✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
⛄ 内容介绍
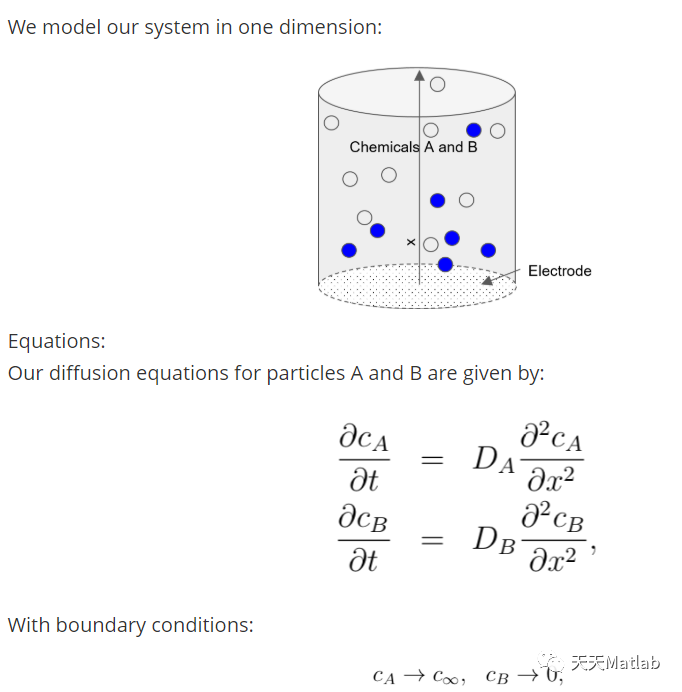
An electrochemical system contains two main parts, the electrode, an electronic conductor, and the electrolyte, an ionic conductor containing electroactive chemicals. Our measurements will simulate a three-electrode potentiostat, where we will apply a time-dependent potential between the ‘working’ electrode and the reference electrode and measure the current that flows between the working and the auxiliary electrodes as a response. We simplify our system by focussing on the reactions taking place at the working electrode and the electrolyte. By applying a potential, additional energy can be supplied or taken from the electrons in the electrode. For metallic conductors, this means an increase or decrease in their highest possible energy for the electrons in the electron cloud, called the Fermi-energy. As the electrons in metals do not posses discrete energy levels (due their overlaps in electron orbits) they form a continuous spectrum up to the Fermi- energy. Hence by increasing the potential, the Fermi-level can be lowered below the highest occupied molecular orbit (HOMO) of the reactant particles A, favouring a transfer of electrons as it releases energy. This will lead to a formation of oxidised B particles at the electrode and a peak in our (simulated) measurement. Conversely, the potential can also be lowered such that an reduction process will be favourable and the electrons move from the electrode to the lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) of the reactant re-forming A particles.

⛄ 部分代码
%% varying E0
clear all
gamma=1;
alpha=0.5;
E0_collection=[-5, -2, 0, 2, 5];
k=1;
K0=0.1;
n= 500;
h=0.1;
for E0=E0_collection
[~,~, I(k,:), E(k,:)]= sweep2(K0, E0, alpha, gamma, n,h);
k=k+1
end
%%
figure
for i=1:length(E0_collection)
h=plot(E(i,:), I(i,:));hold on
n=legend('E0= -5','E0= -2','E0= 0','E0= 2','E0= 4.5', 'Location','northwest', 'fontsize', 15);hold on
set(h,'linewidth',2);
set(n,'fontsize', 15)
ylabel('I(t)', 'fontsize', 20);hold on
xlabel('E(t)', 'fontsize', 20);hold on
title('Varying E_0', 'fontsize', 20);hold on
end
set(gca,'FontName','Times');
saveas(gcf,'vary_E0.png')
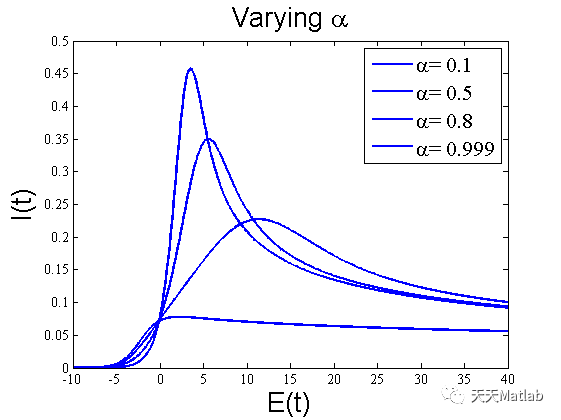
⛄ 运行结果
⛄ 参考文献
[1] 张焕.基于液相氧化还原反应的电化学储能体系[D].厦门大学,2012.DOI:http://dspace.xmu.edu.cn:8080/dspace/handle/2288/34555.
[2] 张焕.基于液相氧化还原反应的电化学储能体系[J]. 2012.
⛳️ 代码获取关注我
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料






















 3410
3410











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








