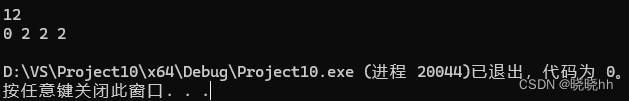
Q:四平方和
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int a = 0; a * a < n; a++) {
for (int b = a; b * b + a * a < n; b++) {
for (int c = b; c * c + a * a + b * b < n; c++) { //要求字典序更小
for (int d = c; d * d + c * c + a * a + b * b <= n; d++) {
if (d * d + c * c + a * a + b * b == n) {
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << " " << d << endl;
return 0;
}
}
}
}
}
}
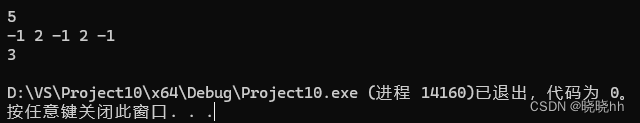
Q:装饰效果
#include <iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int a[1005] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
int maxn = 0;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
sum += a[j];
maxn = max(maxn, sum);
}
sum = 0;
}
cout << maxn << endl;
return 0;
}
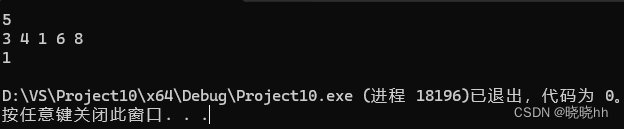
Q:双截棍
#include <iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n;
cin >> n;
int L[105] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cin >> L[i];
}
int cha = 10000, mixn = 10000;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
cha = abs(L[i] - L[j]);
mixn = min(mixn, cha);
}
}
cout << mixn << endl;
return 0;
}
——————————————————————————————
视频学习:09-常用 STL视频讲解(C++ 版)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
S:
vector(int) v; //存放int类型的数组(动态数组)
插入: v.push_back(1) //[1]
获取长度并访问元素: int len = v.size(); v[0]
删除: v.pop_back(); //[1,2]变成[1]
清空元素:v.clear()
——————————————————————————————
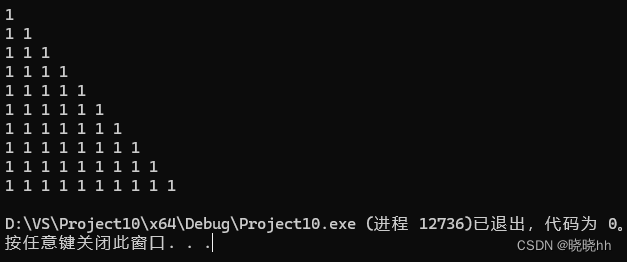
二维动态数组:
#include<vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> v2;
int n = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
vector<int> x(i + 1, 1);
v2.push_back(x);
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < v2[i].size(); j++) {
cout << v2[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
————————————
n行m列的二维数组,初始化位0
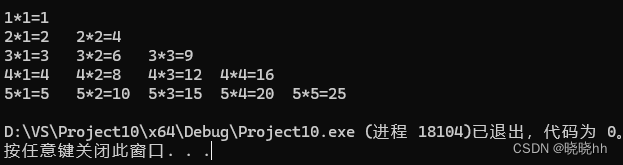
vector<vector<int>> v2(n,vector<int>(m,0))Q:乘法表
#include<vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> v2;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
v2.push_back(vector<int>());
}
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++) {
v2[i].push_back((i + 1) * (j + 1));
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < v2.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < v2[i].size(); j++) {
cout << i + 1 << "*" << j + 1 << "=" << v2[i][j] << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
S:集合
引用
#include<set>插入:insert
删除:erase
判断元素是否存在:count
#include<vector>
#include<set> //集合(each元素唯一不重复)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
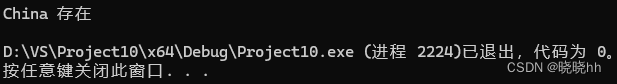
int main() {
set<int> aa;
set<string> bb;
bb.insert("China"); //插入
bb.insert("America");
bb.insert("China"); //不会报错,但是也不会执行(元素不重复)
bb.erase("France"); //删除(删不存在的也不会报错)
if (bb.count("China")) { //某元素是否在集合中出现
cout << "China 存在" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
遍历:用一个迭代器,写法固定
for (set<string>::iterator it = bb.begin(); it != bb.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << endl; //注意要打*,指针!!
}#include<vector>
#include<set> //集合(each元素唯一不重复)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
set<int> aa;
set<string> bb;
bb.insert("China"); //插入
bb.insert("America");
bb.insert("China"); //不会报错,但是也不会执行(元素不重复)
bb.erase("France"); //删除(删不存在的也不会报错)
if (bb.count("China")) { //某元素是否在集合中出现
cout << "China 存在" << endl;
}
//遍历用迭代器,写法固定
for (set<string>::iterator it = bb.begin(); it != bb.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << endl; //注意要打*,指针!!
}
//注意:set是从小到大便利的,即set会帮我们排序
return 0;
}
清空:clear
#include<vector>
#include<set> //集合(each元素唯一不重复)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
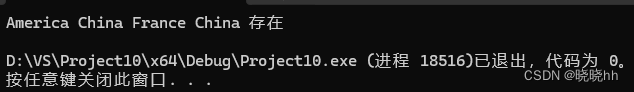
int main() {
set<string> bb;
bb.insert("China");
bb.insert("America");
bb.insert("France");
set<string>::iterator it;
for (it = bb.begin(); it != bb.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
bb.erase("English");
bb.erase("America");
if (bb.count("China")) {
cout << "China 存在" << '\n';
}
bb.clear();
return 0;
}
S:set和结构体
//重载 < 操作符,这样结构体才能集合排序输出
//表示:按照x的排前面,如果x相等,y小的排前面。
struct Node {
int x, y;
bool operator<(const Node& rhs) const {
if (x == rhs.x)
return y < rhs.y;
else
return x < rhs.x;
}
};
Q:练习
#include<vector>
#include<set> //集合(each元素唯一不重复)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int x, y;
bool operator<(const Node& rhs) const {
if (x == rhs.x)
return y < rhs.y;
else
return x < rhs.x;
}
};
int main() {
int n;
set<Node> N;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Node n;
cin >> n.x >> n.y;
N.insert(n);
}
cout << '\n';
for (set<Node>::iterator it = N.begin(); it != N.end(); it++) {
cout << it->x << " " << it->y << endl;
}
return 0;
}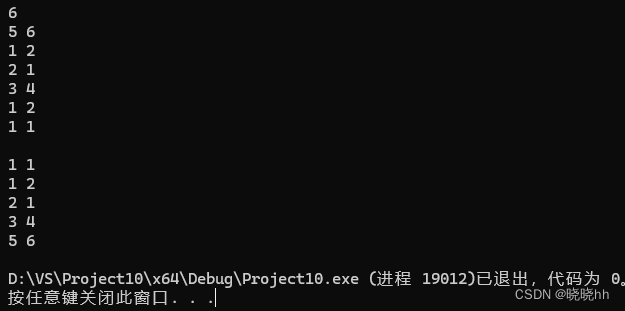 、
、
S:映射表
#include<map>构造语句:
map<T1,T2> m; //把T1映射成T2类型借助pair, 在头文件<utility>里面
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
map<string, int> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("Tom", 1));
dict.insert(make_pair("Jone", 2));
dict.insert(make_pair("Mary", 1));
//{"Tom"->1, "Jone"->2,"Mary"->1}
return 0;
}———————————————————————————学了六个小时,吃饭去,明天继续。







 文章介绍了C++中的枚举算法实现以及常用STL容器如vector,set,map的基本操作,包括动态数组、插入、删除、遍历和集合元素的特性。
文章介绍了C++中的枚举算法实现以及常用STL容器如vector,set,map的基本操作,包括动态数组、插入、删除、遍历和集合元素的特性。















 1676
1676











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










