

1、bootstraps是一种将线性回归参数 B^,通过多次求解后再进行求方差得出的,过程称为自助采样。
2、Bagging是由 Bootstraps 演化而来的
3、Bagging的核心在于自助采样(bootstrap)这一概念,即有放回的从数据集中进行采样,也就是说,同样的一个样本可能被多次进行采样。一个自助采样的小例子是我们希望估计全国所有人口年龄的平均值,那么我们可以在全国所有人口中随机抽取不同的集合(这些集合可能存在交集),计算每个集合的平均值,然后将所有平均值的均值作为估计值。
4、Bagging的一个典型应用是随机森林。顾名思义,“森林”是由许多“树”bagging组成的。在具体实现上,用于每个决策树训练的样本和构建决策树的特征都是通过随机采样得到的,随机森林的预测结果是多个决策树输出的组合(投票)。
5、查看笔记可得出
# test classification dataset
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_informative=15,
n_redundant=5, random_state=5)
# summarize the dataset
print(X.shape, y.shape)
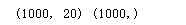
# evaluate bagging algorithm for classification
from numpy import mean
from numpy import std
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.model_selection import RepeatedStratifiedKFold
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
# define dataset
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_informative=15, n_redundant=5, random_state=5)
# define the model
model = BaggingClassifier()
# evaluate the model
cv = RepeatedStratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, n_repeats=3, random_state=1)
n_scores = cross_val_score(model, X, y, scoring='accuracy', cv=cv, n_jobs=-1, error_score='raise')
# report performance
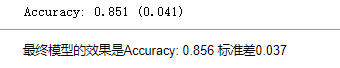
print('Accuracy: %.3f (%.3f)' % (mean(n_scores), std(n_scores)))






















 4540
4540











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








