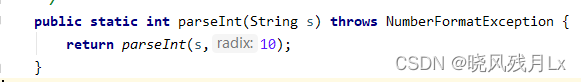
其重载方法,实际上还是调用了parseInt(s,10);
5.2 valueOf
共有三种重载方法,其中两种都是调用了ValueOf(int i) public static Integer valueOf(String s, int radix) throws NumberFormatException { return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s,radix)); }public static Integer valueOf(String s) throws NumberFormatException { return Integer.valueOf(parseInt(s, 10)); }public static Integer valueOf(int i) { if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high) return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)]; return new Integer(i); }
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
// 如果在Integer缓存类中,直接通过缓存获取
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
// 重新在堆中构建 一般来说大于127的数 比较两个Integer是否相等都是false
}






















 229
229











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










