BFS叫做广度优先搜索算法,通过BFS来实现一个走迷宫问题。
前言
BFS叫做广度优先搜索算法,我们通过BFS来实现一个走迷宫问题。
一、BFS是什么?
1.BFS定义
BFS(又称广度优先搜索或者宽度优先搜索)是最简便的图的搜索算法之一。Dijkstra单源最短路径算法和Prim最小生成树算法都采用了深度游优先搜索类似的思想。它是尽可能的找到与当前结点连接的所有结点,按照层级进行搜索,使用队列来维持待访问结点的顺序。
2.BFS模拟实现
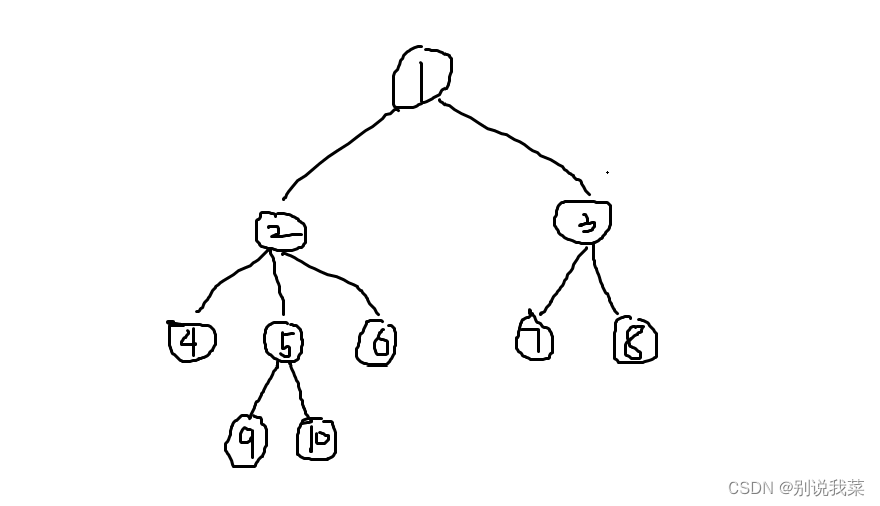
图 2.1树
我们还是通过图2.1的树来模拟一下BFS的整个流程,具体流程如下:
1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9->10
相同颜色的结点是一层的,所以BFS的特点就是我们把这一层的结点全部搜索完毕后才会去搜索下一层的结点。
通常我们是通过队列来模拟宽度优先搜索:
- 我们创建一个队列。
- 将根结点入队。
- 判断队列是否为空,不为空时,队列弹出一个结点,然后将它的左结点和右节点入队,重复上述操作,直到队列为空时退出循环。
二、走迷宫问题
1.问题描述
给定一个 n×m的二维整数数组,用来表示一个迷宫,数组中只包含 00 或 11,其中 00 表示可以走的路,11 表示不可通过的墙壁。
最初,有一个人位于左上角 (1,1) 处,已知该人每次可以向上、下、左、右任意一个方向移动一个位置。
请问,该人从左上角移动至右下角 (n,m) 处,至少需要移动多少次。
数据保证 (1,1) 处和 (n,m)处的数字为 00,且一定至少存在一条通路。
2.算法思路
我们以一个样例为基础来进行描述,输入数据如下:
5 5
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0正常情况下我们可以这样走
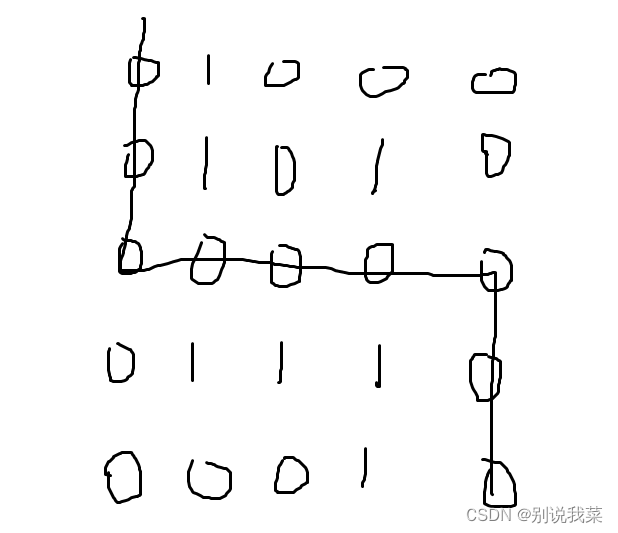
图2.1路径图
如果我们采用BFS,路径如下:
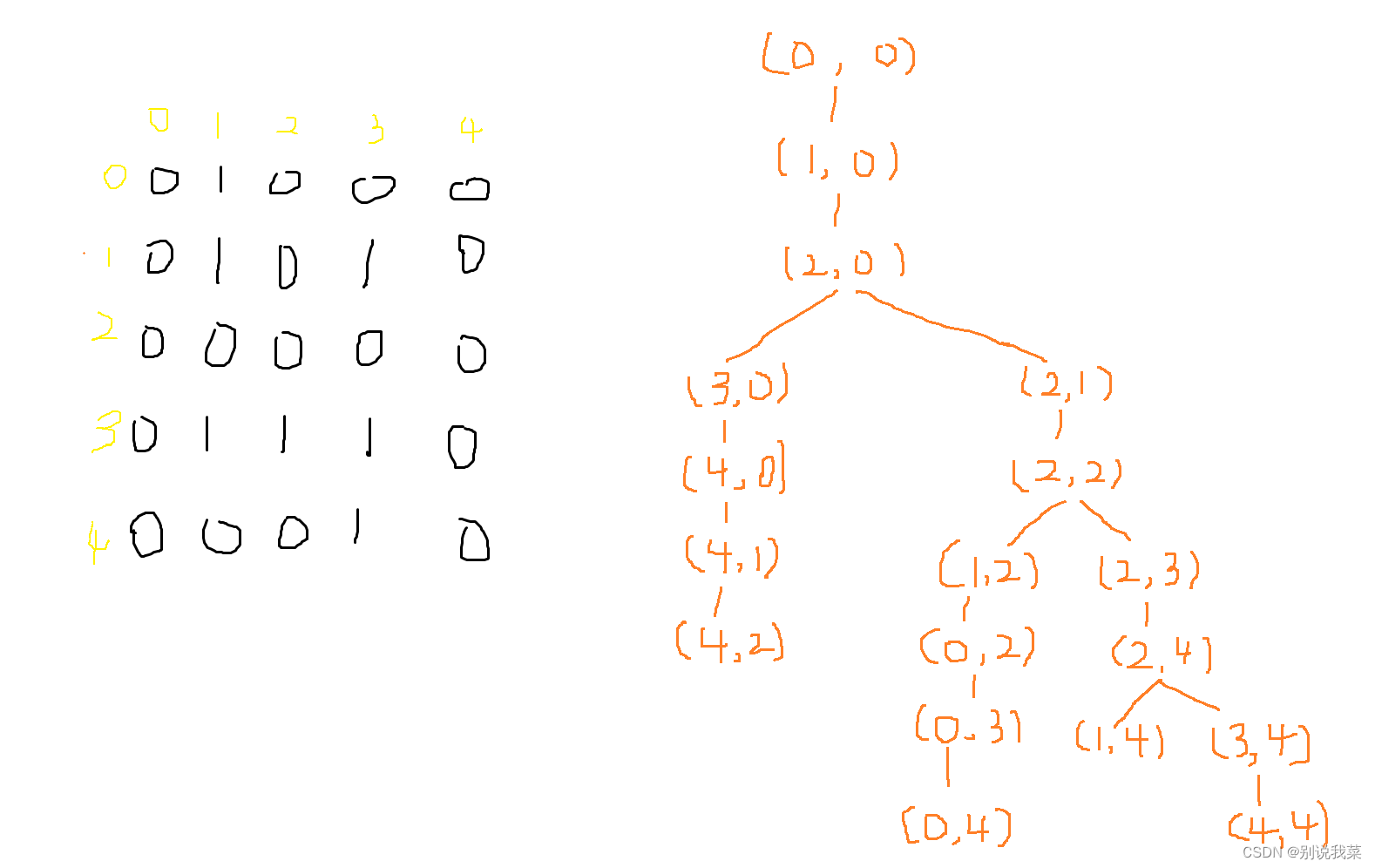
图2.2模拟路径
我们引入二维数组map用来记录迷宫地图,二维数组d表示走到从起点走到当前结点所需要的步数。我们引入一个外部类Pair,用来表示当前结点是从哪一个坐标移动过来的,同时用一个二维数组prev来存储我们的路径。
bfs实现如下:
public static int bfs(){
//初始化队列
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();
int[] dy = {0,1,0,-1};
int[] dx = {-1,0,1,0};
q.add(new Pair(0,0));
while (!q.isEmpty()){
Pair pair = q.poll();
if(pair.x == n-1 && pair.y == m-1){
break;
}
//上下左右遍历
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++){
int x = pair.x + dx[i];
int y = pair.y + dy[i];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && map[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == 0){
//入队
q.offer(new Pair(x,y));
//位移之后的路径长度
d[x][y] = d[pair.x][pair.y] + 1;
//存储路径
prev[x][y] = pair;
}
}
}
//打印路径
int x = n-1,y = m-1;
while (x != 0 || y != 0){
pw.println(x +" "+y);
Pair pair = prev[x][y];
x = pair.x;
y = pair.y;
}
return d[n-1][m-1];
}三、代码
1.代码如下:
package AcWing;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class BFS走迷宫 {
static PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static int n,m;
//用来记录路径长度
static int[][] d = null;
//用于记录当前位置是从哪个位置过来的
static Pair[][] prev = null;
//地图
static int[][] map = null;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(br);
n = sc.nextInt();
m = sc.nextInt();
map = new int[n][m];
d = new int[n][m];
prev = new Pair[n][m];
for(int i = 0; i< n;i++){
for(int j = 0;j < m;j++){
map[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
pw.println(bfs());
pw.flush();
}
public static int bfs(){
//初始化队列
Queue<Pair> q = new LinkedList<>();
//用两个一维数组分别表示上下左右位移
int[] dy = {0,1,0,-1};
int[] dx = {-1,0,1,0};
q.add(new Pair(0,0));
while (!q.isEmpty()){
Pair pair = q.poll();
if(pair.x == n-1 && pair.y == m-1){
break;
}
//上下左右遍历
for(int i = 0;i < 4;i++){
int x = pair.x + dx[i];
int y = pair.y + dy[i];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m && map[x][y] == 0 && d[x][y] == 0){
q.offer(new Pair(x,y));
//位移之后的路径长度
d[x][y] = d[pair.x][pair.y] + 1;
//记录路径
prev[x][y] = pair;
}
}
}
//打印路径
int x = n-1,y = m-1;
while (x != 0 || y != 0){
pw.println(x +" "+y);
Pair pair = prev[x][y];
x = pair.x;
y = pair.y;
}
return d[n-1][m-1];
}
}
class Pair{
int x;
int y;
public Pair(int x,int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
2.读入数据
代码如下(示例):
5 5
0 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 03.代码运行结果
最短路径:
4 4
3 4
2 4
2 3
2 2
2 1
2 0
1 0
最短步数:
8
总结
走迷宫跟bfs的基本思路一样,其中只不过是增加了走的方向和限制条件,只要理解了bfs的基本思路,那么走迷宫问题很容易得到解决。





















 387
387











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








