系列文章目录
文章目录
前言
本章导读
主要内容
❀MVC介绍
❀JSP中的MVC模式
❀模型的生命周期与视图更新
❀MVC模式的简单实例
难点
❀模型的生命周期与视图更新
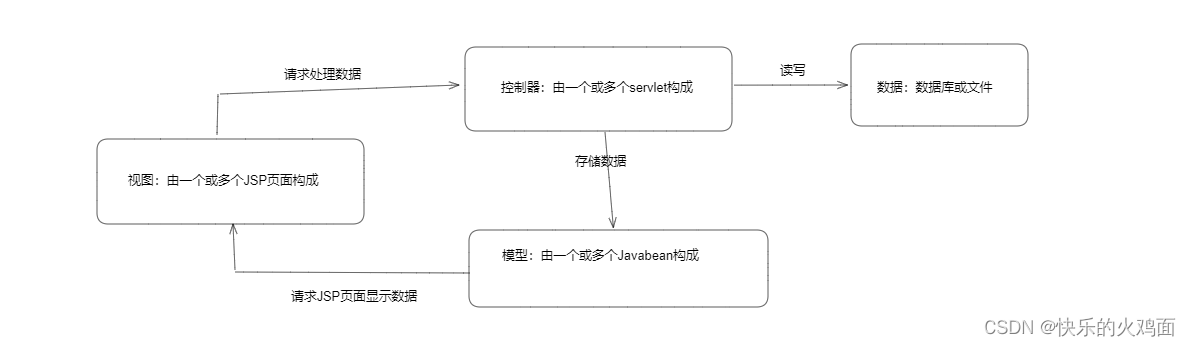
7.1 MVC模式介绍
模型-视图-控制器(Model-View-Controller),简称为MVC。MVC已经成为软件设计者必须熟练使用的开发模式。本章必须理解、掌握在JSP程序设计中怎样具体体现MVC开发模式(其他语言的程序设计是非常类似的,仅仅是具体使用的API不同而已)。
MVC是一种通过三部分构造一个软件或组件的理想办法。
❀模型(model):用于存储数据的对象。
❀视图(view):向控制器提交所需数据、显示模型中的数据。
❀控制器(cohtroller):负责具体的业务逻辑操作,即控制器根据视图提出的要求对数据做出(商业)处理,将有关结果存储到模型中,并负责让模型和视图进行必要的交互,当棋型币的数据变化时,让视图更新显示。
从面向对象的角度看,MVC 开发模式可以使程序容易维护,也更容易扩展。在设计程序时,可以将某个对象看作“模型”,然后为“模型”提供恰当的显示组件,即“视图”。在MVC模式中,“视图”“模型”和“控制器”之间是松耦合结构,便于系统的维护和扩展。
7.2 JSP中的MVC模式
7.3 模型的生命周期与视图更新
使用MVC模式和前面学习的JSP+JavaBean模式有很大的不同。在JSP+JavaBean模式中,由JSP页面通过使用useBean标记创建bean。而MVC模式中,由控制器servlet创建bean,并将有关数据存储到所创建的bean中,然后servlet请求某个JSP页面使用getProperty动作标记:
<jsp:getProperty name = "名字" property = "bean的属性"/>
显示数据
7.3.1 request bean
①bean 的创建
servlet创建 request bean 的步骤如下
(1)用BeanClass类的某个构造方法创建bean对象
BeanClass bean = new BeanClass();
(2)将所创建的bean对象存放到HttpServletRequest对象request中,并指定查找该bean的id。
request.setAttribute("keyWord",bean)
②视图更新
在MVC模式中,由servlet(控制器)负责根据模型中数据的变化通知JSP页面(视图)更新,其手段是使用转发,即使用RequestDispatcher对象向某个JSP页面发出请求,让所请求的JSP 页面显示bean(模型)中的数据(不能使用重定向,即不能用sendRedirect方法)。
因为servlet创建bean的步骤(2)决定了bean为request bean,因此,当servlet使用RequestDispatcher 对象向某个JSP页面发出请求时(进行转发操作),该request bean只对servlet 所请求的JSP页面有效,该JSP页面对请求作出响应之后,request bean所占有的内存被释放,结束自己的生命。
7.3.2 session bean
①bean的创建
servlet 创建session bean的步骤如下:
(1)用BeanClass类的某个构造方法创建bean 对象,例如:
BeanClass bean = new BeanClass();
(2)将所创建的bean 对象存放到HttpServletSession对象session中,并指定查找该
bean 的id。该步骤决定了bean为 session bean。例如:
HttpSession session= request. getSession(true)/
session.setAttribute("keyWord",bean)/
②视图更新
servlet 创建bean 的步骤(2)决定了bean为session bean,只要用户的session没有消失,
该session bean就一直存在。Web服务目录的各个JSP都可以使用
<jsp:useBean id ="keyWord"class ="save. data. BeanClass" scope ="session"/>
标记获得servlet 所创建的session bean(ia 的值是servlet 创建session bean时,为bean 指定
的关键字),然后使用相应的标记或程序片显示该session bean中的数据,例如使用
<jsp:getProperty name ="keyWord" property="bean的变量”/>
标记显示该session bean中的数据。
对于session bean,如果servlet希望某个JSP显示其中的数据,可以使用RequestDispatcher 对象转发到该页面,也可以使用HttpServletResponse类中的重定向方法(sendRedirect)定向到该页面。
需要注意的是,不同用户的session bean是互不相同的,即占有不同的内存空间。
7.3.3 application bean
①bean的创建
servlet 创建application bean的步骤如下:
(1)用BeanClass类的某个构造方法创建bean对象,例如:
BeanClass bean = new BeanClass();
(2)servlet 使用getServletContext()方法返回服务器的ServletContext内置对象的引用,将所创建的bean 对象存放到服务器这个ServletContext内置对象中,并指定查找该bean的关键字。该步骤决定了bean的生命周期为application。例如:
getServletContext().setAttribute("keyWord",bean);
这样就会把bean存放到Tomcat 服务器管理的内置对象pageContext中,该bean 被指定
的id是keyWord,生命周期是PageCentext.APPLICATION_SCOPE(application)。
②视图更新
servlet 创建 bean的步骤(2)决定了bean 为 application bean。当servlet 创建application bean后,只要Tomcat 服务器不关闭,该bean就一直存在。一个用户在访问:Web服务目录的各个JSP中都可以使用
<jsp:useBean id = "keyWord"class = "save. data. BeanClass" scope = "application"/>
标记获得servlet 所创建的application bean(id的值是servlet 创建 application bean 时为bean
指定的关键字),然后使用相应的标记或程序片显示该application bean中的数据,例如使用
<jsp:getProperty name ="keyWord" property="bean 的变量”>
标记显示该application bean中的数据。
对于 application bean,如果servlet希望某个JSP显示其中的数据,可以使用RequestDispatcher对象向该JSP页面发出请求,也可以使用HttpServletResponse类中的重定向方法(sendRedirect)
❀所有用户在同一个Web服务目录中的application bean 是相同的,即占有相同的内存空间。
7.4 MVC模式的简单实例
7.4.1简单的计算器
java文件
package save.data;
public class Example7_1_Bean {
double numberOne,numberTwo,result;
String operator="+";
public void setNumberOne(double n){
numberOne=n;
}
public double getNumberOne(){
return numberOne;
}
public void setNumberTwo(double n){
numberTwo=n;
}
public double getNumberTwo(){
return numberTwo;
}
public void setOperator(String s){
operator=s.trim();;
}
public String getOperator(){
return operator;
}
public void setResult(double r){
result=r;
}
public double getResult(){
return result;
}
}jsp文件
<%@ page contentType="text/html" %>
<%@ page pageEncoding = "utf-8" %>
<jsp:useBean id="digitBean" class ="save.data.Example7_1_Bean" scope="request"/>
<style>
#tom{
font-family:宋体;font-size:26;color:blue
}
</style>
<HTML><body bgcolor=#ffccff>
<form action="computer" id =tom method=post>
<table>
<tr><td id =tom> 输入两个数:</td>
<td id =tom>
<input type=text name="numberOne"
value=<%= digitBean.getNumberOne() %> id =tom size=6/></td>
<td><input type=text name="numberTwo"
value=<%=digitBean.getNumberTwo()%> id =tom size=6/></td>
</tr>
<tr><td id =tom>选择运算符号:</td>
<td id =tom>
<select id =tom name="operator">
<option value="+">+(加)
<option value="-">-(减)
<option value="*">*(乘)
<option value="/">/(除)
</select>
</td>
<td><input type="submit" id =tom value="提交" name="sub"/></td>
</tr>
</table></form>
<p id=tom>
运算结果:
<jsp:getProperty name="digitBean" property="numberOne"/>
<jsp:getProperty name="digitBean" property="operator"/>
<jsp:getProperty name="digitBean" property="numberTwo"/> =
<jsp:getProperty name="digitBean" property="result"/>
</p></body></HTML>servlet(控制器)
package handle.data;
import save.data.*;
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class Example7_1_Servlet extends HttpServlet{
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException{
super.init(config);
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException,IOException{
Example7_1_Bean digitBean = null;
digitBean = new Example7_1_Bean(); //创建Javabean对象.
//digitBean 是request bean:
request.setAttribute("digitBean",digitBean);
String str1 = request.getParameter("numberOne");
String str2 = request.getParameter("numberTwo");
if(str1==null||str2==null)
return;
if(str1.length()==0||str2.length()==0)
return;
double numberOne = Double.parseDouble(str1);
double numberTwo = Double.parseDouble(str2);
String operator = request.getParameter("operator");
double result=0;
if(operator.equals("+"))
result = numberOne+numberTwo;
else if(operator.equals("-"))
result = numberOne-numberTwo;
else if(operator.equals("*"))
result = numberOne*numberTwo;
else if(operator.equals("/"))
result = numberOne/numberTwo;
digitBean.setNumberOne(numberOne); //将数据存储在digitBean中
digitBean.setNumberTwo(numberTwo);
digitBean.setOperator(operator);
digitBean.setResult(result);
//请求example7_1.jsp显示digitBean中的数据:
RequestDispatcher dispatcher= request.getRequestDispatcher("example7_1.jsp");
dispatcher.forward(request,response);
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException,IOException{
doPost(request,response);
}
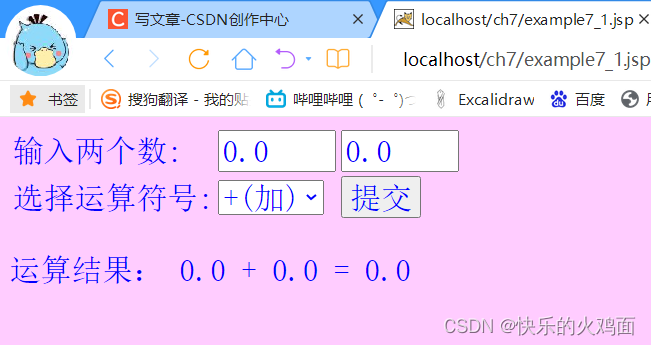
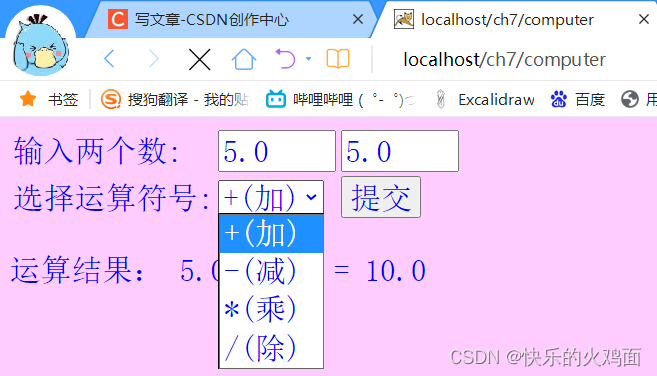
} 结果图

7.4.2 表白墙
java文件
package save.data;
public class ExpressWish {
String contents ; //表白内容。
String title; //标题。
String dateTime; //时间。
String peopleName; //表白人。
String id;
public void setId(String id){
this.id = id;
}
public String getId(){
return id;
}
public void setPeopleName(String s){
peopleName = s;
}
public String getPeopleName(){
return peopleName;
}
public void setContent(String s){
contents = s;
}
public String getContent(){
return contents;
}
public void setTitle(String s){
title = s;
}
public String getTitle(){
return title;
}
public void setDateTime(String s){
dateTime = s;
}
public String getDateTime(){
return dateTime ;
}
}
package save.data;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class ExpressWish_Bean {
public HashMap<String,ExpressWish> wishList;
ArrayList<ExpressWish> wishes;//存放wishList中的表白信息的ArrayList。
public ExpressWish_Bean(){
wishList = new HashMap<String,ExpressWish>();
wishes = new ArrayList<ExpressWish>();
}
public void addExpressWish(String id,ExpressWish expressWish){
wishList.put(id,expressWish);
putToArrays(wishList);//再把全部表白放到ArrayList wishes。
}
public void removeExpressWish(String id){
wishList.remove(id);
putToArrays(wishList);
}
public String getId(int index) {//返回某个表白者。
return wishes.get(index).getId();
}
public String getPeopleName(int index) {//返回某个表白者。
return wishes.get(index).getPeopleName();
}
public String getTitle(int index){
return wishes.get(index).getTitle();
}
public String getContent(int index){
return wishes.get(index).getContent();
}
public String getDateTime(int index){
return wishes.get(index).getDateTime();
}
public int size() {
return wishes.size();
}
void putToArrays(HashMap<String,ExpressWish> list){//把表白放到wishes。
wishes.clear();
Iterator<ExpressWish> iterator = list.values().iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
ExpressWish wish = iterator.next();
wishes.add(wish);
}
}
}JSP页面视图
example7_2
<%@ page contentType="text/html" %>
<%@ page pageEncoding = "utf-8" %>
<HTML>
<style>
#tom{
font-family:宋体;font-size:18;color:blue
}
</style>
<body bgcolor = #ffccff>
<form action="handleExpress" id="tom" method="post" >
表白者:<input type="text" id = "tom" name="peopleName" size = 28/>
<br>标题:<input type="text" id = "tom" name="title" size = 30/>
<br>内容:<br>
<textArea name="contents" id = "tom" rows="10" cols=36 >
</textArea>
<br><input type="submit" id="tom" value="提交表白" name="submit"/>
</form>
<p id="tom">
<a href="example7_2_show.jsp">查看表白墙</a>
</p></body></HTML> example7_2_delete
<%@ page contentType="text/html" %>
<%@ page pageEncoding = "utf-8" %>
<jsp:useBean id="wishWallBean" class ="save.data.ExpressWish_Bean" scope="application"/>
<HTML><body bgcolor = pink>
<p style="font-family:宋体;font-size:18;color:blue">
管理员删除表白的页面。
<form action="" method=post >
输入密码:<input type="password" name="password" size=12 /><br>
输入表白id:<input type="text" name="peopleId" size=6 />
<br><input type="submit" name="submit" value="删除"/>
</form>
<% request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
String password=request.getParameter("password");
String id=request.getParameter("peopleId");
if(password == null ) password = "";
if(id == null ) id = "";
if(password.equals("123456")){
wishWallBean.removeExpressWish(id);
}
%>
<a href="example7_2_show.jsp">查看表白墙</a>
</p></body></HTML>
example7_2_show
<%@ page contentType="text/html" %>
<%@ page pageEncoding = "utf-8" %>
<jsp:useBean id="wishWallBean" class ="save.data.ExpressWish_Bean" scope="application"/>
<style>
#tom{
font-family:宋体;font-size:26;color:blue
}
</style>
<HTML><body bgcolor=white>
<table border=1>
<tr><th id=tom>id</th><th id=tom>表白人</th><th id=tom>标题</th>
<th id=tom>时间</th><th id=tom>表白内容</th>
<% for(int i=0;i<wishWallBean.size();i++){
out.print("<tr>");
out.print("<td id=tom>"+wishWallBean.getId(i)+"</td>");
out.print("<td id=tom>"+wishWallBean.getPeopleName(i)+"</td>");
out.print("<td id=tom>"+wishWallBean.getTitle(i)+"</td>");
out.print("<td id=tom>"+wishWallBean.getDateTime(i)+"</td>");
out.print("<td ><textArea rows=5 cols=20 id=tom>"+wishWallBean.getContent(i)+
"</textArea></td>");
out.print("</tr>");
}
%> </table>
<a id =tom href="example7_2.jsp">去表白</a>
</body></HTML>servlet控制器
package handle.data;
import save.data.ExpressWish;
import save.data.ExpressWish_Bean;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class ExpressWish_Servlet extends HttpServlet{
int index; //做id。
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException{
super.init(config);
}
synchronized long getIndex() { //synchronized修饰的方法
index = index+1;
return index;
}
public void service(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException,IOException{
request.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
ExpressWish_Bean wishWallBean = null; //wishWallBean存放表白墙内容。
ServletContext application = getServletContext();
wishWallBean = (ExpressWish_Bean)application.getAttribute("wishWallBean");
if(wishWallBean == null ){//wishWallBean不存在就创建wishWallBean。
wishWallBean = new ExpressWish_Bean();
application.setAttribute("wishWallBean",wishWallBean);//appication bean。
}
String peopleName = request.getParameter("peopleName");//表白者。
String title = request.getParameter("title"); //标题。
String content = request.getParameter("contents");//表白内容。
ExpressWish wish = new ExpressWish();
if(peopleName.length()==0||title.length()==0||content.length()==0){
response.sendRedirect("example7_2.jsp");
return;
}
wish.setPeopleName(peopleName);
wish.setTitle(title);
wish.setContent(content);
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
String str = dateTime.toString();
String time =str.substring(0,str.lastIndexOf("."));//不要纳秒。
wish.setDateTime(time);
long number = getIndex();
wish.setId(""+number);
wishWallBean.addExpressWish(""+number,wish);//添加一条表白。
response.sendRedirect("example7_2_show.jsp"); //显示表白墙。
}
}
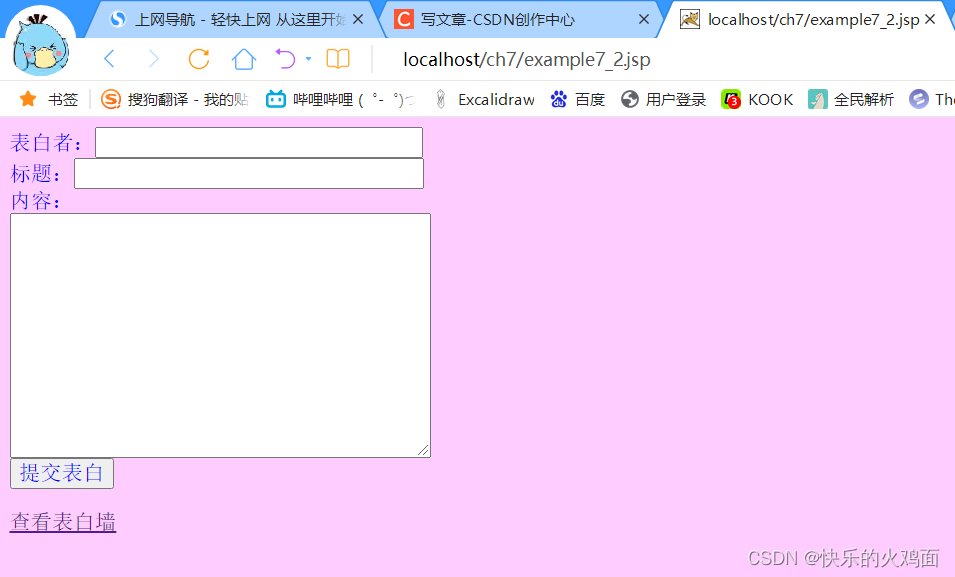
运行结果


总结
本章学习的MVC模式核心思想是将“模型”“视图”和“控制器”进行有效组合。掌握该模式对于设计合理的Web应用以及学习使用某些流行的Web框架。总体来说,本章学习的内容还是较为难的。
模型的生命周期和视图的更新
这些都是一些难点
MVC的学习还需要更多的课外学习。





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








