第一部分:HandlerMapping结构
首先我们要搞清楚HandlerMapping是一个处理器映射器。也就是需要要根据用户的提交的请求找到对应的处理该请求的过滤器链
1. HandlerMapping接口
在HandlerMapping中声明了一堆常量和一个 getHandler方法。
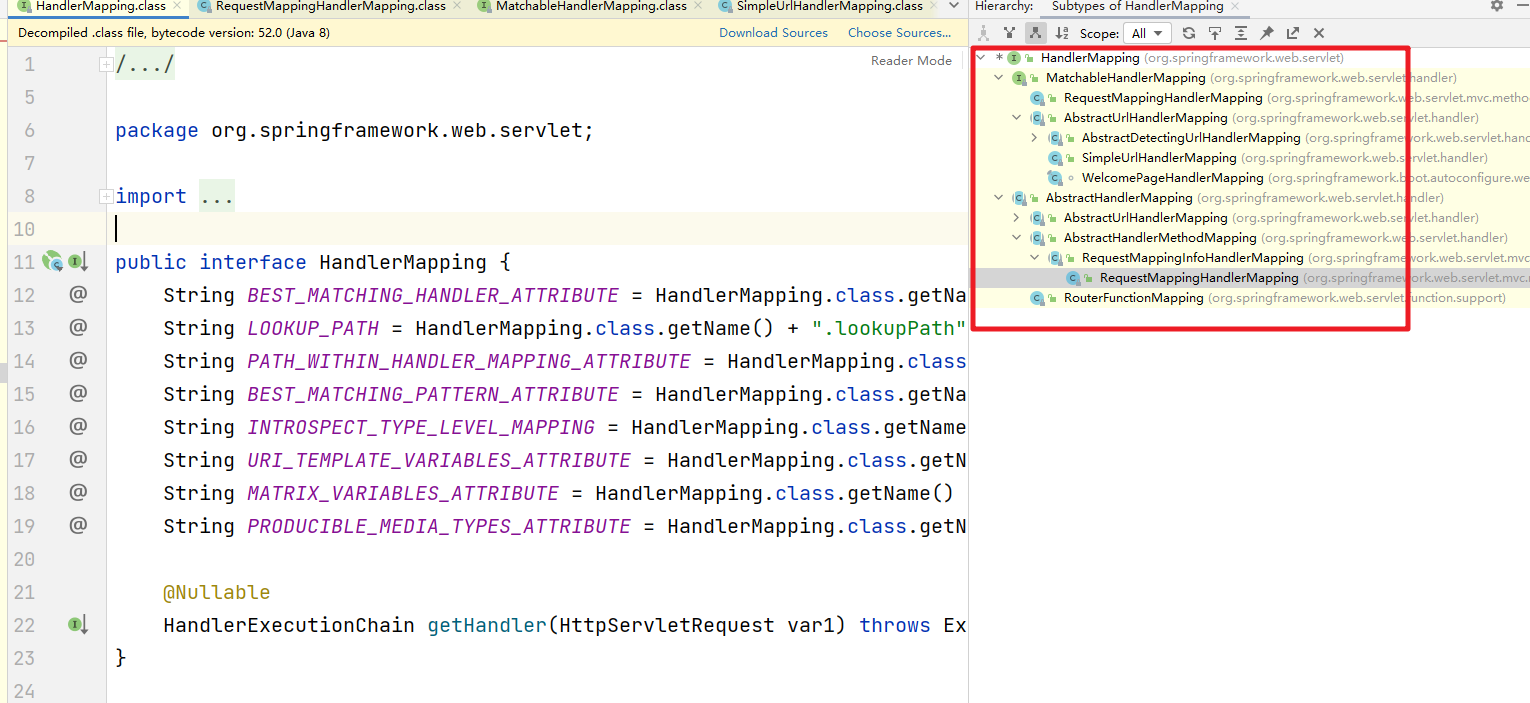
该方法返回的就是对应的处理器链。对应的体系结构
2. MatchableHanderMapping
在MatchableHandlerMapping中定义了匹配请求的方法
public interface MatchableHandlerMapping extends HandlerMapping {
@Nullable
RequestMatchResult match(HttpServletRequest var1, String var2);
}
3. AbstractHandlerMapping
AbstractHandlerMapping是HandlerMapping的抽象实现,同时实现了Order接口继承了WebApplicationObjectSupport类,order接口主要是为了如果spring容器中有多个HandlerMapping,则按照order 排序去一次使用HandlerMapping获取handler对象,order小的优先被使用。由于该处理器抽象类继承WebApplicationObjectSupport对象,通过查看WebApplicationObjectSupport的继承关系,其也间接实现了ApplicationContextAware和ServlerContextAware,意味着该类在spring容器中被初始化完成后自动拥有ApplicationContext对象和ServletContext对象。
public abstract class AbstractHandlerMapping extends WebApplicationObjectSupport
implements HandlerMapping, Ordered, BeanNameAware {
}
先来看看相关的属性信息
@Nullable // 对于通过该处理器映射器如果没有获取到对应的Handlerm,则使用的默认Handler, 可以通过xml/注解的形式配置。 private Object defaultHandler; //Url路径匹配的帮助类,包含ur编码方式设置获取,或者根据请求请求路径等方法 private UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper(); // Spring提供的路径匹配策略接口的路径匹配器 private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher(); // 我们可以通过该属性来设置相关的拦截器,设置的方式可以通过xml配置,也可以通过子类的钩子extendInterceptors扩展设置 private final List<Object> interceptors = new ArrayList(); //该集合下的拦截器不需要匹配会通过getHandler()方法全部添加到HandlerExecutionChain中 private final List<HandlerInterceptor> adaptedInterceptors = new ArrayList(); // 跨域相关的 @Nullable private CorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource; private CorsProcessor corsProcessor = new DefaultCorsProcessor(); //排序属性 默认最大值,如果不设置意味着其对应的处理器对象优先级最小 private int order = 2147483647; @Nullable private String beanName;
重点方法:
initApplicationContext
AbstractHandlerMapping继承了WebApplicationObjectSupport对象,提供了一个initApplicationContext()方法,这个方法主要是对上面的三种类型的拦截器集合进行相关处理。
结构是 ApplicationContextAware 接口IoC实例化对应的对象的时候会执行 setApplicationContext方法
public interface ApplicationContextAware extends Aware {
void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException;
}
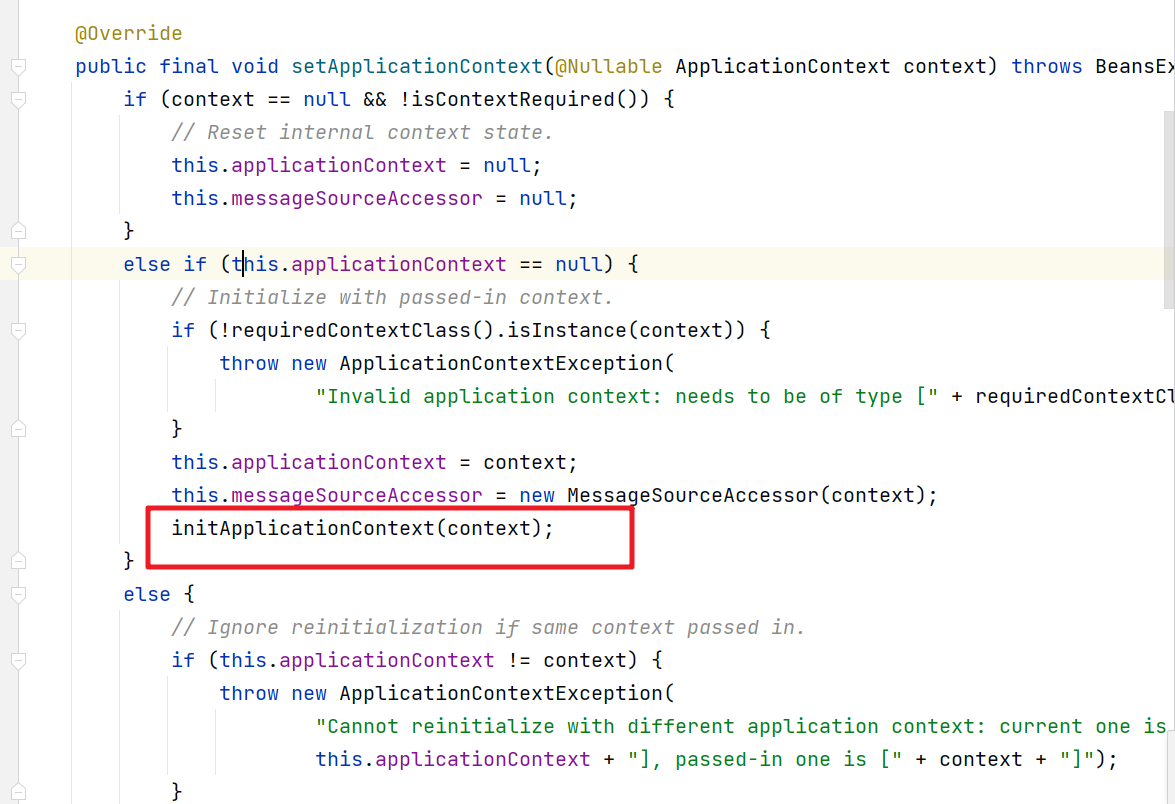
initApplicationContext方法:
@Override
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
//spring提供钩子函数,子类可以实现该方法来为集合设置拦截器
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
//从spring容器中获取所有MappedInterceptor
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
//将所有设置在interceptors中的拦截器按照类型添加到adaptedInterceptors中
initInterceptors();
}
BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping
基于Controller接口的实现。可以看看对应的实现
AbstractDetectingUrlHandlerMapping中间的具体实现
@Override
public void initApplicationContext() throws ApplicationContextException {
super.initApplicationContext();
detectHandlers();
}
然后进入detectHandlers方法
protected void detectHandlers() throws BeansException {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = obtainApplicationContext();
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlersInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, Object.class) :
applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
// Take any bean name that we can determine URLs for.
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
String[] urls = determineUrlsForHandler(beanName);
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(urls)) {
// URL paths found: Let's consider it a handler.
registerHandler(urls, beanName);
}
}
if (mappingsLogger.isDebugEnabled()) {
mappingsLogger.debug(formatMappingName() + " " + getHandlerMap());
}
else if ((logger.isDebugEnabled() && !getHandlerMap().isEmpty()) || logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Detected " + getHandlerMap().size() + " mappings in " + formatMappingName());
}
}
在进入子类中
@Override
protected String[] determineUrlsForHandler(String beanName) {
List<String> urls = new ArrayList<>();
if (beanName.startsWith("/")) {
urls.add(beanName);
}
String[] aliases = obtainApplicationContext().getAliases(beanName);
for (String alias : aliases) {
if (alias.startsWith("/")) {
urls.add(alias);
}
}
return StringUtils.toStringArray(urls);
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping:基于注解的方式@Controller @RequestMapping
我们先进入父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping 中,我们可以看到实现了
public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
这个接口。所以我们需要看的是 afterPropertiesSet 方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
进入 initHandlerMethods()方法中
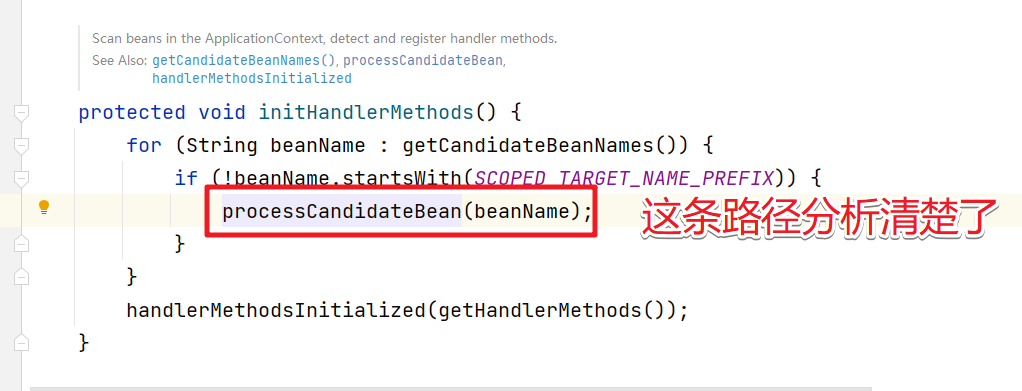
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
for (String beanName : getCandidateBeanNames()) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
processCandidateBean(beanName);
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
processCandidateBean方法会做相关的判断
protected void processCandidateBean(String beanName) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Could not resolve type for bean '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
isHandler方法就是要找到满足条件的控制器了.找到@Controller或者@RequestMapping标注的java类。
@Override
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
然后再通过detectHandlerMethods来找到对应的处理请求的方法。
/**
* 根据自定义的metadataLookup参数在指定类上查询符合要求的method结果集作为结果返回
*
* targetType: 方法搜索所基于的目标类的类型
* metadataLookup: 自定义的metadataLookup参数。如果存在匹配,则返回要与给定方法关联的非空元数据,如果没有匹配,则返回null
*/
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, final MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {
final Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {
// 如果是代理类,找到实际的类型
specificHandlerType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetType);
handlerTypes.add(specificHandlerType);
}
handlerTypes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetType));
// 遍历所有找到的class对象:包括当前类自身、其父类、其实现的接口
for (Class<?> currentHandlerType : handlerTypes) {
final Class<?> targetClass = (specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType);
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, method -> {
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
// 获取方法关联的元数据,这里实际是指注解
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
// 找到所提供的Method的原始方法
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
}
return methodMap;
}
doWithMethods:反射获取每个方法
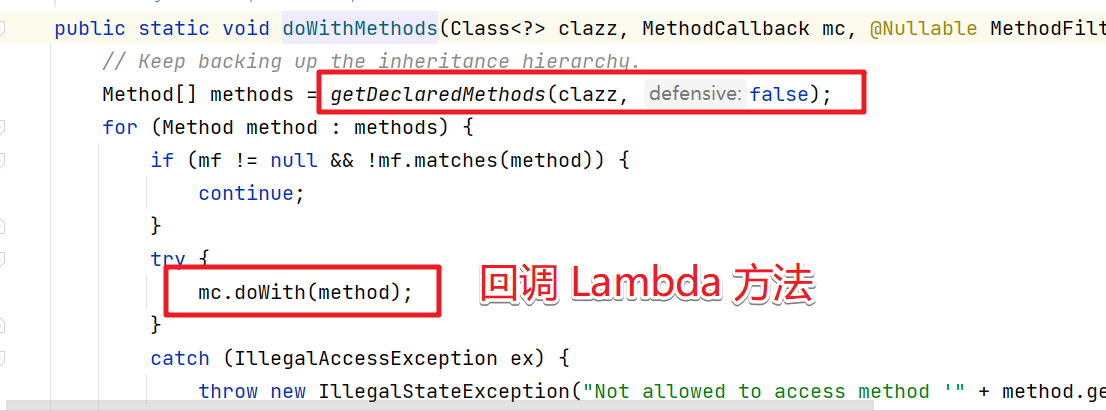
getMappingForMethod方法。根据方法获取对应的RequestMappingInfo
@Override
@Nullable
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
String prefix = getPathPrefix(handlerType);
if (prefix != null) {
info = RequestMappingInfo.paths(prefix).options(this.config).build().combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
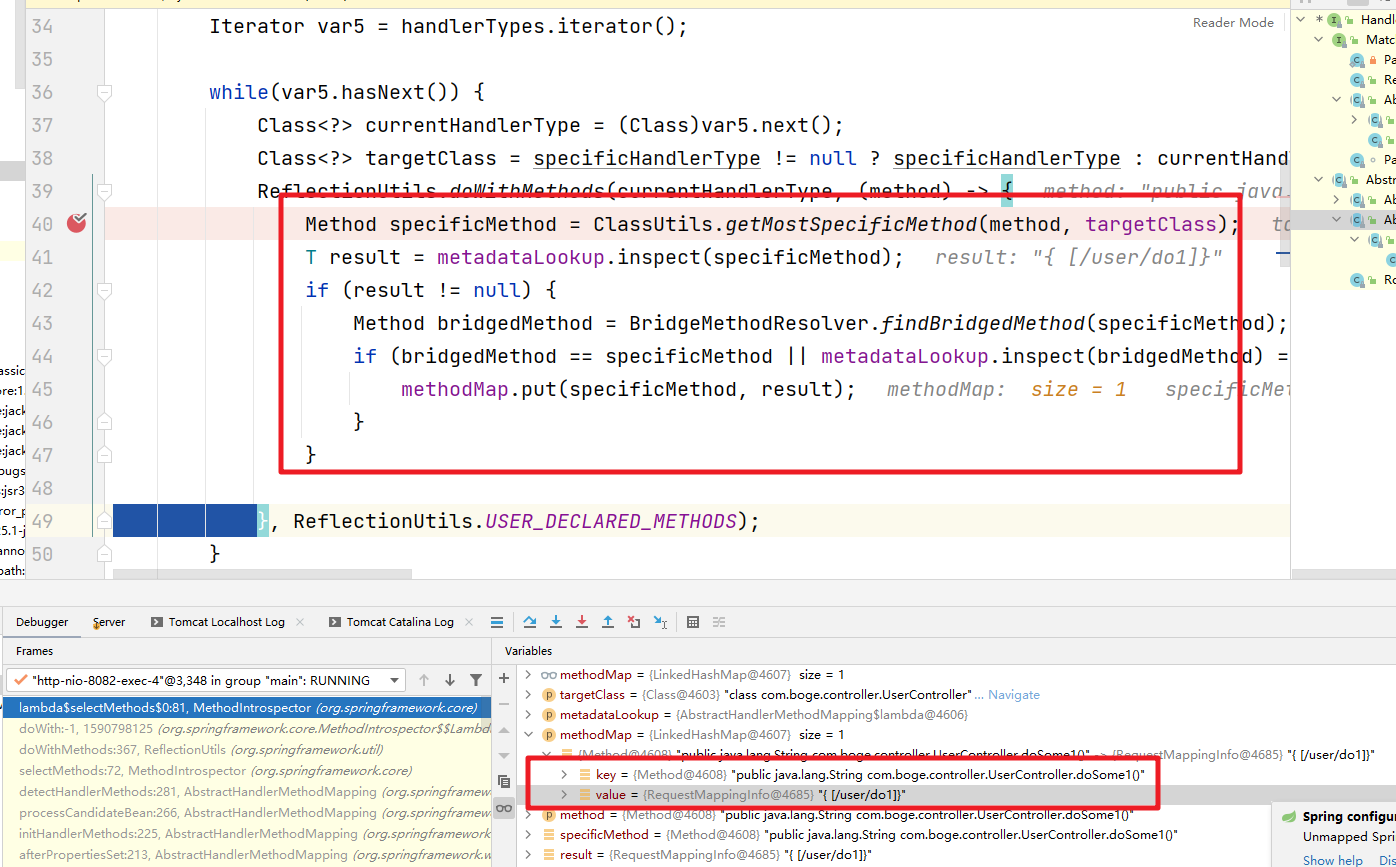
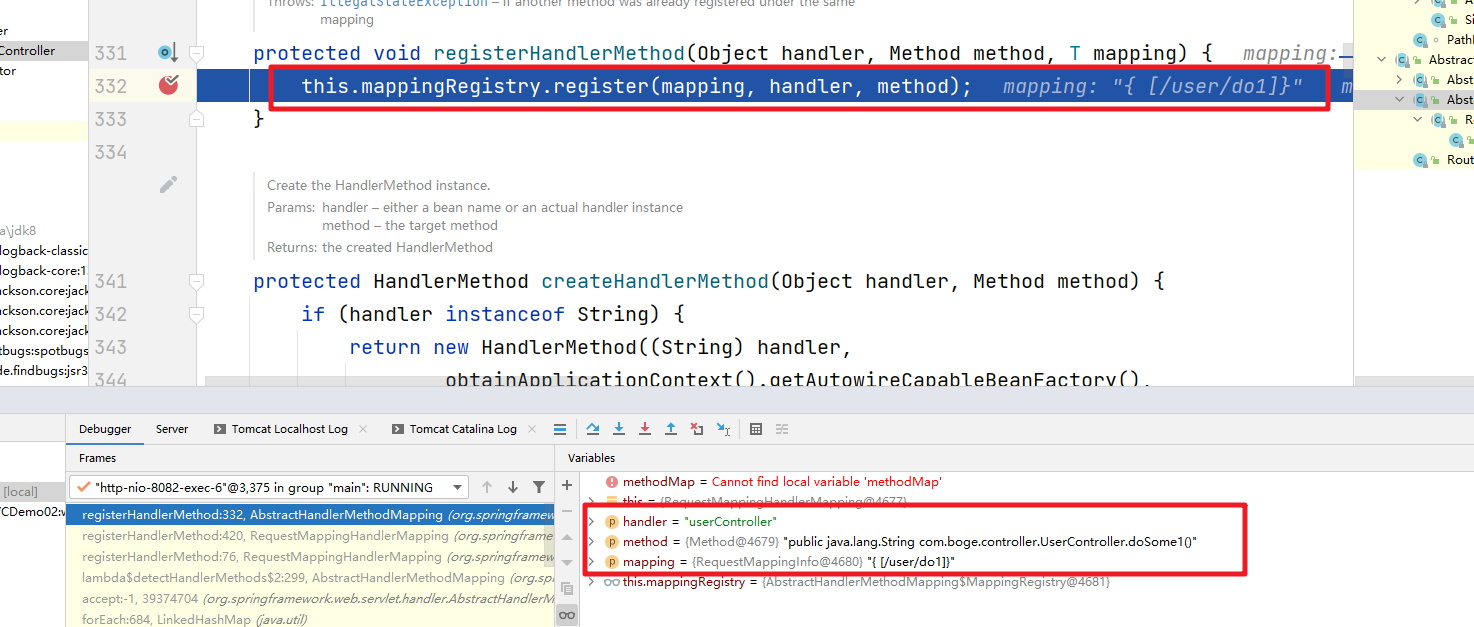
调试跟踪可以发现 mappingRegistry 中记录了 处理器 方法 和 RequestMappingInfo的相关信息
再往下面看 handlerMethodsInitialized 方法。做了简单的统计
getHandler方法
上面的方法介绍了初始化的过程。接下来看看。当具体请求到来的时候是如何获取对应的Handler的。也就是getHandler方法。
AbstractHandlerMapping的核心方法就是该方法,主要作用是根据请求获取包装了Handler对象和拦截器的HandlerExecutionChain对象。该方法采用模板方法获取拦截器处理器链。
/**
* 根据请求对象获取对应的HandlerExecutionChain 对象
* @param request 请求对象
* @return 返回处理器执行链
* @throws Exception
*/
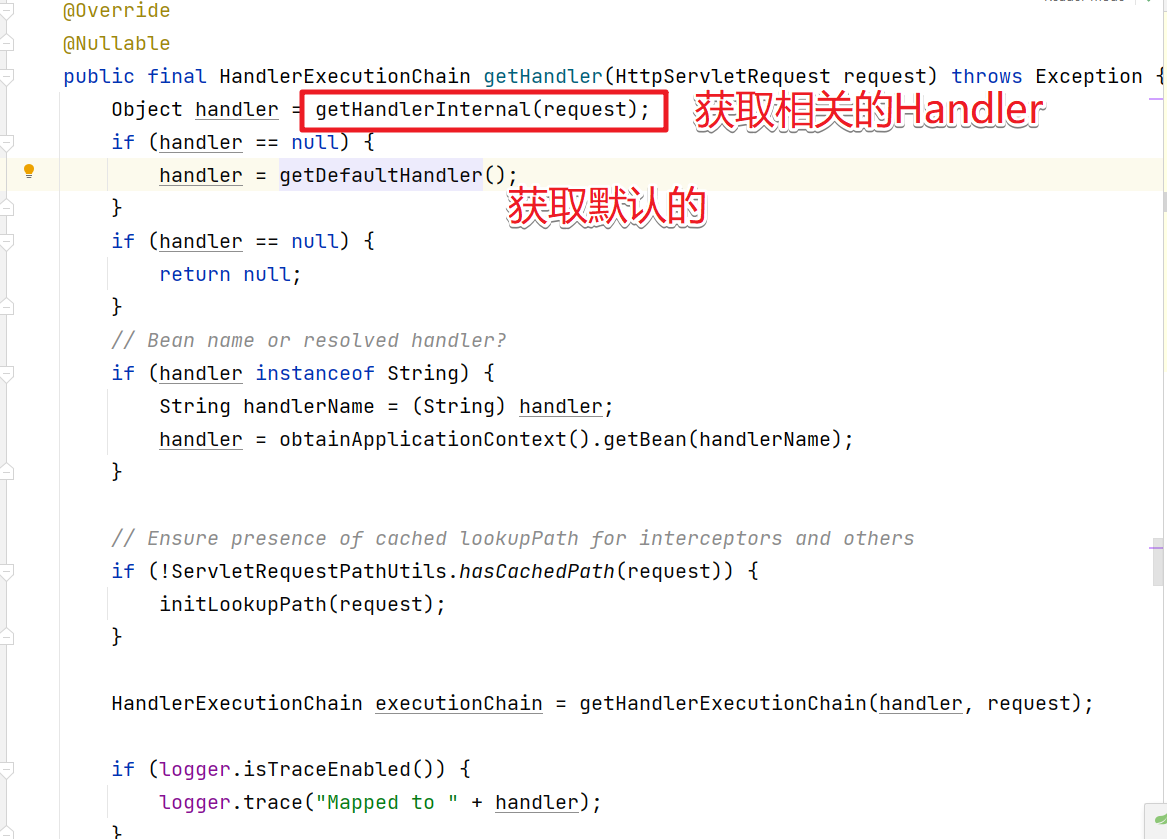
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
//交由子类实现的根据请求获取处理器的具体逻辑 不同的子类获取Handler的逻辑不同
//这个也是众多子类的扩展点
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
//如果没有获取到Handler 则获取默认的Handler
//默认的处理器可以通过配置映射器实例的时候通过属性设置
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
//如果默认的Handler还是没有则返回空
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
//Handler处理器是字符串类型 说明获取的Handler是beanName
//则从spring 容器中获取bean实例对象
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
//为Handler添加拦截器,并最终返回HandlerExecutionChain对象
return getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
}
getHandlerInternal方法是交给子类来处理的。先看看Controller 接口的方式,进入到 AbstractHandlerMapping中
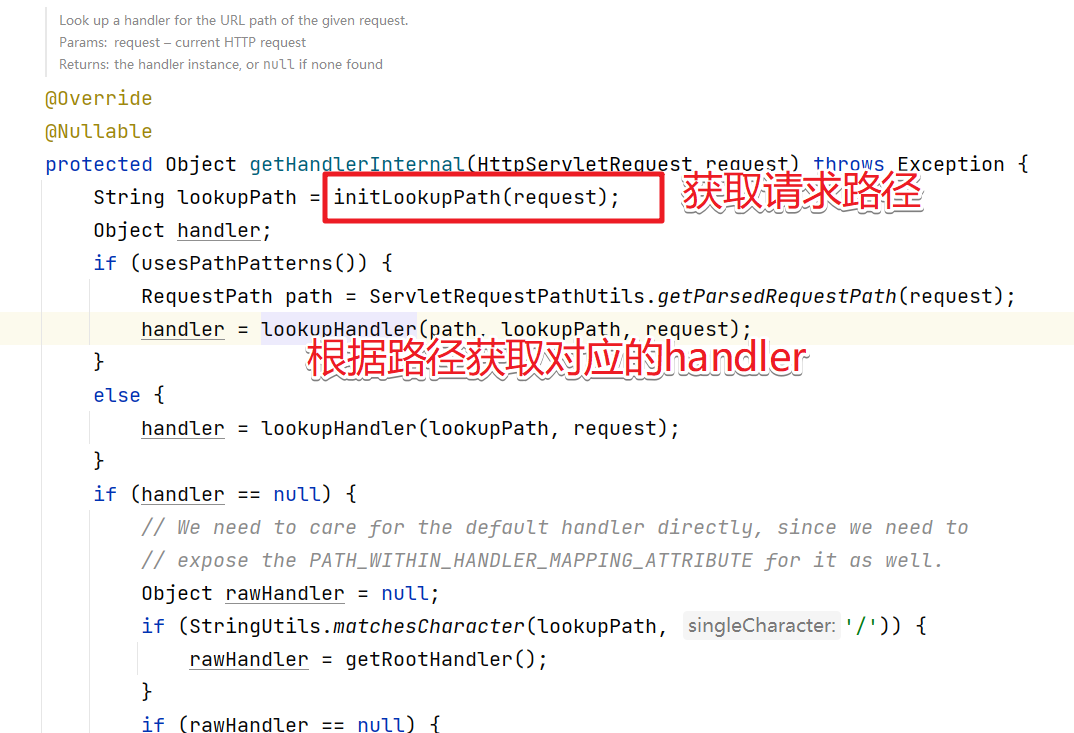
进入到lookupHandler方法中
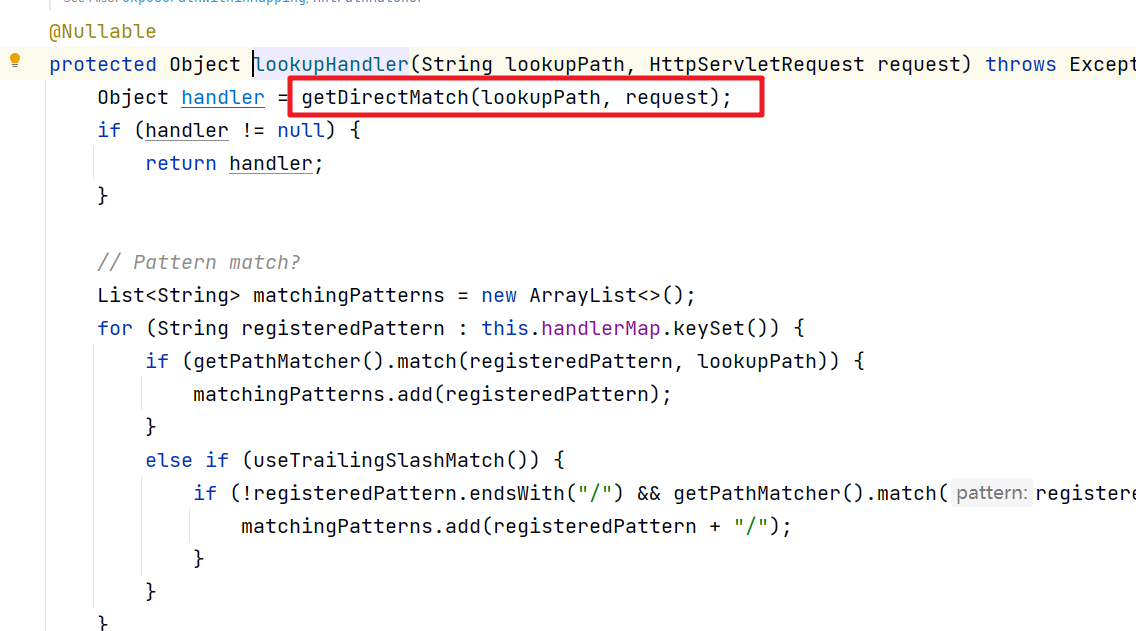
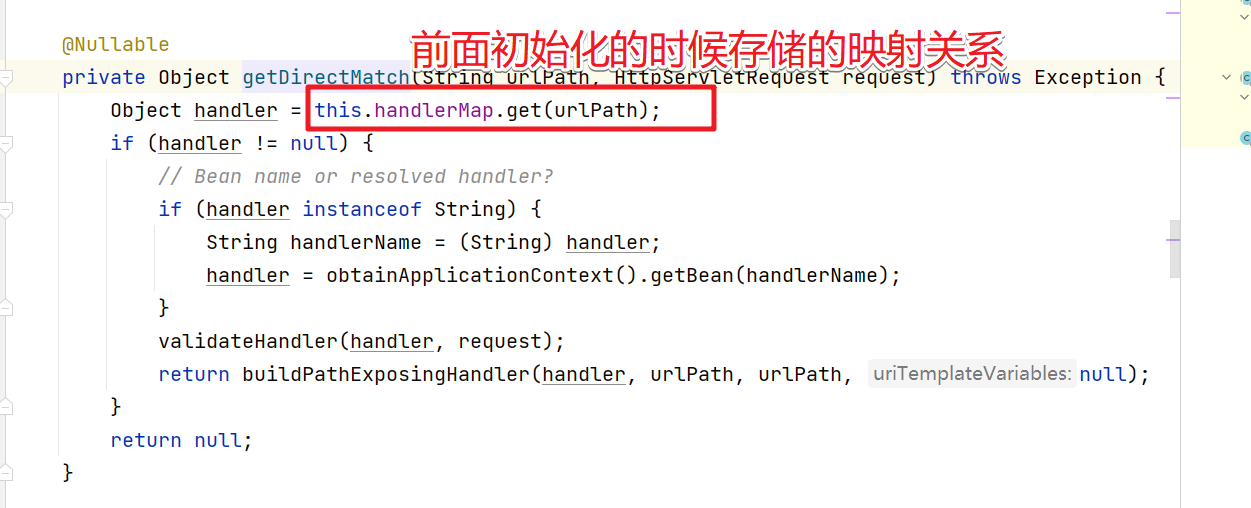
进入到getDirectMathch方法中找到对应的Handler
然后再看看 @Controller注解的方式的处理,进入getHandlerInternal方法查看
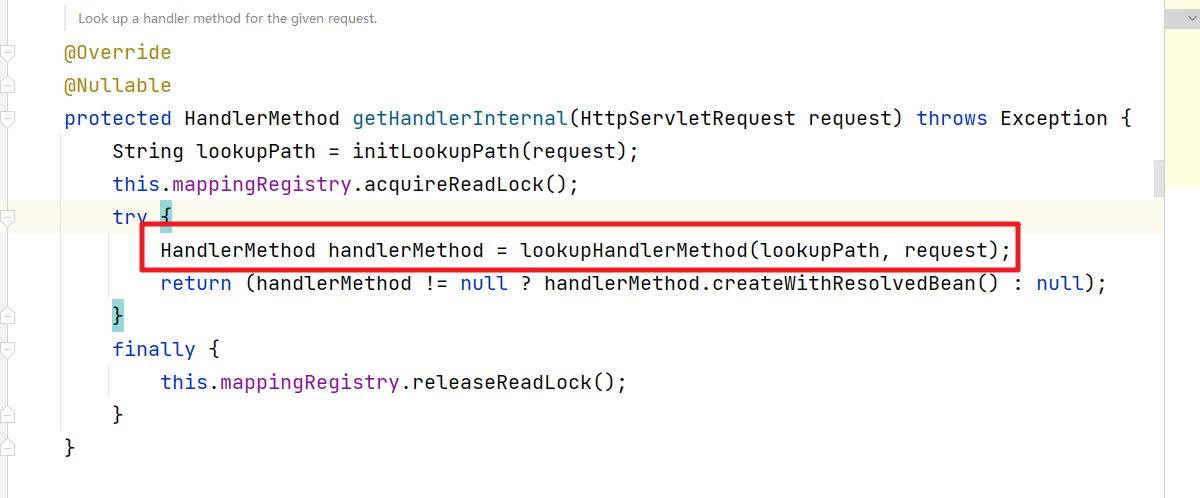
进入lookupHandlerMethod方法

回来继续看
getHandlerExecutionChain
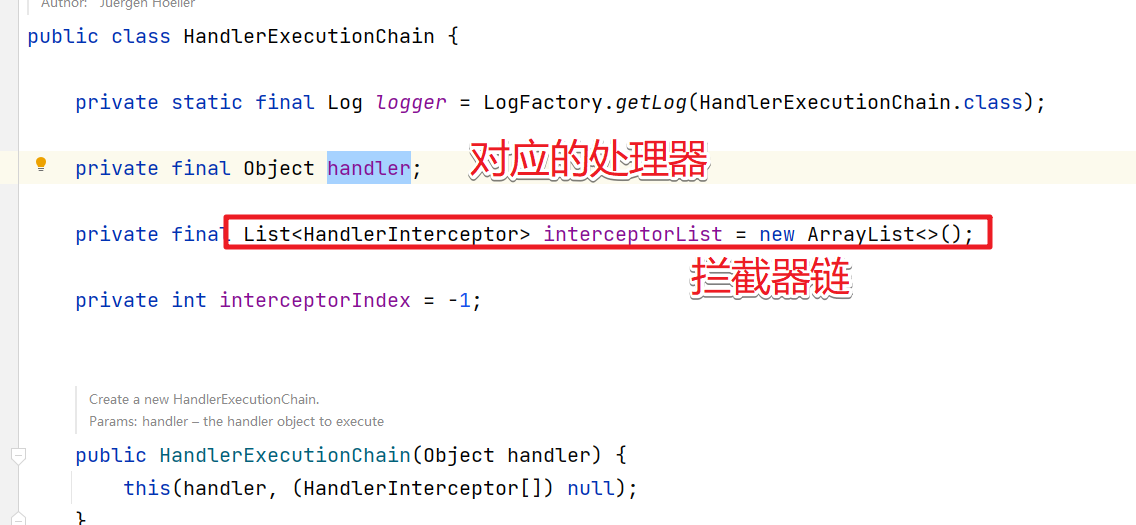
该方法主要是对getHandlerInternal()方法返回的Handler对象,将其包装成HandlerExecutionChain对象。
/**
* 将Handler对象包装成 HandlerExecutionChain
*/
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
//判断如果当前的Handler本身是HandlerExecutionChain对象 则强转
//否则创建HandlerExecutionChain对象
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
//将AdaptedInterceptors 中的所有拦截器添加到 (不需要进行匹配)
chain.addInterceptors(getAdaptedInterceptors());
//根据request找寻对应的逻辑处理路径 lookupPath
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
//因为mappedInterceptors里面的拦截器都需要匹配成功才可以所以此处需要对所有的
// MappedInterceptor拦截器判断其是否匹配,匹配成功才将其添加到HandlerExecutionChain对象
for (MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor : this.mappedInterceptors) {
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
return chain;
}
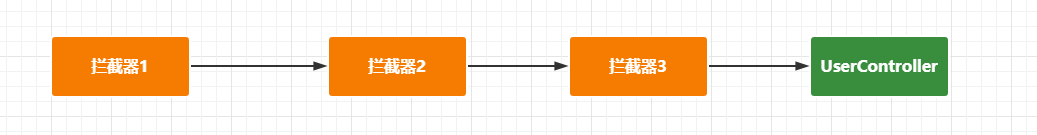
最后关联到DispatcherServlet中的代码
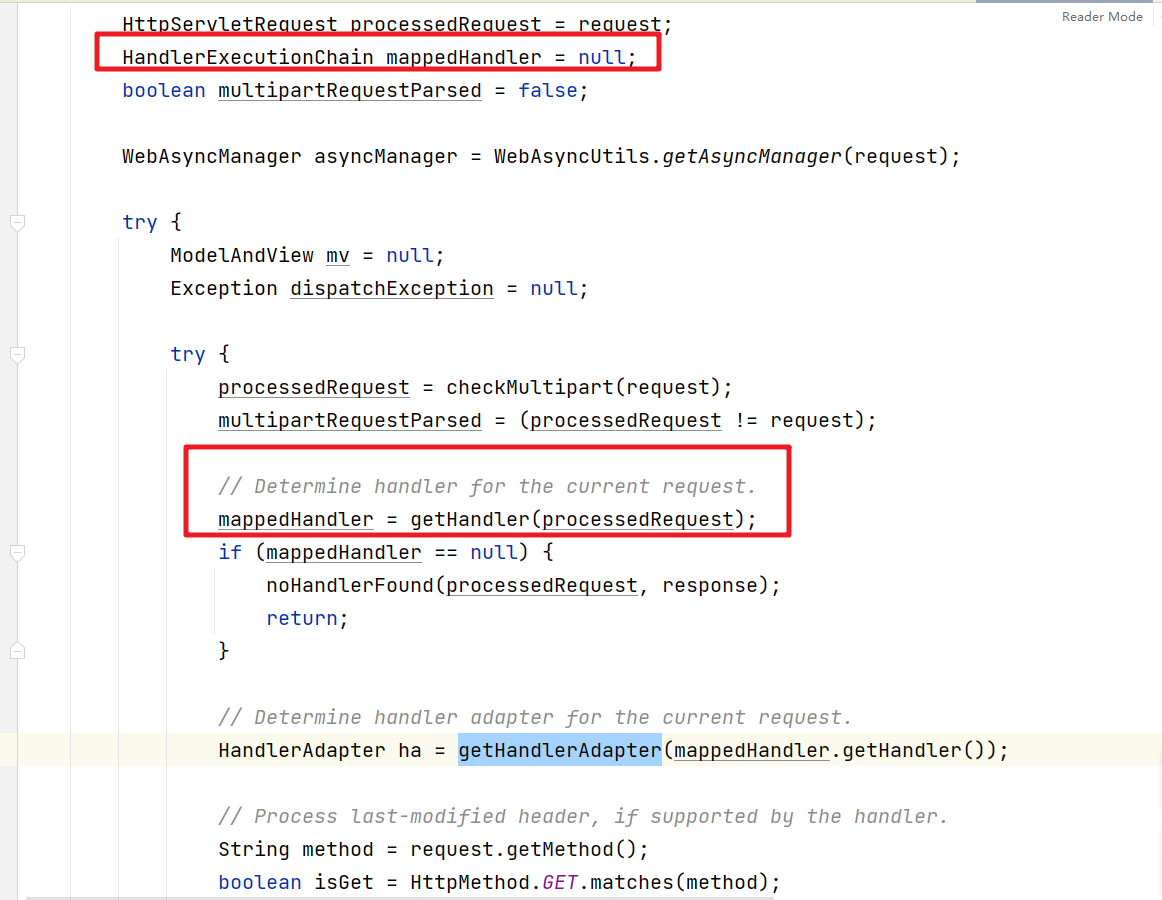
我们就请求了相关的含义了
第二部分、HandlerAdapter
然后再看看对应的处理器适配器
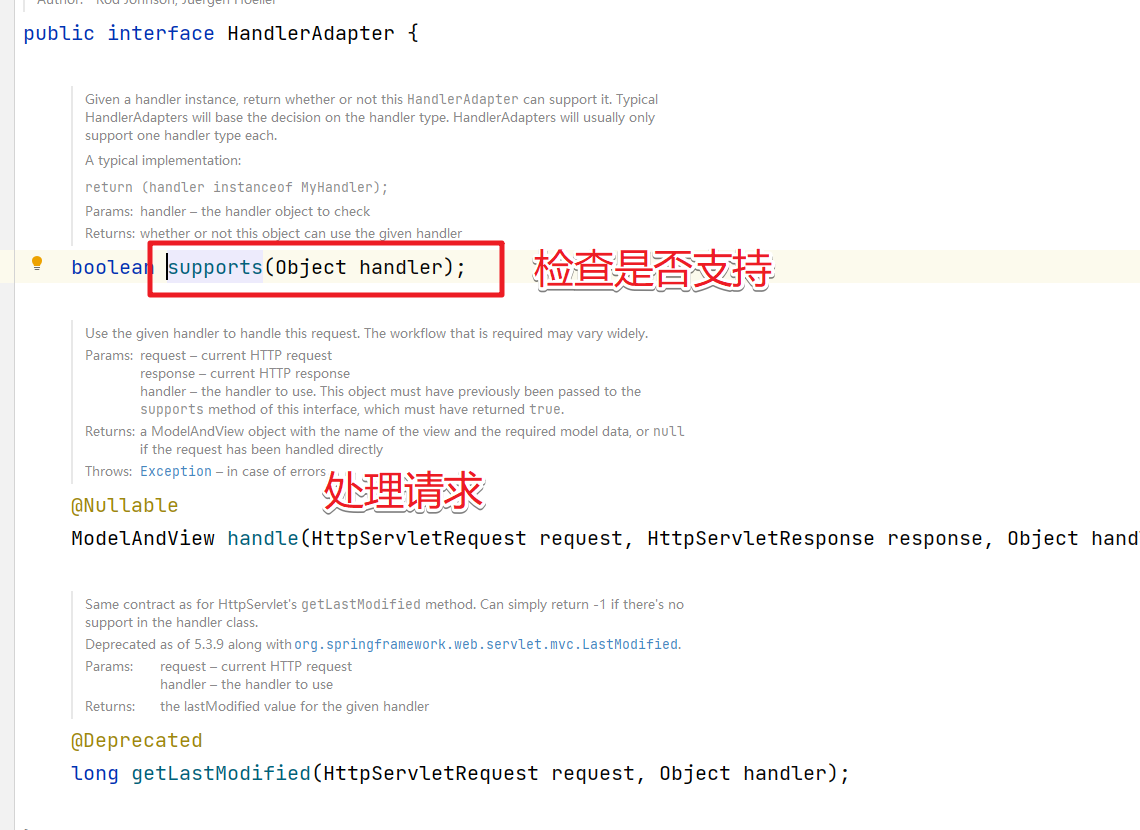
1.supports方法
supports方法的作用是判断当前请求的Handler是否适配
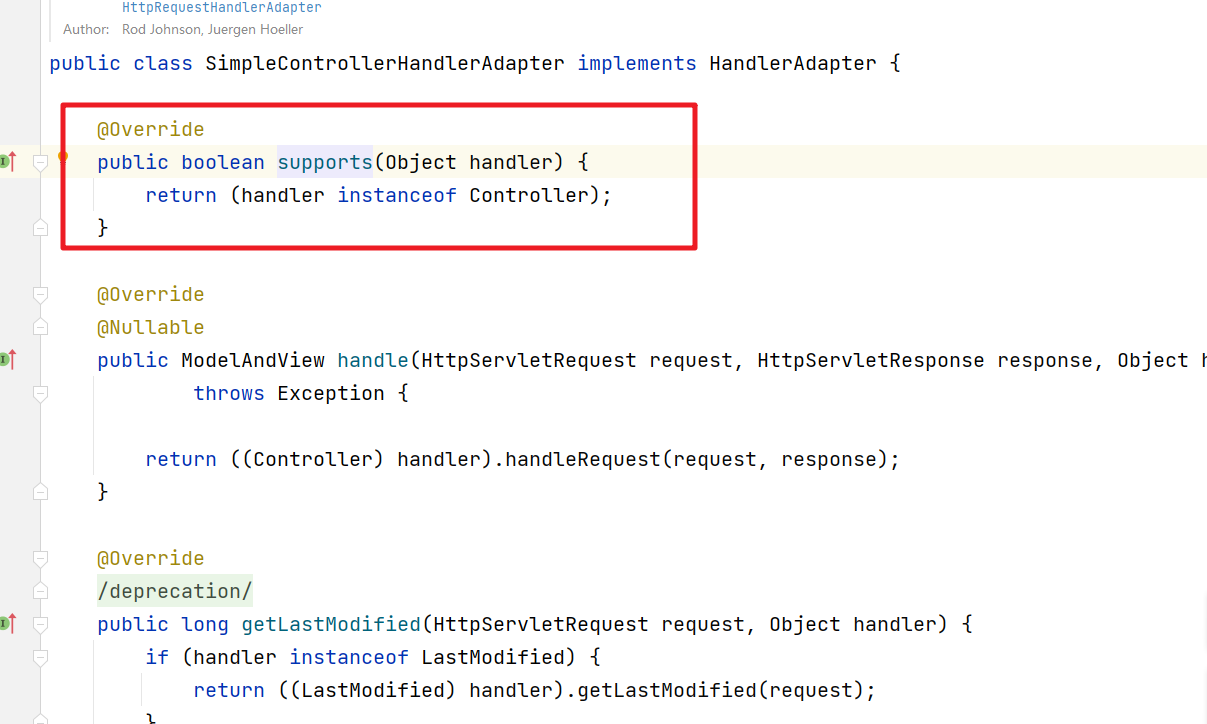
1.1 Controller接口
Controller接口的方式。判断handler是否实现了Controller接口
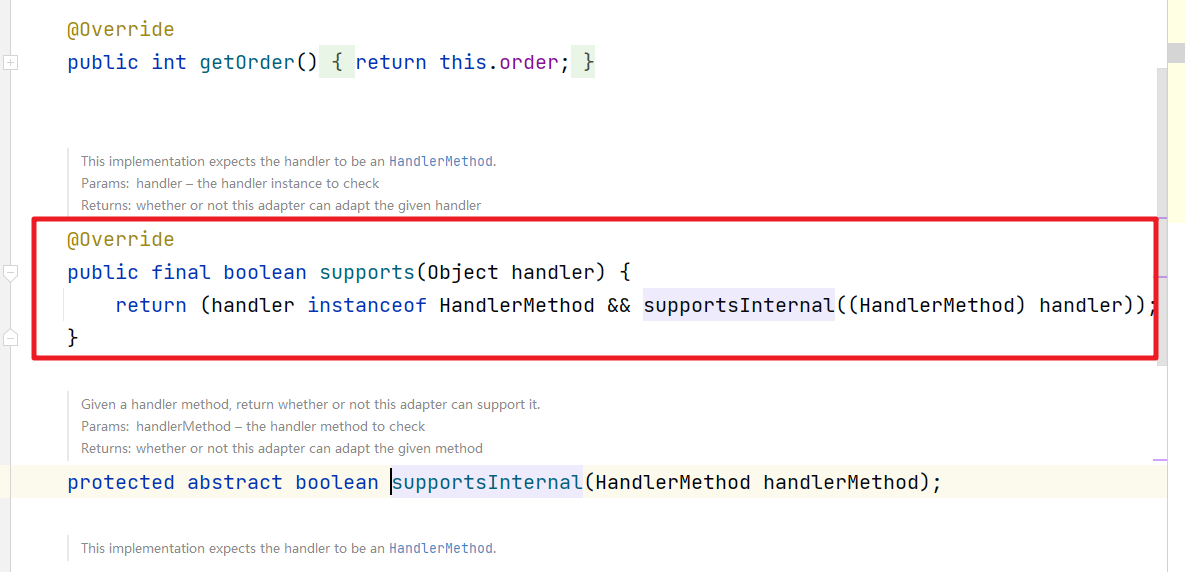
1.2 Controller注解
然后看看基于注解的方式的判断
2. handle
然后看看handle方法的处理
2.1 Controller接口
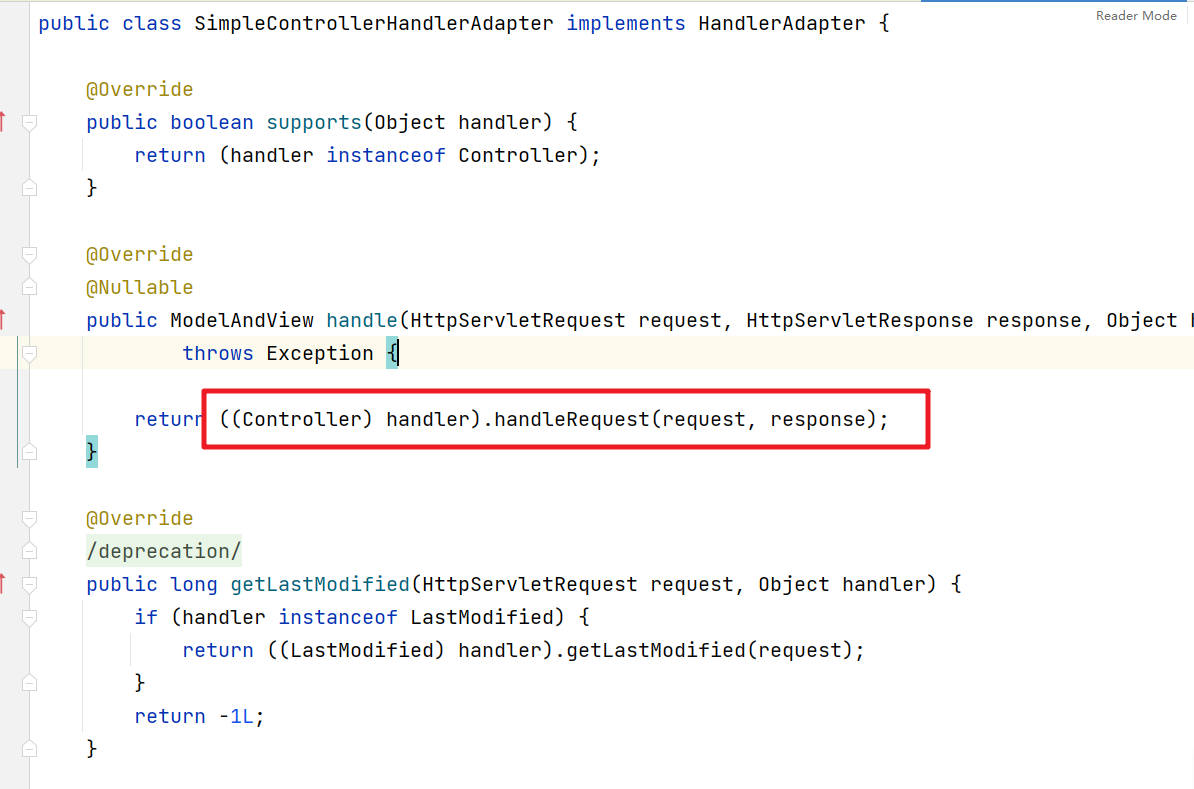
2.2 Controller注解
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
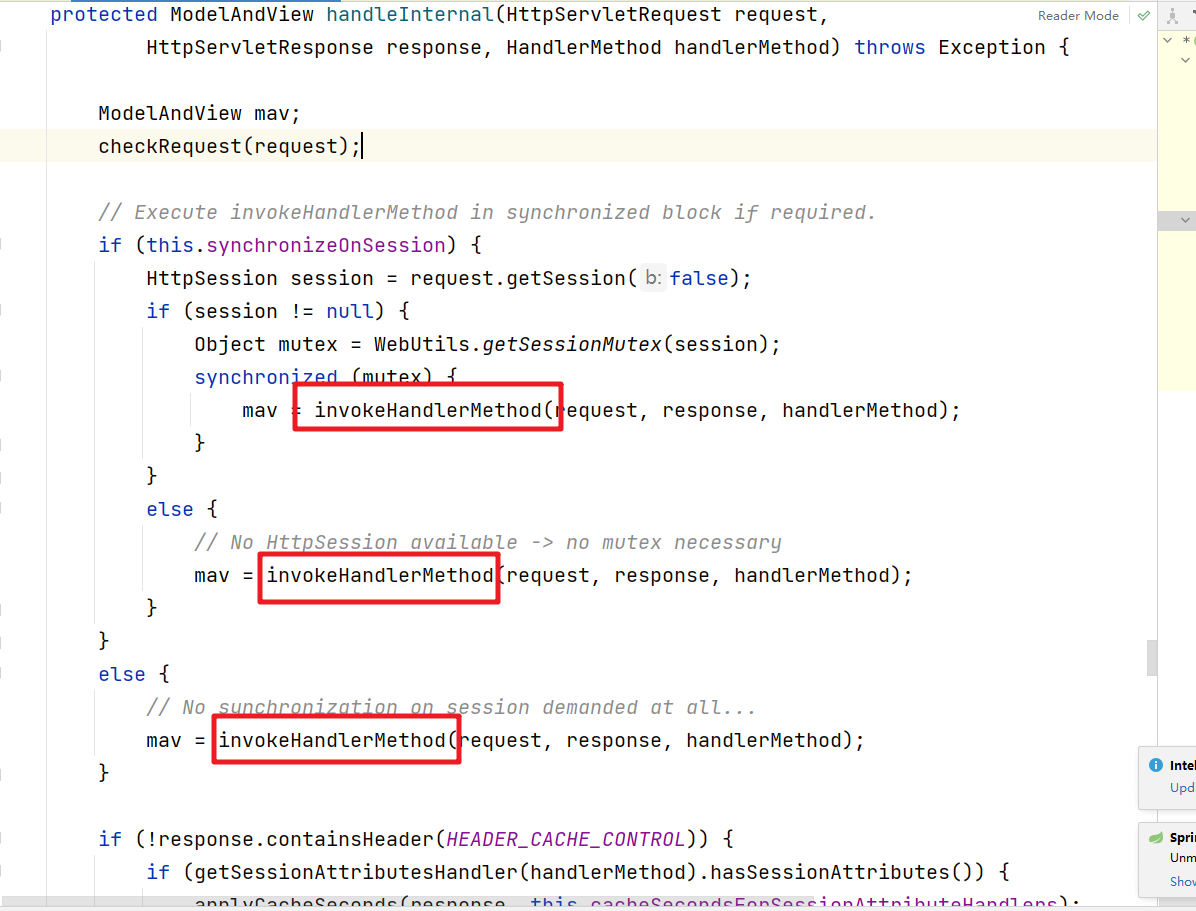
进入到关键的invokeHandlerMethod方法中
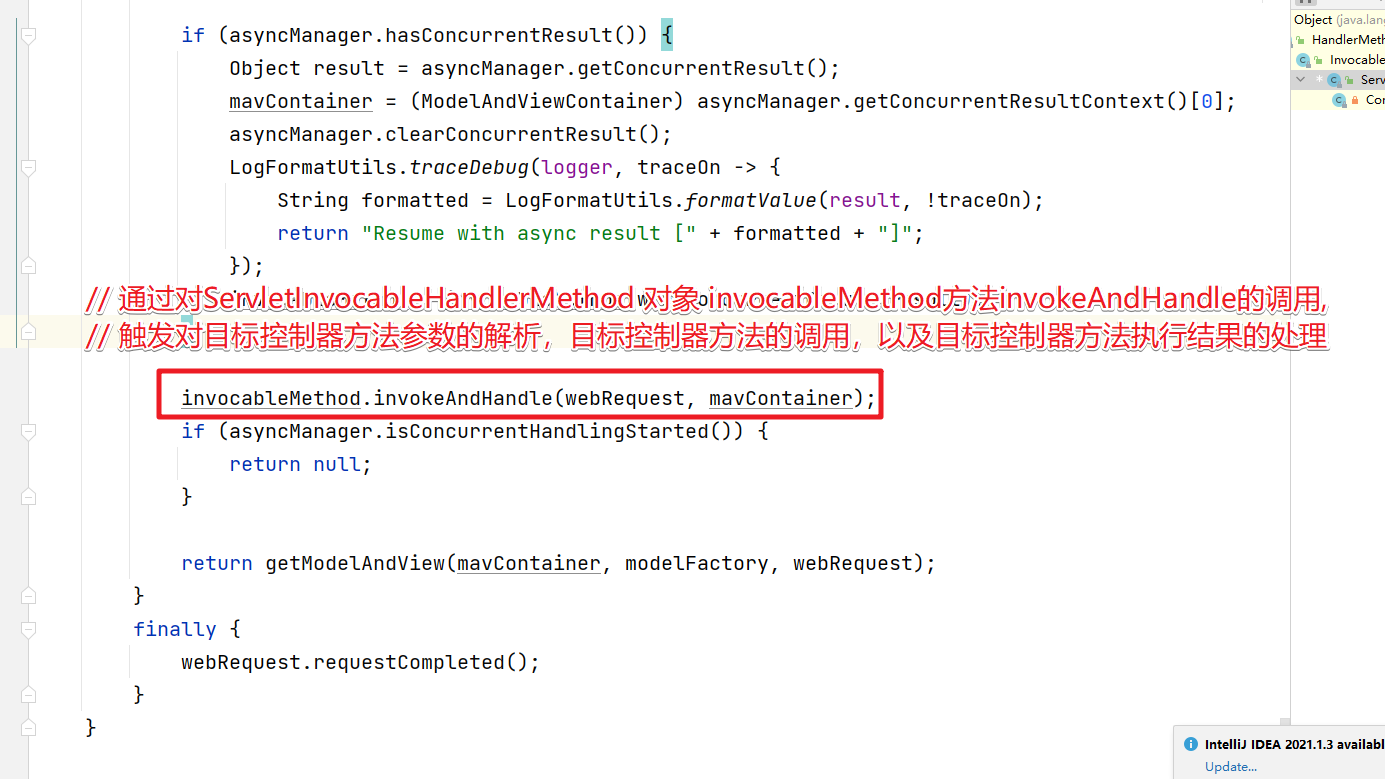
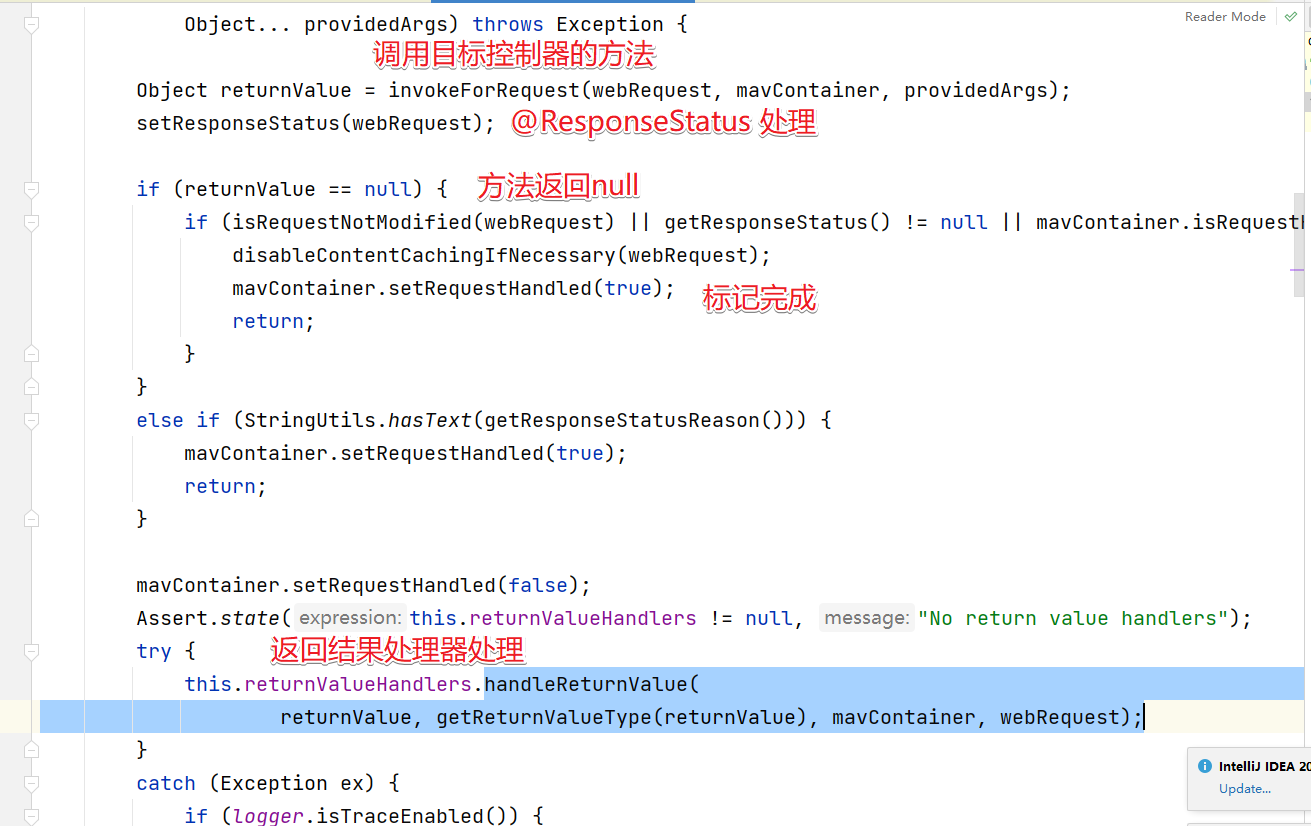
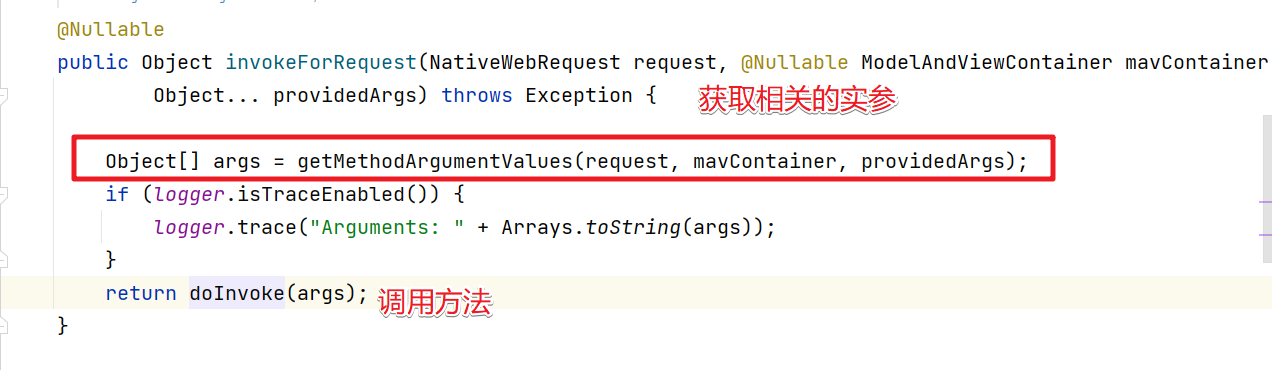
invokeForRequest方法






















 1711
1711











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








