
感谢每一个认真阅读我文章的人,看着粉丝一路的上涨和关注,礼尚往来总是要有的:
① 2000多本Python电子书(主流和经典的书籍应该都有了)
② Python标准库资料(最全中文版)
③ 项目源码(四五十个有趣且经典的练手项目及源码)
④ Python基础入门、爬虫、web开发、大数据分析方面的视频(适合小白学习)
⑤ Python学习路线图(告别不入流的学习)
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
新建labelme2coco.py
import argparse
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import skimage.io as io
import cv2
from labelme import utils
import numpy as np
import glob
import PIL.Image
REQUIRE_MASK = False
labels = {‘aircraft’: 1, ‘oiltank’: 2}
class labelme2coco(object):
def init(self, labelme_json=[], save_json_path=‘./new.json’):
‘’’
:param labelme_json: the list of all labelme json file paths
:param save_json_path: the path to save new json
‘’’
self.labelme_json = labelme_json
self.save_json_path = save_json_path
self.images = []
self.categories = []
self.annotations = []
self.data_coco = {}
self.label = []
self.annID = 1
self.height = 0
self.width = 0
self.require_mask = REQUIRE_MASK
self.save_json()
def data_transfer(self):
for num, json_file in enumerate(self.labelme_json):
if not json_file == self.save_json_path:
with open(json_file, ‘r’) as fp:
data = json.load(fp)
self.images.append(self.image(data, num))
for shapes in data[‘shapes’]:
print("label is ")
print(shapes[‘label’])
label = shapes[‘label’]
if label[1] not in self.label:
if label not in self.label:
print("find new category: ")
self.categories.append(self.categorie(label))
print(self.categories)
self.label.append(label[1])
self.label.append(label)
points = shapes[‘points’]
self.annotations.append(self.annotation(points, label, num))
self.annID += 1
def image(self, data, num):
image = {}
img = utils.img_b64_to_arr(data[‘imageData’])
height, width = img.shape[:2]
img = None
image[‘height’] = height
image[‘width’] = width
image[‘id’] = num + 1
image[‘file_name’] = data[‘imagePath’].split(‘/’)[-1]
self.height = height
self.width = width
return image
def categorie(self, label):
categorie = {}
categorie[‘supercategory’] = label
categorie[‘supercategory’] = label
categorie[‘id’] = labels[label] # 0 默认为背景
categorie[‘name’] = label
return categorie
def annotation(self, points, label, num):
annotation = {}
print(points)
x1 = points[0][0]
y1 = points[0][1]
x2 = points[1][0]
y2 = points[1][1]
contour = np.array([[x1, y1], [x2, y1], [x2, y2], [x1, y2]]) # points = [[x1, y1], [x2, y2]] for rectangle
contour = contour.astype(int)
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
print("contour is ", contour, " area = ", area)
annotation[‘segmentation’] = [list(np.asarray([[x1, y1], [x2, y1], [x2, y2], [x1, y2]]).flatten())]
[list(np.asarray(contour).flatten())]
annotation[‘iscrowd’] = 0
annotation[‘area’] = area
annotation[‘image_id’] = num + 1
if self.require_mask:
annotation[‘bbox’] = list(map(float, self.getbbox(points)))
else:
x1 = points[0][0]
y1 = points[0][1]
width = points[1][0] - x1
height = points[1][1] - y1
annotation[‘bbox’] = list(np.asarray([x1, y1, width, height]).flatten())
annotation[‘category_id’] = self.getcatid(label)
annotation[‘id’] = self.annID
return annotation
def getcatid(self, label):
for categorie in self.categories:
if label[1]==categorie[‘name’]:
if label == categorie[‘name’]:
return categorie[‘id’]
return -1
def getbbox(self, points):
polygons = points
mask = self.polygons_to_mask([self.height, self.width], polygons)
return self.mask2box(mask)
def mask2box(self, mask):
np.where(mask==1)
如果你也是看准了Python,想自学Python,在这里为大家准备了丰厚的免费学习大礼包,带大家一起学习,给大家剖析Python兼职、就业行情前景的这些事儿。
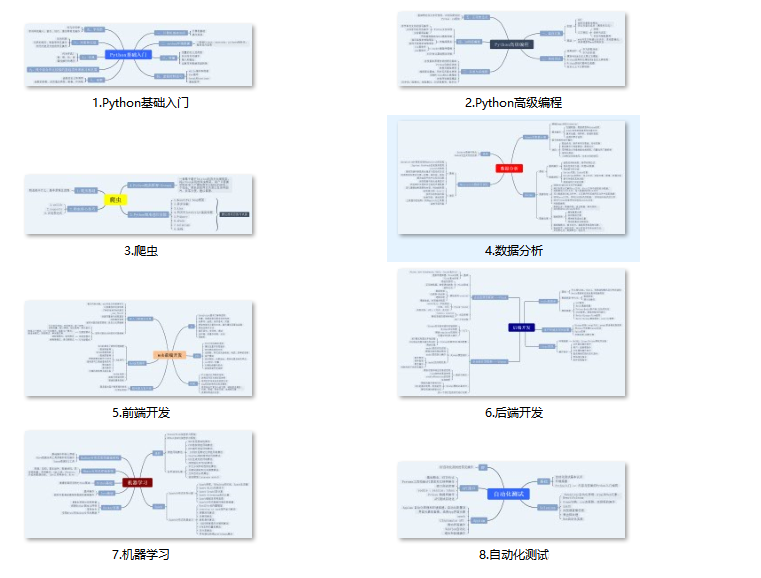
一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向路线就是把Python常用的技术点做整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
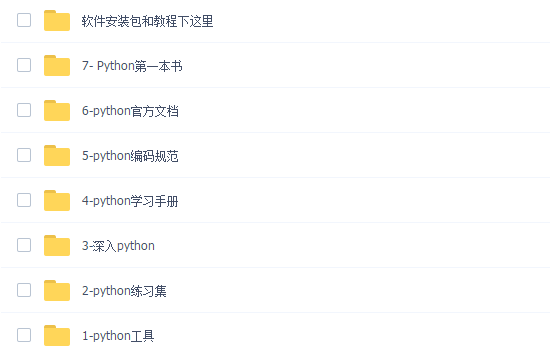
二、学习软件
工欲善其必先利其器。学习Python常用的开发软件都在这里了,给大家节省了很多时间。
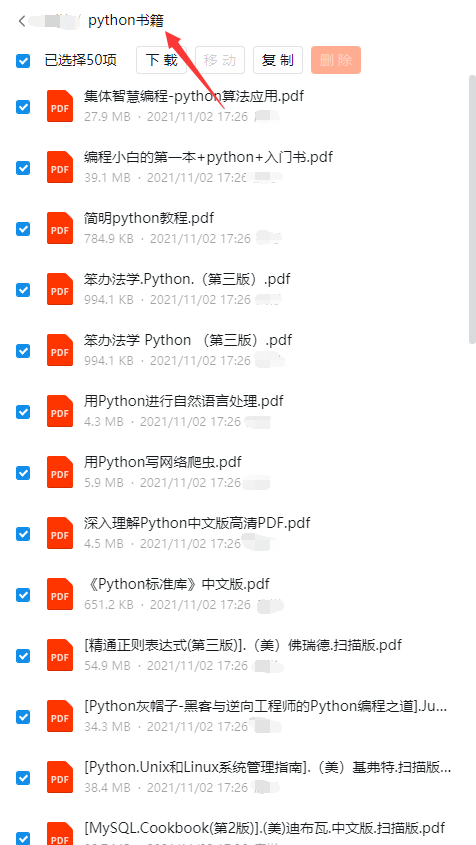
三、全套PDF电子书
书籍的好处就在于权威和体系健全,刚开始学习的时候你可以只看视频或者听某个人讲课,但等你学完之后,你觉得你掌握了,这时候建议还是得去看一下书籍,看权威技术书籍也是每个程序员必经之路。
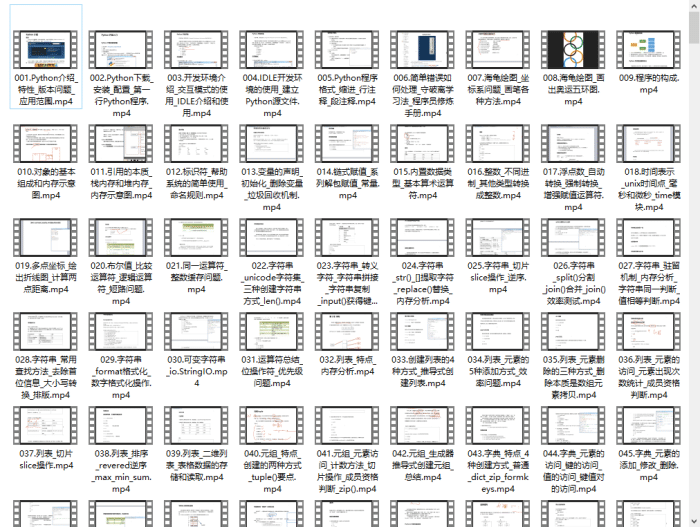
四、入门学习视频
我们在看视频学习的时候,不能光动眼动脑不动手,比较科学的学习方法是在理解之后运用它们,这时候练手项目就很适合了。
四、实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。
五、面试资料
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。
成为一个Python程序员专家或许需要花费数年时间,但是打下坚实的基础只要几周就可以,如果你按照我提供的学习路线以及资料有意识地去实践,你就有很大可能成功!
最后祝你好运!!!
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 77
77

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








