一、栈
1、初识栈
栈是一种先进后出的数据结构,可以用数组或链表来实现。Stack底层是一个数组。
栈中的方法:
- push:压栈
- pop:出栈
- peek:获取栈顶元素但不删除
- empty:判断栈是否为空
- size:获取栈中的元素个数
2、用数组和链表实现栈
(1)数组:
用数组实现的栈,也可以叫做顺序栈。
用数组实现栈时,压栈出栈都是对栈最后的下标(elem[size])进行操作,时间复杂度为O(1)
public class MyStack {
private int[] elem;
private int size;
public MyStack(){
this.elem = new int[10];
}
public boolean isFull(){
return this.size >= this.elem.length;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.size == 0;
}
//压栈
public void push(int data){
if(isFull()){
this.elem = Arrays.copyOf(this.elem,this.elem.length*2);
}
this.elem[size] = data;
this.size++;
}
//出栈
public int pop(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
this.size--;
return this.elem[this.size];
}
//获取栈顶元素
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
return this.elem[this.size-1];
}
}(2)链表:
用链表实现的栈,也可以叫做链式栈。
可以用单向链表或双向链表来实现栈,双向链表更适合。
单向链表:头插头删,时间复杂度为O(1)
不尾插尾删的原因:尾插需要找尾巴,时间复杂度为O(n),尾删,需要定义一个前驱,时间复杂度也是O(n)
//单向链表实现栈:头插头删
public class MyStack2 {
static class ListNode {
private int val;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
private ListNode head;
//方法
public void push(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
return;
}
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
public int pop(){
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
int ret = this.head.val;
this.head = this.head.next;
return ret;
}
public int peek(){
if(empty()){
throw new EmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
return head.val;
}
public boolean empty(){
return this.head == null;
}
}
双向链表:头插头删、尾插删都可以,时间复杂度为O(1)
//双向链表实现栈:尾插尾删
public class MyStack3 {
static class ListNode{
private int val;
private ListNode prev;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode tail;
//方法
public void push(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
return;
}
ListNode cur = this.tail;
cur.next = node;
node.prev = cur;
tail = node;
}
public int pop(){
if(this.head == null){
throw new EmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
if(this.tail.prev == null){
int ret = this.tail.val;
this.tail = null;
this.head = null;
return ret;
}
int ret = this.tail.val;
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
return ret;
}
public int peek(){
if(this.head == null){
throw new EmptyStackException("栈为空!");
}
return this.tail.val;
}
public boolean empty(){
return this.head == null;
}
}
3、栈的一些题目
(1)选择题:中缀表达式 转 后缀表达式(逆波兰表达式)
如:将中缀表达式 1+2*3 +(4*5+6)*7 转成 后缀表达式。
- 从左向右,先乘除后加减,进行加括号((1 +(2 * 3)) +(((4 * 5)+ 6)* 7))
- 把运算符挪到所在括号的后面((1(2 3)*)+ (((4 5)* 6)+ 7)*)+
- 去掉所有的括号 1 2 3 * + 4 5 * 6 + 7 * +
(2)逆波兰表达式求值 链接
String是引用类型,字符串比较要使用equals
将String类型的数据s转为Integer类型:Integer.parseInt(s);
是操作数(+、-、*、/ )就出栈2次,不是操作数就入栈
public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < tokens.length; i++){
String s = tokens[i];
if(s.equals( "+") || s.equals( "-") || s.equals( "*") || s.equals( "/")){
int num2 = stack.pop();
int num1 = stack.pop();
switch(s){
case "+":
stack.push(num1+num2);
break;
case "-":
stack.push(num1-num2);
break;
case "*":
stack.push(num1*num2);
break;
case "/":
stack.push(num1/num2);
break;
}
}else{
stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
}
}
return stack.pop();
}(3)将递归转换为非递归,如:逆序打印链表
逆序打印链表有 递归 和 非递归 两种做法。
递归:
递归的终止条件
递推公式
public void display1(ListNode cur){
if(cur == null){
return;
}
display1(cur.next);//递推公式
System.out.print(cur.val+" ");
}非递归:可以使用栈
public void display2(){
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode cur = this.head;
while(cur != null){
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
while(!stack.empty()){
ListNode ret = stack.pop();
System.out.print(ret.val+" ");
}
}(4)括号匹配 链接
我们使用栈来做这一题,是左括号就入栈,是右括号就出栈
括号全部都匹配的情况:
- 括号遍历完了,与此同时,栈也为空了
所以,括号不匹配的情况就有以下3种:
- 括号没遍历完,栈已经空了,即到右括号时没左括号与之匹配
- 括号遍历完了,栈里面还有括号,即右括号都没了,栈里还剩左括号没人匹配
- 括号没遍历完,栈里面也还有括号,即左括号匹配到了不对应的右括号
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if(ch == '(' || ch == '[' || ch == '{'){
stack.push(ch);
}else{
if(stack.empty()){
//不匹配的第一种情况,右括号还没遍历完,栈已经空了
return false;
}
char ret = stack.pop();
if(!(ret == '(' && ch == ')' || ret == '[' && ch == ']' || ret == '{' && ch == '}')){
//不匹配的第三种情况,右括号与左括号不对应
return false;
}
}
}
//不匹配的第二种情况,左括号还剩在栈里
if(!stack.empty()){
return false;
}
return true;
}(5)出栈入栈次序匹配 链接
进栈过程中可以出栈,判断第二个序列是否可能为该栈的弹出顺序
做题思路:
- 定义i下标,遍历pushA数组,如果i < pushA.length,就往栈中放元素
- 然后peek一下,看栈顶的元素和pop[j]元素是否一样
- 一样就出栈,j++,然后判断栈是否为空,栈不为空,再peek一下,看栈顶的元素和pop[j]元素是否一样,一样继续出栈,j++
- 不一样或栈为空就 i++,如果i < pushA.length,就往栈中放元素如果i < pushA.length,就继续往栈中放元素。然后继续 2~4 的操作
- 直到 i < pushA.length不满足,pushA数组遍历完了
- 此时看栈是否为空,栈为空则出栈入栈次序匹配,栈不为空则次序不匹配
public boolean IsPopOrder (int[] pushV, int[] popV) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int j = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < pushV.length; i++){
stack.push(pushV[i]);
while(!stack.empty() && stack.peek().equals(popV[j])){
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
//pushV走完了,栈中还有元素
if(!stack.empty()){
return false;
}
return true;
}(6)最小栈 链接
Integer是引用数据类型,引用数据类型比较不能使用 == ,要使用 equals() !!!
解题思路:
- 定义2个栈,
- 普通栈中一定要放,
- 最小栈中,
- 当前元素 <= 最小栈的栈顶元素时,放
- 当前元素 > 最小栈的栈顶元素时,放
class MinStack {
private Stack<Integer> stack;
private Stack<Integer> minStack;
public MinStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
minStack = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int val) {
if(stack.empty()){
stack.push(val);
minStack.push(val);
}else{
stack.push(val);
if(val <= minStack.peek()){
minStack.push(val);
}
}
}
public void pop() {
/**
if(!stack.empty()) {
int x = stack.pop();
if(x == minStack.peek()) {
minStack.pop();
}
}
*/
if(!stack.empty()) {
if(stack.peek().equals( minStack.peek())){
stack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}else{
stack.pop();
}
}
}
public int top() {
if(stack.empty()){
return -1;
}
return stack.peek();
}
public int getMin() {
if(minStack.empty()){
return -1;
}
return minStack.peek();
}
}
4、栈、虚拟机栈、栈帧有什么区别?
栈:是一种先进后出的数据结构。
虚拟机栈:是JVM的一块内存空间。
栈帧:是在调用函数的过程当中,在Java虚拟机栈上开辟的一块内存。
二、队列
1、初识队列
队列是一种先进后出的数据结构,从队尾(tail/rear)入,从队头(head/front)出
Queue是个接口,实现类是LinkedList
LinkedList底层是双向链表,可以当做链表、栈、队列 来使用。
队列中的方法:
- offer:入队
- poll:出队
- peek:获取队头元素但不删除
- isEmpty:判断队列是否为空
- size:获取队列中的元素个数
2、用链表和数组实现队列
(1)链表:
用链表实现的队列,也可以叫做链式队列。
可以用单向链表或双向链表来实现队列,双向链表更适合。
单向链表:定义一个tail,然后 尾增头删(从tail 入队,从 head 出队),时间复杂度是O(1)
因为单向链表 头增头删,时间复杂度为O(1),
尾删,需要找尾巴节点的前驱,时间复杂度为O(n)
尾增,有tail,时间复杂度为O(1);无tail,需要找尾巴,时间复杂度为O(n)
//单向链表实现队列:尾入头出
public class MyQueue {
static class ListNode{
private int val;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
//头
public ListNode head;
//尾
public ListNode tail;
//从尾入队
public void offer(int data) {
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(this.head == null){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
return;
}
tail.next = node;
tail = node;
}
//从头出队
public int poll(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
int ret = this.head.val;
if(this.head.next == null){
this.tail = null;
}
this.head = this.head.next;
return ret;
}
//获取队头元素但不删除
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return this.head.val;
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.head == null;
}
}
双向链表:尾增头删、头增尾删都可以,时间复杂度为O(1)
//双向链表实现队列:头入尾出
public class MyQueue2 {
static class ListNode{
private int val;
private ListNode prev;
private ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val){
this.val = val;
}
}
public ListNode head;
public ListNode tail;
public void offer(int data){
ListNode node = new ListNode(data);
if(isEmpty()){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
return;
}
node.next = head;
head.prev = node;
head = node;
}
public int poll(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
if(this.head.next == null){
int ret = this.head.val;
head = null;
tail = null;
return ret;
}
int ret = tail.val;
tail = tail.prev;
tail.next = null;
return ret;
}
public int peek(){
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return this.tail.val;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.head == null;
}
}(2)数组:
循环队列通常用数组实现。
front 指向 队头,rear指向队尾。队尾入,队头出
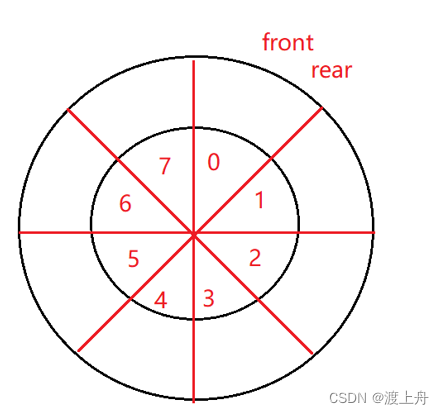
front 与 rear 相遇了,队列是空还是满呢?
1)添加size属性,记录队列的长度
2)浪费一个空间
如何从7下标到0下标呢?
rear = (rear+1)%(this.elem.length);
front = (front+1)%(this.elem.length);
if(rear == 0){
return elem[this.elem.length-1];
}
return this.elem[rear-1];
方法一:添加size属性,记录队列的长度
//数组实现循环队列
public class MyCircularQueue1 {
//数组
private int[] elem;
//队列的长度
private int size;
//队头和队尾的下标
private int front;
private int rear;
public MyCircularQueue1(int k) {
//数组的长度
this.elem = new int[k];
}
//循环队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
//循环队列是否满了
public boolean isFull() {
return this.size == this.elem.length;
}
//入队
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
this.elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%(this.elem.length);
this.size++;
return true;
}
//出队
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
front = (front+1)%(this.elem.length);
this.size--;
return true;
}
//获取队头元素但不删除
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return this.elem[front];
}
//获取队尾元素但不删除
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
if(rear == 0){
return elem[this.elem.length-1];
}
return this.elem[rear-1];
}
}方法二:浪费一个空间
每次放元素的时候,都去检查一下,当前rear的下一个是不是front,不是就说明队列没满可以放。
public class MyCircularQueue2 {
//数组
private int[] elem;
//队头和队尾的下标
private int front;
private int rear;
public MyCircularQueue2(int k) {
//数组的长度
this.elem = new int[k];
}
//循环队列是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return rear == front;
}
//循环队列是否满了
public boolean isFull() {
int ret = (rear+1)%this.elem.length;
return ret == front;
}
//入队
public boolean enQueue(int value) {
if(isFull()){
return false;
}
this.elem[rear] = value;
rear = (rear+1)%(this.elem.length);
return true;
}
//出队
public boolean deQueue() {
if(isEmpty()){
return false;
}
front = (front+1)%(this.elem.length);
return true;
}
//获取队头元素但不删除
public int Front() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
return this.elem[front];
}
//获取队尾元素但不删除
public int Rear() {
if(isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
if(rear == 0){
return elem[this.elem.length-1];
}
return this.elem[rear-1];
}
}3、队列的一些面试题
(1)用队列实现栈 链接
入栈:入到不为空的队列中
出栈:出size-1个元素到空队列中,则这个队列中剩余的那个就是要出的元素
//用队列实现栈
public class QueueAchieveStack {
//队列
public Queue<Integer> queue1;
public Queue<Integer> queue2;
public QueueAchieveStack() {
this.queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
this.queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
//入栈
public void push(int x) {
if(!queue1.isEmpty()){
queue1.offer(x);
}else if(!queue2.isEmpty()){
queue2.offer(x);
}else{
queue1.offer(x);
}
}
//出栈
public int pop() {
//栈为空
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
int tmp = -1;
if(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
tmp = queue1.poll();
if (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue2.offer(tmp);
}
}
}else{
while (!queue2.isEmpty()) {
tmp = queue2.poll();
if (!queue2.isEmpty()) {
queue1.offer(tmp);
}
}
}
return tmp;
}
//获取栈顶元素但不删除
public int top() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
int tmp = -1;
if(!queue1.isEmpty()) {
while (!queue1.isEmpty()) {
tmp = queue1.poll();
queue2.offer(tmp);
}
}else{
while (!queue2.isEmpty()) {
tmp = queue2.poll();
queue1.offer(tmp);
}
}
return tmp;
}
//判断栈是否为空
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.isEmpty() && queue2.isEmpty();
}
}
(2)用栈实现队列 链接
入队:入stack1
出队:出stack2,如果stack2为空,就把stack1中的所有元素都入栈到stack2
//用栈实现队列
public class StackAchieveQueue {
public Stack<Integer> stack1;
public Stack<Integer> stack2;
public StackAchieveQueue() {
this.stack1 = new Stack<>();
this.stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
//入队
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
//出队
public int pop() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()){
int size = stack1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
//获取队头元素但不删除
public int peek() {
if(empty()){
return -1;
}
if(stack2.empty()){
int size = stack1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
//判断队列是否为空
public boolean empty() {
return stack1.empty() && stack2.empty();
}
}





















 1319
1319











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








