上一篇: TensorFlow笔记_01——安装tensoflow2.0
下一篇: TensorFlow笔记_03——神经网络优化过程
2. 张量
张量(Tensor):多维数组(列表),阶:张量的维度
| 维数 | 阶 | 名字 | 例子 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0-D | 0 | 标量 scalar | s=1 2 3 |
| 1-D | 1 | 向量 vector | v=[1,2,3] |
| 2-D | 2 | 矩阵 matrix | m=[[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] |
| N-D | n | 张量 tensor | t=[[[n个 |
张量可以表示0阶到n阶数组(列表)
数据类型
tf.int,tf.float......
tf.int32,tf.float,tf.float64
tf.bool
tf.constant([True,False])
tf.string
tf.constant("Hello,world!")
2.1 创建Tensor
创建一个张量
x=tf.constant([1,5],dtype=tf.int64)
print(x)
print(x.dtype)
print(x.shape)
'''
tf.Tensor([1 5], shape=(2,), dtype=int64) 看shape的逗号隔开了几个数字就是几维的。
<dtype: 'int64'>
(2,)
'''
将numpy的数据类型转换为Tensor数据类型
a=np.arange(0,5)
b=tf.convert_to_tensor(a,dtype=tf.int64)
print(a)
print(b)
#[0 1 2 3 4]
#tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3 4], shape=(5,), dtype=int64)
创建全为0的张量
#tf.zeros(维度)
a=tf.zeros(2)
print(a)
#tf.Tensor([0. 0.], shape=(2,), dtype=float32)
创建一个全为1的张量
#tf.noe(维度)
a=tf.ones([1,3])
print(a)
#tf.Tensor([[1. 1. 1.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
创建一个全为指定值的张量
#tf.fill(维度,指定值)
b=tf.fill([1,3],3.)
print(b)
#tf.Tensor([[3. 3. 3.]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
生成正态分布的随机数,默认均值为0,标准差为1
#tf.random.normal(维度,mean=均值,stddv=标准差)
d=tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=0.5,stddev=1)
print(d)
'''
tf.Tensor(
[[1.6505516 3.1428373 ]
[0.88254464 0.67587733]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32)
'''
生成阶段式正态分布的随机数
#tf.random.truncated_normal(维度,mean=均值,stddv=标准差)
e=tf.random.truncated_normal([2,2],mean=0.5,stddev=1)
print(e)
'''
tf.Tensor(
[[1.6450552 0.40628934]
[0.37144333 0.6191346 ]], shape=(2, 2), dtype=float32)
'''
在tf.truncated_noemal中如果随借生成数据的取值在(μ-2σ,μ+2σ)之外,则重新生成,保证了生成值在均值附近。
μ:均值 σ:标准差
标准差计算公式:
σ
=
∑
i
=
1
n
(
x
i
−
x
ˉ
)
2
n
标准差计算公式:σ=\sqrt{\frac{\sum_{i=1}^n(x_i-\bar{x})^2}n}
标准差计算公式:σ=n∑i=1n(xi−xˉ)2
2.2 常用函数
强制tensor转换为该数据类型
#tf.cast(张量名,dtype=数据类型)
x1=tf.constant([1,2,3],dtype=tf.float64)
print(x1)
#tf.Tensor([1. 2. 3.], shape=(3,), dtype=float64)
x2=tf.cast(x1,tf.int32)
print(x2)
#tf.Tensor([1 2 3], shape=(3,), dtype=int32)
计算张量维度上元素的最小值于最小值
#tf.reduce_min(张量名)
#tf.reduce_max(张量名)
print(tf.reduce_min(x2),tf.reduce_max(x2))
#tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32) tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
理解axis
在一个二维张量或者数组中,可以通过调整axis等于0或1控制执行维度。
- axis=0代表跨行(维度,down),而axis=1代表跨列(维度,across)
- 如果不指定axis,则所有元素参与计算。
计算张量沿着指定维度的平均值
#tf.reduce_mean(张量名,axis=操作轴)
x=tf.constant([[1,2,3],[2,2,3]])
print(x)
print(tf.reduce_mean(x))
'''
tf.Tensor(
[[1 2 3]
[2 2 3]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=int32)
tf.Tensor(2, shape=(), dtype=int32)
'''
计算张量沿着指定维度的和
#tf.reduce_sum(张量名,axis=操作轴)
print(tf.reduce_sum(x,axis=1))
#tf.Tensor([6 7], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
tf.Variable
tf.Variable()将变量标记为"可训练",别标记的变量会在反向传播中记录梯度信息。神经网络训练中,常用该函数标记待训练参数。
#tf.Variable(初始值)
w=tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([2,2],mean=0,stffev=1))
tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices
切分传入张量的第一维度,生成输入特征/标签对,构建数据集data=tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(输入特征,标签)
(Numpy和Tensor格式都可用该语句读入数据)
features=tf.constant([12,23,10,17])
labels=tf.constant([0,1,1,0])
dataset=tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((features,labels))
print(dataset)
for element in dataset:
print(element)
'''
<TensorSliceDataset element_spec=(TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.int32, name=None), TensorSpec(shape=(), dtype=tf.int32, name=None))>
(<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=12>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=0>)
(<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=23>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1>)
(<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=10>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=1>)
(<tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=17>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(), dtype=int32, numpy=0>)
'''
tf.GradientTape
with结构记录计算过程,gradient求出张量的梯度。
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
w=tf.Variable(tf.constant(3.0))
loss=tf.pow(w,2)
grad=tape.gradient(loss,w)
print(grad)
#tf.Tensor(6.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
σ w 2 σ w = 2 w = 2 ∗ 3.0 = 6.0 \frac{σ{w^2}}{σw}=2w=2*3.0=6.0 σwσw2=2w=2∗3.0=6.0
enumerate
enumerate是python的内建函数,它可遍历每个元素(如列表、元组或字符串)。组合为:索引 元素,常在for循环中使用。
#enumerate(列表名)
seq=['one','two','three']
for i,element in enumerate(seq):
print(i,element)
'''
0 one
1 two
2 three
'''
tf.one_hot
独热编码(one-hot encoding):在分类问题中,常用独热码做标签
标记类别:1表示是;0表示非
#tf.one_hot(待转换数据,depth=几分类)
classes=3
label=tf.constant([1,0,2])#输入的元素值最小为0,最大为2
output=tf.one_hot(label,depth=classes)
print(output)
'''
tf.Tensor(
[[0. 1. 0.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
'''
tf.nn.softmax
S
o
f
t
m
a
x
(
y
i
)
=
e
y
i
∑
j
=
0
n
e
y
i
Softmax(y_i)=\frac{e^y{_i}}{\sum^{n}_{j=0}e^y{_i}}
Softmax(yi)=∑j=0neyieyi
tf.nn.softmax(x)使输出符合概率分布。
当
n
分类的
n
个输出
(
y
0
,
y
1
,
y
2
.
.
.
y
n
−
1
)
通过
s
o
f
t
m
a
x
(
)
函数,使符合概率分布了。
当n分类的n个输出(y_0,y_1,y_2...y_{n-1})通过softmax()函数,使符合概率分布了。
当n分类的n个输出(y0,y1,y2...yn−1)通过softmax()函数,使符合概率分布了。
∀ x P ( X = x ) ∈ [ 0 , 1 ] 且 ∑ x P ( X = x ) = 1 ∀_xP(X=x)∈[0,1]且\sum_x P(X=x)=1 ∀xP(X=x)∈[0,1]且x∑P(X=x)=1
y=tf.constant([1.01,2.01,-0.66])
y_pro=tf.nn.softmax(y)
print("After softmax,y_pro is:",y_pro)
#After softmax,y_pro is: tf.Tensor([0.25598174 0.69583046 0.04818781], shape=(3,), dtype=float32)
assign_sub
赋值操作,更新参数的值并返回。
调用assign_sub前,先用tf.Variable定义变量w为可训练(可自更新)。
#w.assign_sub(w要自减的内容)
w=tf.Variable(4)
w.assign_sub(1)
print(w)
#<tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=() dtype=int32, numpy=3>
tf.argmax
返回张量沿指定维度最大值的索引。
#tf.argmax(张量名,axis=操作轴)
import numpy as np
test=np.array([[1,2,3],[2,3,4],[5,4,3],[8,7,2]])
print(test)
'''
[[1 2 3]
[2 3 4]
[5 4 3]
[8 7 2]]
'''
print(tf.argmax(test,axis=0))#返回每一列(经度)最大值的索引
#tf.Tensor([3 3 1], shape=(3,), dtype=int64)
print(tf.argmax(test,axis=1))#返回每一行(维度)最大值的索引
#tf.Tensor([3 3 1], shape=(3,), dtype=int64)
2.2.1 数学运算
2.2.1.1 四则运算
两个张量的对应元素相加
#tf.add(张量1,张量2)
a=tf.ones([1,3])
b=tf.fill([1,3],3)
print(tf.add(a,b))
#tf.Tensor([[4. 4. 4]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
两个张量的对应元素相减
#tf.subtract(张量1,张量2)
print(tf.subtract(a,b))
#tf.Tensor([[-2. -2. -2]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
两个张量对应的元素相乘
#tf.multiply(张量1,张量2)
print(tf.multiply(a,b))
#tf.Tensor([[3. 3. 3]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
两个张量的对应元素相除
#tf.divide(张量1,张量2)
print(tf.divide(b,a))
#tf.Tensor([[3. 3. 3]], shape=(1, 3), dtype=float32)
只有维度相同的张量才能做四则运算
2.2.1.2 平方、次方与开方
计算某个张量的平方
#tf.square(张量名)
print(tf.square(a))
#tf.Tensor([[9. 9.]], shape=(1, 2), dtype=float32)
计算某个张量的n次方
#tf.pow(张量名,n次方数)
print(tf.pow(a,3))
#tf.Tensor([[27. 27.]], shape=(1, 2), dtype=float32)
计算某个张量的开方
#tf.sqrt(张量名)
print(tf.sqrt(a))
#tf.Tensor([[1.7320508 1.7320508]], shape=(1, 2), dtype=float32)
2.2.1.3 矩阵乘
实现两个矩阵相乘
#tf.matmul(矩阵1,矩阵2)
a=tf.ones([3,2])
print(a)
'''
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]
[1. 1.]], shape=(3, 2), dtype=float32)
'''
b=tf.fill([2,3],3)
print(b)
'''
tf.Tensor(
[[3. 3. 3.]
[3. 3. 3.]], shape=(2, 3), dtype=float32)
'''
print(tf.matmul(a,b))
'''
tf.Tensor(
[[6. 6. 6.]
[6. 6. 6.]
[6. 6. 6.]], shape=(3, 3), dtype=float32)
'''
2.3 鸢尾花分类
#数据集读入
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
x_data=load_iris().data #返回iris数据集所有输入属性
y_data=load_iris().target #返回iris数据集所有标签
#数据集乱序
np.random.seed(116) #使用相同的seed,使输入特征/标签一一对应
np.random.shuffle(x_data)
np.random.seed(116)
np.random.shuffle(y_data)
tf.random.set_seed(116)
#数据集分割出永不相见的训练集和测试集
x_train=x_data[:-30]
y_train=y_data[:-30]
x_test=x_data[-30:]
y_test=y_data[-30:]
#数据类型转换
x_train=tf.cast(x_train,tf.float32)
x_test=tf.cast(x_test,tf.float32)
#配成[输入特征,标签]对,每次喂一小撮(batch)
train_db=tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_train,y_train)).batch(32)
test_db=tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test,y_test)).batch(32)
#定义神经网络中所有可训练参数
w1=tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([4,3],stddev=0.1,seed=1))
b1=tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([3],stddev=0.1,seed=1))
lr=0.1 #学习率为0.1
train_loss_results=[]#将每轮的loss记录在此列表中,为后续的loss曲线提供数据
test_acc=[]#将每轮的acc记录在此列表中,为后续acc曲线提供数据
epoch=500#循环500轮
loss_all=0#每轮分4个step,loss_all记录四个step生成的4个loss的和
#原理
#嵌套循环迭代,with更新参数,显示当前loss
for epoch in range(5):#数据集级别迭代
for step,(x_train,y_train) in enumerate(train_db):#batch级别迭代
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
y=tf.matmul(x_train,w1)+b1#神经网络乘加运算
y=tf.nn.softmax(y)#使输出的y符合概率分布
y_=tf.one_hot(y_train,depth=3)#将标签值转换成独热码格式,方便计算loss
loss=tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_-y))#采用均方误差损失函数
loss_all+=loss.numpy()
#计算loss对各个参数的梯度
grads=tape.gradient(loss,[w1,b1])
#实现梯度更新w1=w1-lr*w1_grad
w1.assign_sub(lr*grads[0])
b1.assign_sub(lr*grads[1])
#每个epoch,打印loss信息
print("epoch:{},loss:{}".format(epoch,loss_all/4))
train_loss_results.append(loss_all/4)#将四个step的loss求平均记录在此变量中
loss_all=0#loss_all归零,为记录下一个epoch的loss做准备
#测试部分
#total_correct为预测对的样本个数,total_number为测试的总样本数,将这两个变量都初始化为0
total_correct,total_number=0,0
for x_test,y_test in test_db:
#使用更新后的参数进行预测
y=tf.matmul(x_test,w1)+b1
y=tf.nn.softmax(y)
pred=tf.argmax(y,axis=1)#返回y中最大值的索引,即预测分类
#将pred转换为y_test的数据类型
pred=tf.cast(pred,dtype=y_test.dtype)
#若分类正确,则correct=1,否则为0,将bool型的值转化为int型
correct=tf.cast(tf.equal(pred,y_test),dtype=tf.int32)
#将每个batch的correct数加起来
correct=tf.reduce_sum(correct)
#将所有batch的correct数加起来
total_correct+=int(correct)
#total_number为测试的总样本数,也就是x_test的行数,shape[0]返回变量的行数
total_number+=x_test.shape[0]
#总的准确率等于total_correct/total_number
acc=total_correct/total_number
test_acc.append(acc)
print("Test_acc:",acc)
print("--------------")
'''
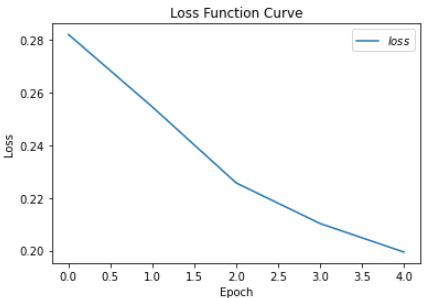
epoch:0,loss:0.2821310982108116
Test_acc: 0.16666666666666666
--------------
epoch:1,loss:0.25459614023566246
Test_acc: 0.16666666666666666
--------------
epoch:2,loss:0.22570249065756798
Test_acc: 0.16666666666666666
--------------
epoch:3,loss:0.21028400212526321
Test_acc: 0.16666666666666666
--------------
epoch:4,loss:0.19942264631390572
Test_acc: 0.16666666666666666
--------------
'''
#绘制loss曲线
plt.title('Loss Function Curve')#图片标题
plt.xlabel('Epoch')#x轴变量
plt.ylabel('Loss')#y轴变量
plt.plot(train_loss_results,label="$loss$") #逐点画出train_loss_results值并连线
plt.legend()#画出曲线坐标
plt.show()#画出图像
#绘制Accurach曲线
plt.title('Acc Cure')#图片标题
plt.xlabel('Epoch')#x轴变量
plt.ylabel('Acc')#y轴变量名称
plt.plot(test_acc,label="$Accurach$")#逐点画出test_acc曲线,连线图标Accurach
plt.legend()
plt.show()
























 787
787











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










