1 简介
针对原始蝴蝶优化算法容易陷入局部最优解,收敛速度慢及寻优精度低等问题,提出分段权重和变异反向学习的蝴蝶优化算法.通过飞行引领策略来矫正邻域内蝴蝶的自身飞行,降低盲目飞行,增强算法跳出局部最优的能力;引入分段权重来平衡全局勘探及局部开发的能力,进而实现蝴蝶位置动态更新;使用变异反向学习对位置进行扰动,增加种群多样性以及提高算法的收敛速度.通过对9个测试函数和部分CEC2014函数及Wilcoxon秩和检验来评估改进算法的寻优能力,实验结果表明改进算法的收敛速度及寻优精度得到了极大改进.








2 部分代码
%% Monarch Butterfly Optimization (MBO)
% % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%% Notes:
% Different run may generate different solutions, this is determined by
% the the nature of metaheuristic algorithms.
%%
function [MinCost] = MBO(ProblemFunction, DisplayFlag, RandSeed)
% Monarch Butterfly Optimization (MBO) software for minimizing a general function
% The fixed Function Evaluations (FEs) is considered as termination condition.
% INPUTS: ProblemFunction is the handle of the function that returns
% the handles of the initialization, cost, and feasibility functions.
% DisplayFlag = true or false, whether or not to display and plot results.
% ProbFlag = true or false, whether or not to use probabilities to update emigration rates.
% RandSeed = random number seed
% OUTPUTS: MinCost = array of best solution, one element for each generation
% Hamming = final Hamming distance between solutions
% CAVEAT: The "ClearDups" function that is called below replaces duplicates with randomly-generated
% individuals, but it does not then recalculate the cost of the replaced individuals.
tic
if ~exist('ProblemFunction', 'var')
ProblemFunction = @Ackley;
end
if ~exist('DisplayFlag', 'var')
DisplayFlag = true;
end
if ~exist('RandSeed', 'var')
RandSeed = round(sum(100*clock));
end
[OPTIONS, MinCost, AvgCost, InitFunction, CostFunction, FeasibleFunction, ...
MaxParValue, MinParValue, Population] = Init(DisplayFlag, ProblemFunction, RandSeed);
nEvaluations = OPTIONS.popsize;
% % % % % % % % % % % % Initial parameter setting % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%
%% Initial parameter setting
Keep = 2; % elitism parameter: how many of the best habitats to keep from one generation to the next
maxStepSize = 1.0; %Max Step size
partition = OPTIONS.partition;
numButterfly1 = ceil(partition*OPTIONS.popsize); % NP1 in paper
numButterfly2 = OPTIONS.popsize - numButterfly1; % NP2 in paper
period = 1.2; % 12 months in a year
Land1 = zeros(numButterfly1, OPTIONS.numVar);
Land2 = zeros(numButterfly2, OPTIONS.numVar);
BAR = partition; % you can change the BAR value in order to get much better performance
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Initial parameter setting % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Begin the optimization loop % % % % % % % % % %%%%
% Begin the optimization loop
GenIndex = 1;
% for GenIndex = 1 : OPTIONS.Maxgen
while nEvaluations< OPTIONS.MaxFEs
% % % % % % % % % % % % Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%%
%% Save the best monarch butterflis in a temporary array.
for j = 1 : Keep
chromKeep(j,:) = Population(j).chrom;
costKeep(j) = Population(j).cost;
end
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Divide the whole population into two subpopulations % % % %%%
%% Divide the whole population into Population1 (Land1) and Population2 (Land2)
% according to their fitness.
% The monarch butterflis in Population1 are better than or equal to Population2.
% Of course, we can randomly divide the whole population into Population1 and Population2.
% We do not test the different performance between two ways.
for popindex = 1 : OPTIONS.popsize
if popindex <= numButterfly1
Population1(popindex).chrom = Population(popindex).chrom;
else
Population2(popindex-numButterfly1).chrom = Population(popindex).chrom;
end
end
% % % % % % % % % % % End of Divide the whole population into two subpopulations % % %%%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % %% Migration operator % % % % % % % % % % % %%%%
%% Migration operator
for k1 = 1 : numButterfly1
for parnum1 = 1 : OPTIONS.numVar
r1 = rand*period;
if r1 <= partition
r2 = round(numButterfly1 * rand + 0.5);
Land1(k1,parnum1) = Population1(r2).chrom(parnum1);
else
r3 = round(numButterfly2 * rand + 0.5);
Land1(k1,parnum1) = Population2(r3).chrom(parnum1);
end
end %% for parnum1
NewPopulation1(k1).chrom = Land1(k1,:);
end %% for k1
% % % % % % % % % % % %%% End of Migration operator % % % % % % % % % % % %%%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Evaluate NewPopulation1 % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%% Evaluate NewPopulation1
SavePopSize = OPTIONS.popsize;
OPTIONS.popsize = numButterfly1;
% Make sure each individual is legal.
NewPopulation1 = FeasibleFunction(OPTIONS, NewPopulation1);
% Calculate cost
NewPopulation1 = CostFunction(OPTIONS, NewPopulation1);
% the number of fitness evaluations
nEvaluations = nEvaluations + OPTIONS.popsize;
OPTIONS.popsize = SavePopSize;
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Evaluate NewPopulation1 % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Butterfly adjusting operator % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%% Butterfly adjusting operator
for k2 = 1 : numButterfly2
scale = maxStepSize/(GenIndex^2); %Smaller step for local walk
StepSzie = ceil(exprnd(2*OPTIONS.Maxgen,1,1));
delataX = LevyFlight(StepSzie,OPTIONS.numVar);
for parnum2 = 1:OPTIONS.numVar,
if (rand >= partition)
Land2(k2,parnum2) = Population(1).chrom(parnum2);
else
r4 = round(numButterfly2*rand + 0.5);
Land2(k2,parnum2) = Population2(r4).chrom(1);
if (rand > BAR) % Butterfly-Adjusting rate
Land2(k2,parnum2) = Land2(k2,parnum2) + scale*(delataX(parnum2)-0.5);
end
end
end %% for parnum2
NewPopulation2(k2).chrom = Land2(k2,:);
end %% for k2
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Butterfly adjusting operator % % % % % % % % % % % %
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Evaluate NewPopulation2 % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%% Evaluate NewPopulation2
SavePopSize = OPTIONS.popsize;
OPTIONS.popsize = numButterfly2;
% Make sure each individual is legal.
NewPopulation2 = FeasibleFunction(OPTIONS, NewPopulation2);
% Calculate cost
NewPopulation2 = CostFunction(OPTIONS, NewPopulation2);
% the number of fitness evaluations
nEvaluations = nEvaluations + OPTIONS.popsize;
OPTIONS.popsize = SavePopSize;
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Evaluate NewPopulation2 % % % % % % % % % % % %%
%%
% % % % % % % Combine two subpopulations into one and rank monarch butterflis % % % % % %
%% Combine Population1 with Population2 to generate a new Population
Population = CombinePopulation(OPTIONS, NewPopulation1, NewPopulation2);
% Sort from best to worst
Population = PopSort(Population);
% % % % % % End of Combine two subpopulations into one and rank monarch butterflis % %% % %
%%
% % % % % % % % % % % % Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%% %% %
%% Replace the worst with the previous generation's elites.
n = length(Population);
for k3 = 1 : Keep
Population(n-k3+1).chrom = chromKeep(k3,:);
Population(n-k3+1).cost = costKeep(k3);
end % end for k3
% % % % % % % % % % % % End of Elitism Strategy % % % % % % % % % % % %%% %% %
%%
% % % % % % % % % % Precess and output the results % % % % % % % % % % % %%%
% Sort from best to worst
Population = PopSort(Population);
% Compute the average cost
[AverageCost, nLegal] = ComputeAveCost(Population);
% Display info to screen
MinCost = [MinCost Population(1).cost];
AvgCost = [AvgCost AverageCost];
if DisplayFlag
disp(['The best and mean of Generation # ', num2str(GenIndex), ' are ',...
num2str(MinCost(end)), ' and ', num2str(AvgCost(end))]);
end
% % % % % % % % % % % End of Precess and output the results %%%%%%%%%% %% %
%%
%% Update generation number
GenIndex = GenIndex+1;
end % end for GenIndex
Conclude2(DisplayFlag, OPTIONS, Population, nLegal, MinCost, AvgCost);
toc
% % % % % % % % % % End of Monarch Butterfly Optimization implementation %%%% %% %
%%
function [delataX] = LevyFlight(StepSize, Dim)
%Allocate matrix for solutions
delataX = zeros(1,Dim);
%Loop over each dimension
for i=1:Dim
% Cauchy distribution
fx = tan(pi * rand(1,StepSize));
delataX(i) = sum(fx);
end
3 仿真结果
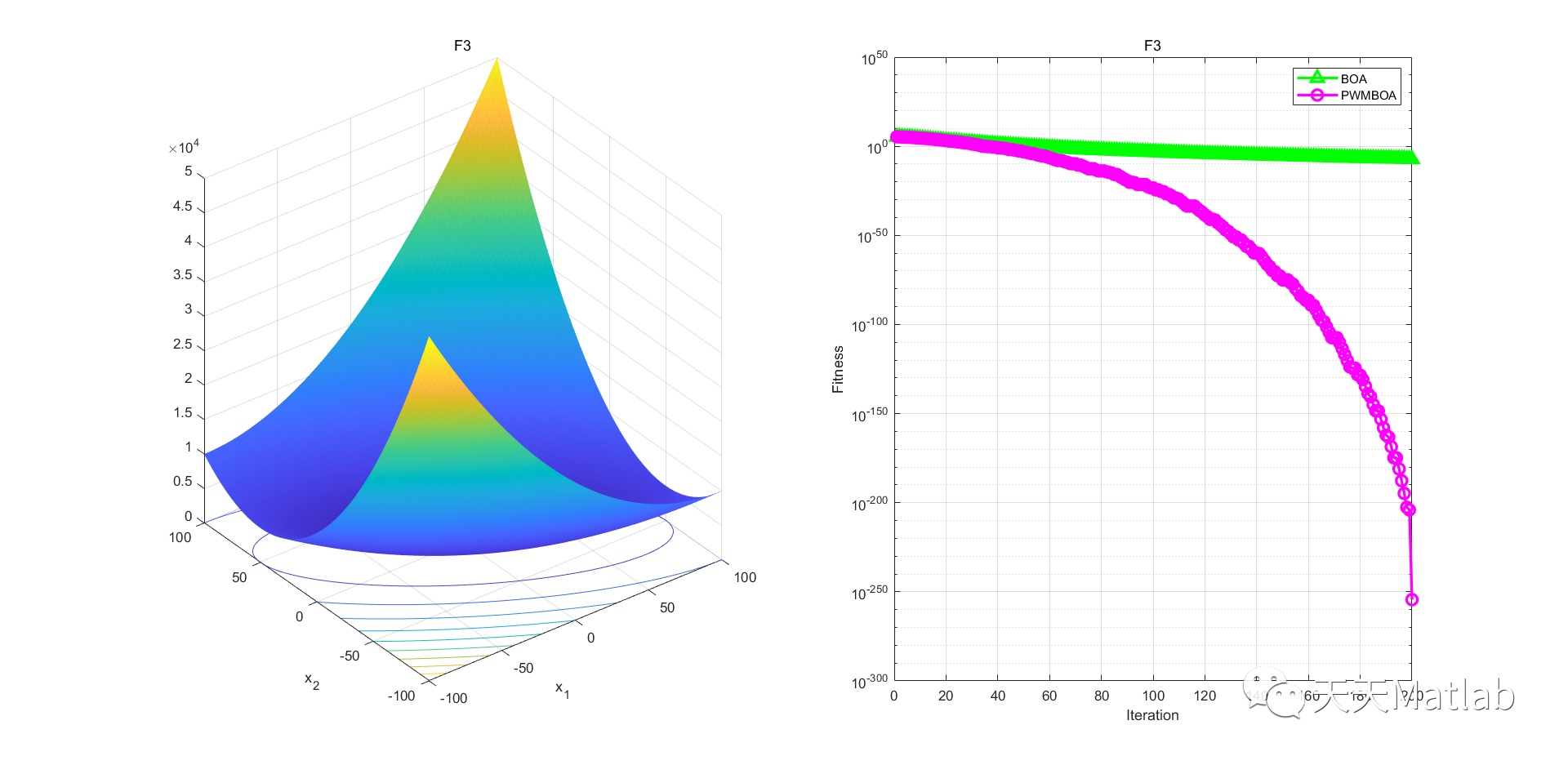
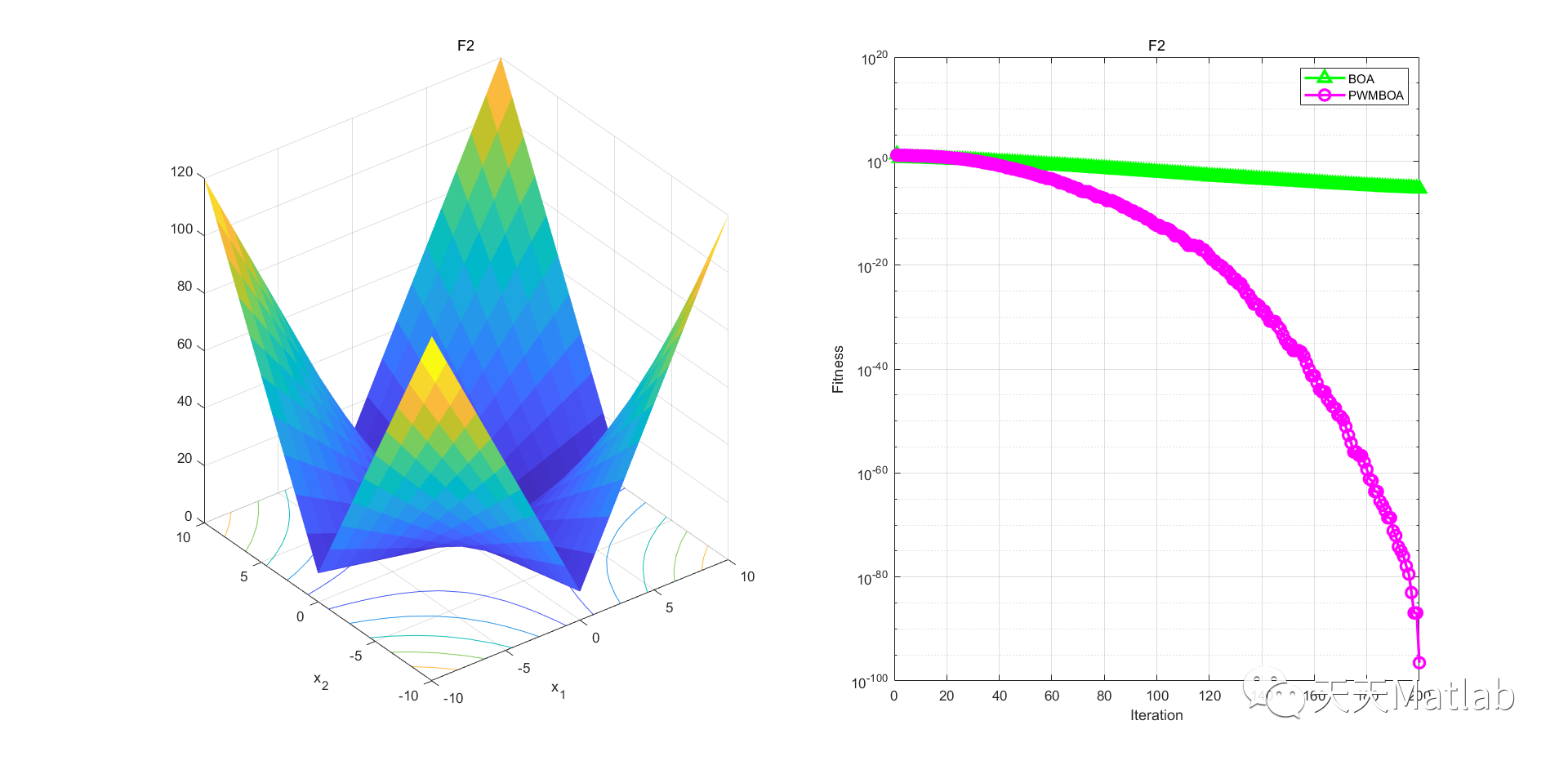
4 参考文献
[1]李守玉,何庆,杜逆索. 分段权重和变异反向学习的蝴蝶优化算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2021, 57(22):10.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。























 184
184

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










