一、背景与需求
1、什么是多路摄像头画面拼接?
想象一下您的汽车有6个摄像头(前、后、左、右等),每个摄像头都在独立录制。多路摄像头画面拼接就是将这6个独立的视频画面智能地组合成一个大的全景画面,就像在监控中心看到的那种多画面监控屏一样。
2、为什么要做这个?
- 全景监控:在自动驾驶、安防监控等场景中,需要同时查看多个角度的画面
- 节省带宽:传输1个拼接后的视频流比传输6个独立的视频流更节省网络资源
- 降低延迟:通过硬件加速处理,减少视频处理的延迟
3、技术挑战
- 高性能要求:需要实时处理6个1080P视频流,对计算能力要求很高
- 低延迟:从采集到显示的全链路延迟要尽可能小
- 低CPU占用:不能因为视频处理而影响其他重要任务
二、优化思路详解
1、核心思想:零拷贝架构
传统视频处理就像搬箱子:每次处理都需要把数据从A地搬到B地,很耗时。我们的目标是让数据"原地处理",减少不必要的搬运。
2、关键技术解析
2.1、DMA缓冲区直接访问
// 使用DMA缓冲区,GPU可以直接访问摄像头数据
buffer_request.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_DMABUF;
通俗解释:就像给GPU开了一个"快捷通道",让它能直接读取摄像头数据,不需要经过CPU中转。
2.2、GPU内存统一管理
// 所有处理都在GPU内存中进行
NvBufSurf::NvAllocate(&cam_params, actual_buffer_count, input_fds.data());
通俗解释:所有视频数据都放在GPU的"工作台"上处理,不需要在CPU和GPU之间来回搬运。
2.3、硬件加速转换和拼接
// 使用GPU进行画面格式转换和拼接
NvBufSurfTransformMultiInputBufCompositeBlend(batch_surf.data(), pdstSurf, &composite_params);
通俗解释:利用GPU的专用电路来快速完成画面格式转换和拼接,就像用专业工具而不是手工操作。
2.4、硬件编码
// 使用NVIDIA硬件编码器
video_encoder_ = NvVideoEncoder::createVideoEncoder("enc0");
通俗解释:用专门的编码芯片来压缩视频,比用CPU软件编码快得多,也省电得多。
三、系统架构
1、数据处理流程
摄像头采集 → DMA缓冲区 → 格式转换 → 画面拼接 → 硬件编码 → RTSP网络传输
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
零拷贝 零拷贝 GPU加速 GPU加速 专用芯片 网络推流
2、各模块职责
2.1、摄像头采集模块 (V4l2CameraSource)
- 负责从物理摄像头读取数据
- 使用DMA缓冲区避免内存拷贝
- 自动进行YUV422到YUV420格式转换
2.2、画面拼接模块 (MultiCameraStreamer)
- 按照预定义的布局将6个画面拼接成1个
- 支持自定义每个画面的位置和大小
- 使用GPU进行高效的图像合成
2.3、视频编码模块 (HwVideoEncoder)
- 使用NVIDIA硬件编码器
- 支持H.264和H.265(HEVC)编码
- 动态码率控制
2.4、网络服务模块
- 提供RTSP视频流服务
- 支持多客户端同时观看
- 可按需调整视频质量
3、性能优势
- CPU占用极低:主要计算都由GPU和专用硬件完成
- 内存效率高:零拷贝架构大幅减少内存带宽占用
- 延迟低:全链路硬件加速,处理延迟在毫秒级别
4、硬件要求
- NVIDIA Jetson平台(内置专用视频处理硬件)
- 多个USB摄像头或MIPI摄像头
- 足够的GPU内存(建议4GB以上)
四、步骤简介
1、环境准备
确保您的Jetson设备已安装:
- JetPack SDK(包含L4T Multimedia API)
- CUDA工具包
- 必要的开发库
2. 配置文件说明
2.1、摄像头布局配置 (camera_cfg.json)
{
"global": {
"camera_bufers": 2, // 每个摄像头的缓冲区数量
"encoder_buffers": 2, // 编码器缓冲区数量
"use_hevc": false, // 是否使用H.265编码
"fps": 15, // 输出帧率
"max_bitrate_mps": 2, // 最大码率( Mbps)
"print_interval_sec": 30 // 统计信息打印间隔
},
"layout": {
"left_front": {
"x":0, "y":190, "width":432, "height":274},
// ... 其他摄像头位置配置
},
"DEV": {
"left_front": {
"dev":"/dev/video1", "width":1920, "height":1080},
// ... 其他摄像头设备配置
}
}
配置说明:
layout:定义每个摄像头画面在最终输出中的位置和大小DEV:定义每个摄像头对应的设备文件和分辨率
2.2、RTSP服务器配置 (mk_mediakit.ini)
[rtp_proxy]
lowLatency=1 # 开启低延迟模式
gop_cache=1 # 开启GOP缓存,改善播放体验
3. 核心代码解析
3.1、摄像头初始化
// 创建摄像头源实例
video_sources.push_back(std::make_unique<V4l2CameraSource>(
config.camera_configs[name].device,
config.camera_configs[name].width,
config.camera_configs[name].height));
// 初始化摄像头
video_sources[i]->Initialize(position.width, position.height);
3.2、画面拼接核心逻辑
// 等待所有摄像头都准备好新帧
waitForAllCamerasReady(video_sources);
// 从编码器获取输出缓冲区
int output_plane_index = m_encoder->deQueue(v4l2_buf);
// 获取所有摄像头的当前帧
for (int i = 0; i < video_sources.size(); i++) {
int buffer_index = video_sources[i]->GetLatestFrame(&out_dmabuf_fd, camera_ts);
// 将帧数据添加到批处理列表
batch_surf.push_back(nvbuf_surf);
}
// 使用GPU进行多画面拼接
composite_params.params.input_buf_count = buffer_index_arr.size();
ret = NvBufSurfTransformMultiInputBufCompositeBlend(batch_surf.data(), pdstSurf, &composite_params);
3.3、编码和网络传输
// 编码回调函数,将编码后的数据通过RTSP发送
static void rtspWriteCallback(const uint8_t *encoded_data, size_t data_size,
bool is_key_frame, void *user_data) {
// 创建RTSP帧
mk_frame frame = mk_frame_create(
VideoConstants::USE_HEVC ? MKCodecH265 : MKCodecH264,
obj->dts, obj->dts,
(const char *)encoded_data, data_size, NULL, NULL);
// 输入到媒体流
mk_media_input_frame(obj->media, frame);
}
4. 编译和运行
4.1、编译命令解释
g++ -o l4t_media_srv l4t_media_srv.cpp \
-std=c++17 \
-I ../3rdparty/include \
-I/usr/src/jetson_multimedia_api/include \ # L4T Multimedia API头文件
-I /usr/local/cuda/include \ # CUDA头文件
-I /usr/include/jsoncpp \ # JSON解析库
# ... 链接必要的库文件
-lcudart -lv4l2 -lpthread -lnvbufsurface -lnvbufsurftransform -lnvv4l2 -lmk_api -ljsoncpp
关键库说明:
libnvbufsurface.so:GPU缓冲区管理libnvbufsurftransform.so:图像变换和拼接libnvv4l2.so:视频4l2操作libmk_api.so:RTSP流媒体服务
4.2、运行程序
./l4t_media_srv DEV
4.3、观看视频流
使用VLC或其他RTSP播放器打开:
rtsp://你的Jetson设备IP:8554/live/multi_view
5. 高级功能
5.1、动态码率调整
支持通过RTSP URL参数动态调整码率:
rtsp://ip:8554/live/multi_view?bitrate=1500
这会在客户端连接时自动将码率调整为1500Kbps。
5.2、强制关键帧
当新的客户端连接时,会自动插入关键帧,减少连接延迟。
5.3、实时统计信息
程序会定期输出:
- 实时帧率(FPS)
- 处理延迟
- 实际输出码率
- 关键帧信息
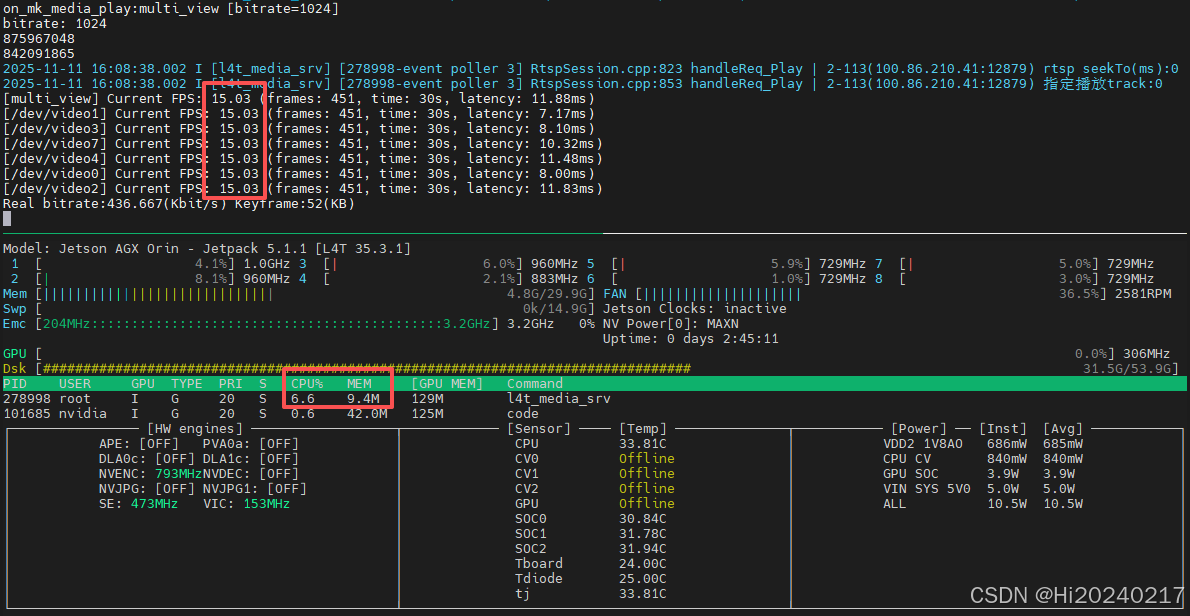
五、资源使用情况
六、完整实现
1、生成主程序代码
cat > l4t_media_srv.cpp << 'EOF'
#include <atomic>
#include <cassert>
#include <chrono>
#include <cmath>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <json/json.h>
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include <npp.h>
#include <nppi.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <queue>
#include <random>
#include <sstream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/poll.h>
#include <thread>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <vector>
#include "NvBufSurface.h"
#include "NvBuffer.h"
#include "NvUtils.h"
#include "NvVideoEncoder.h"
#include "nvbuf_utils.h"
#include "nvbufsurface.h"
#include "mk_mediakit.h"
// 定义相机配置结构体
struct CameraConfig {
std::string device;
int width;
int height;
};
// 定义车辆配置结构体
struct VehicleConfig {
std::map<std::string,CameraConfig> camera_configs;
};
// ============================ 常量定义============================
namespace VideoConstants {
constexpr auto PIXEL_FORMAT = V4L2_PIX_FMT_UYVY;
int IMG_BUFFER_COUNT = 2;
double DEFAULT_FPS = 15.0;
int FPS_CALCULATION_INTERVAL = 30;
bool USE_HEVC = false;
uint32_t MAX_BITRATE_MBPS = 2;
uint32_t ENCODER_BUFFER_COUNT = 1;
} // namespace VideoConstants
// ============================ 数据结构定义============================
/**
* @brief 矩形区域定义
*/
class Rect {
public:
int x, y, width, height;
Rect() = default;
Rect(int x, int y, int width, int height)
: x(x), y(y), width(width), height(height) {
}
};
/**
* @brief 线程安全队列
*/
template <typename T> class ThreadSafeQueue {
private:
mutable std::mutex mutex_;
std::queue<T> queue_;
std::condition_variable cond_;
public:
ThreadSafeQueue() = default;
// 禁止拷贝
ThreadSafeQueue(const ThreadSafeQueue &) = delete;
ThreadSafeQueue &operator=(const ThreadSafeQueue &) = delete;
void push(T value) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
queue_.push(std::move(value));
cond_.notify_one();
}
bool try_pop(T &value) {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
if (queue_.empty()) {
return false;
}
value = std::move(queue_.front());
queue_.pop();
return true;
}
bool empty() const {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
return queue_.empty();
}
size_t size() const {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
return queue_.size();
}
void clear() {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(mutex_);
std::queue<T> empty_queue;
std::swap(queue_, empty_queue);
}
};
/**
* @brief 视频缓冲区结构体
*/
struct VideoBuffer {
int in_dmabuf_fd = -1;
int out_dmabuf_fd = -1;
double timestamp = 0.0;
bool is_in_use = false;
};
/**
* @brief 线程间共享数据结构
*/
struct SharedVideoData {
int device_fd = -1;
std::vector<VideoBuffer> buffers;
std::atomic<bool> is_capturing{
false};
std::atomic<int> latest_buffer_index{
-1};
std::atomic<bool> frame_updated{
false};
std::atomic<int> buffers_in_use_count{
0};
std::mutex buffer_mutex;
};
/**
* @brief 视口配置结构体
*/
struct ViewportConfig {
std::string name;
Rect position;
};
/**
* @brief FPS统计结构体
*/
struct FpsStatistics {
unsigned int frame_count = 0;
std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point last_calc_time;
std::string name;
double current_fps = 0.0;
};
// ============================ 工具函数 ============================
namespace VideoUtils {
/**
* @brief 获取高精度当前时间(秒)
*/
inline double GetHighResolutionTime() {
struct timespec time_spec;
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, &time_spec);
return static_cast<double>(time_spec.tv_sec) +
static_cast<double>(time_spec.tv_nsec) / 1e9;
}
/**
* @brief 打印像素格式信息
*/
inline void PrintPixelFormat(uint32_t pixel_format) {
std::printf("Pixel format: %c%c%c%c\n", pixel_format & 0xFF,
(pixel_format >> 8) & 0xFF, (pixel_format >> 16) & 0xFF,
(pixel_format >> 24) & 0xFF);
}
/**
* @brief 获取当前时间字符串
*/
inline std::string GetCurrentTimeString() {
auto now = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
auto milliseconds = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(
now.time_since_epoch()) %
1000;
auto timer = std::chrono::system_clock::to_time_t(now);
std::tm time_info = *std::localtime(&timer);
std::ostringstream output_stream;
output_stream << std::put_time(&time_info, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S");
output_stream << '.' << std::setfill('0') << std::setw(3)
<< milliseconds.count();
return output_stream.str();
}
/**
* @brief 计算并打印FPS信息
*/
void CalculateAndPrintFps(FpsStatistics &fps_stats, double latency = 0.0) {
auto current_time = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
fps_stats.frame_count++;
auto elapsed_seconds = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::seconds>(
current_time - fps_stats.last_calc_time)
.count();
if (elapsed_seconds >= VideoConstants::FPS_CALCULATION_INTERVAL) {
fps_stats.current_fps =
static_cast<double>(fps_stats.frame_count) / elapsed_seconds;
std::cout << "[" << fps_stats.name << "] Current FPS: " << std::fixed
<< std::setprecision(2) << fps_stats.current_fps
<< " (frames: " << fps_stats.frame_count
<< ", time: " << elapsed_seconds << "s";
if (latency > 0) {
std::cout << ", latency: " << latency << "ms";
}
std::cout << ")" << std::endl;
// 重置计数器
fps_stats.frame_count = 0;
fps_stats.last_calc_time = current_time;
}
}
/**
* @brief 转储DMA缓冲区到文件
*/
int DumpDmaBuffer(const char *file_path, int plane_count, int dmabuf_fd) {
std::FILE *file = std::fopen(file_path, "wb");
if (!file) {
std::perror("Failed to open file for dumping");
return -1;
}
for (int plane = 0; plane < plane_count; ++plane) {
NvBufSurface *nvbuf_surf = nullptr;
int ret =
NvBufSurfaceFromFd(dmabuf_fd, reinterpret_cast<void **>(&nvbuf_surf));
if (ret != 0) {
std::fclose(file);
return -1;
}
ret = NvBufSurfaceMap(nvbuf_surf, 0, plane, NVBUF_MAP_READ_WRITE);
if (ret < 0) {
std::printf("%s NvBufSurfaceMap failed\n", file_path);
std::fclose(file);
return ret;
}
NvBufSurfaceSyncForCpu(nvbuf_surf, 0, plane);
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < nvbuf_surf->surfaceList->planeParams.height[plane




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 1276
1276

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










