1、定时器是什么
定时器:
定时器也是软件开发中的⼀个重要组件. 类似于⼀个 "闹钟". 达到⼀个设定的时间之后, 就执⾏某个指定 好的代码.
定时器是⼀种实际开发中⾮常常⽤的组件
举个例子:
⽐如⽹络通信中, 如果对⽅ 500ms 内没有返回数据, 则断开连接尝试重连.
类似于这样的场景就需要⽤到定时器.
package thread_demo;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class Demo37 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer =new Timer();
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 3000");
}
},3000);
System.out.println("hello main");
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 2000");
}
},2000);
timer.schedule(new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 1000");
}
},1000);
}
}
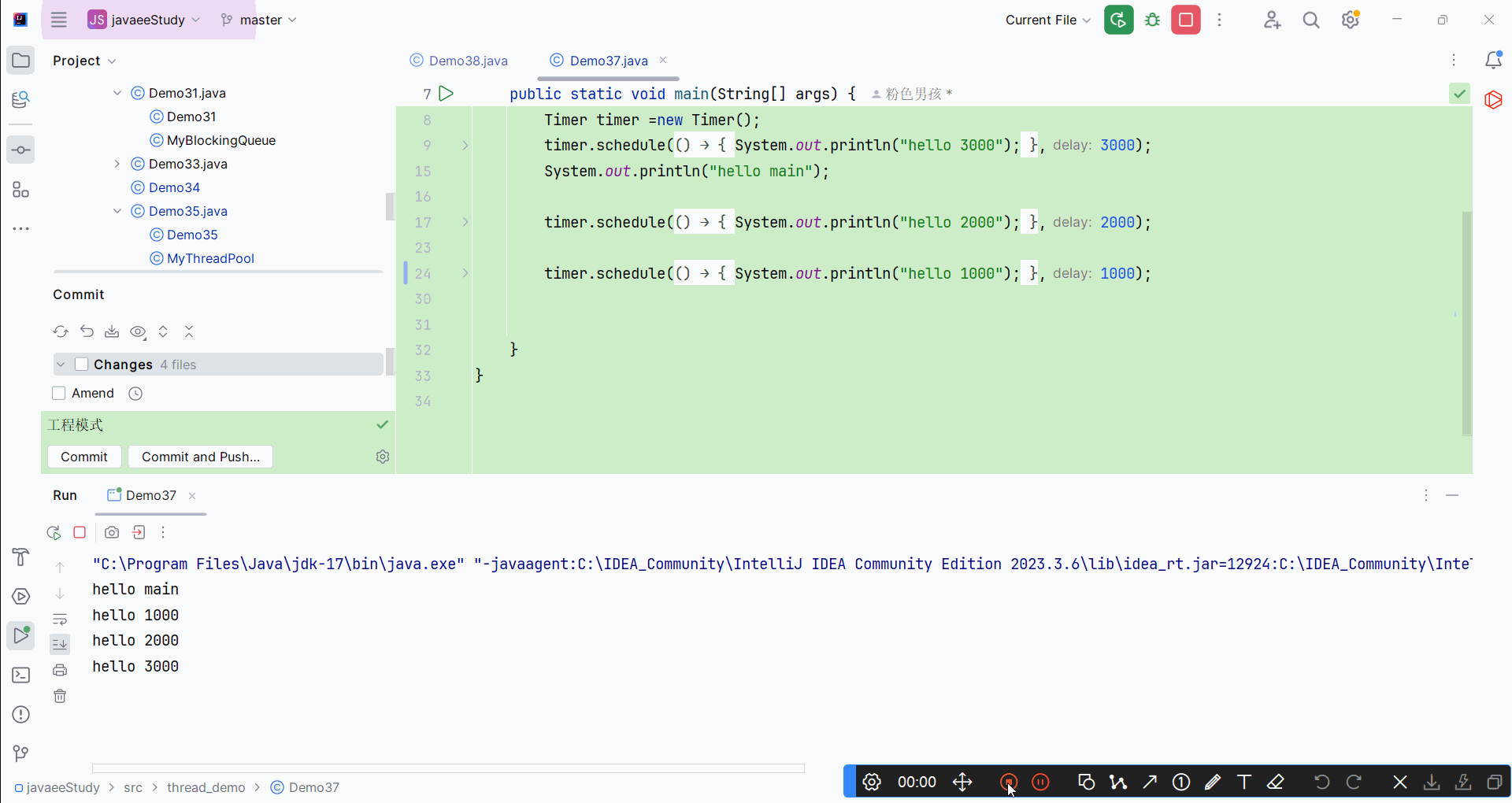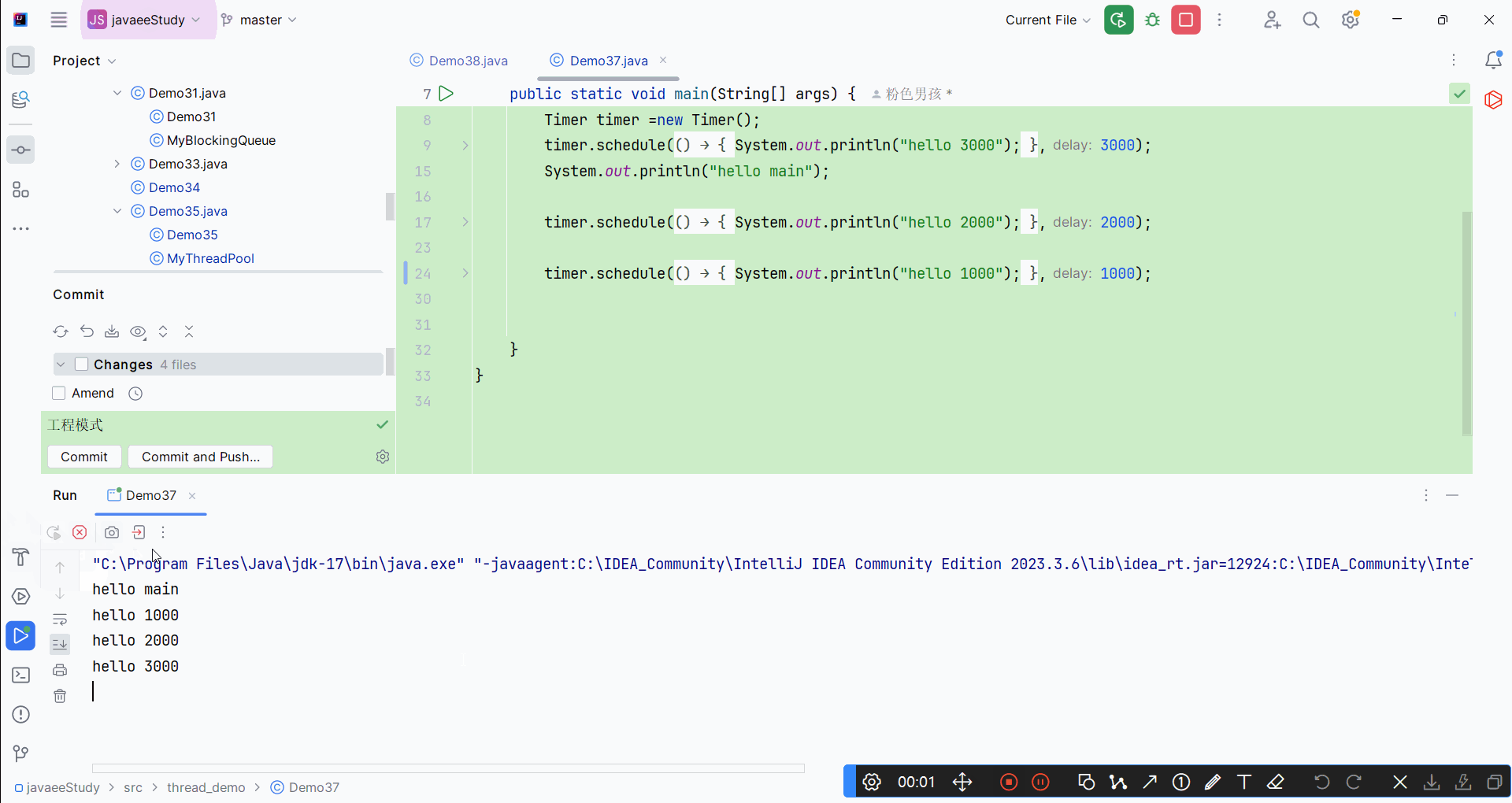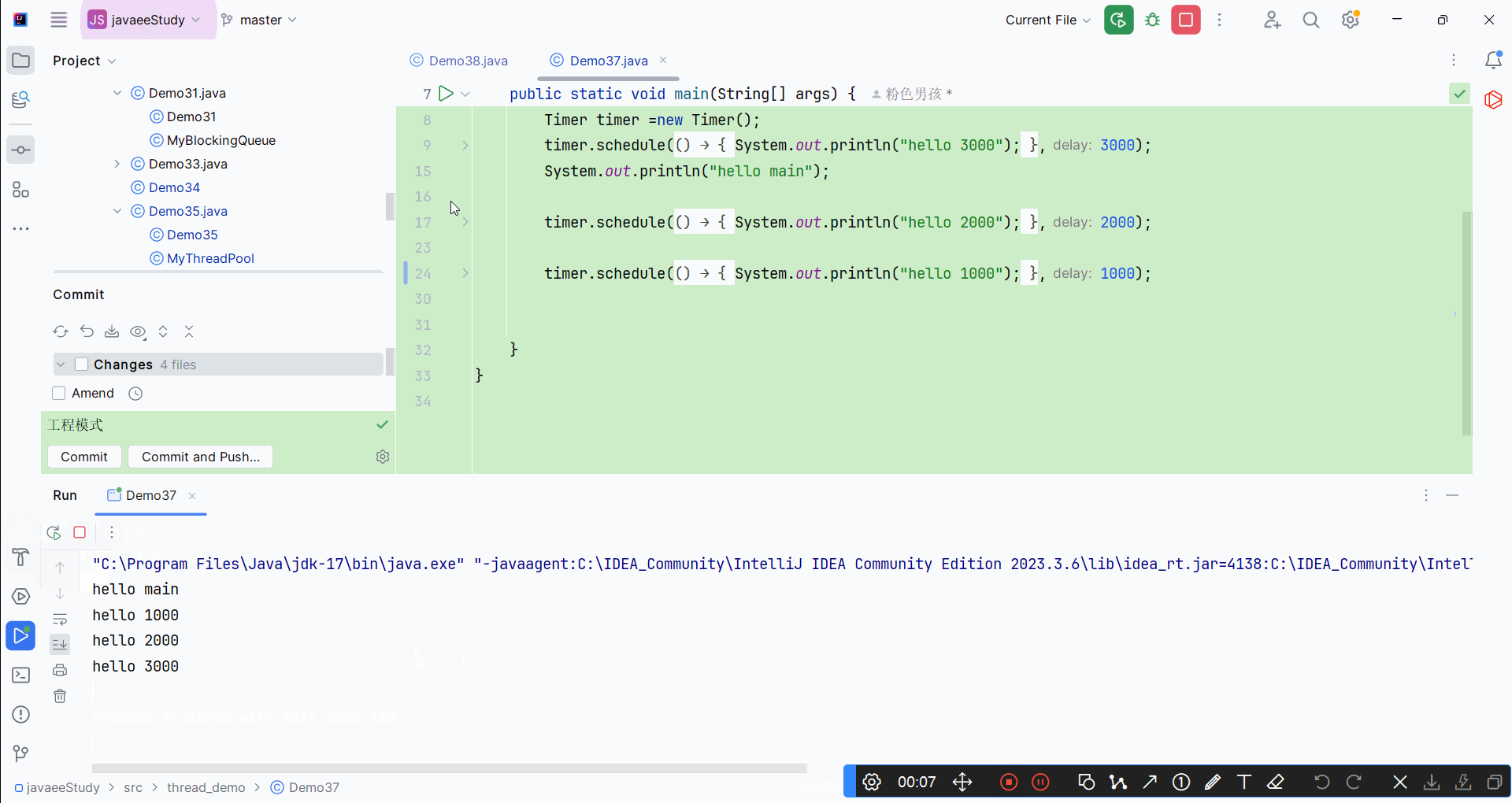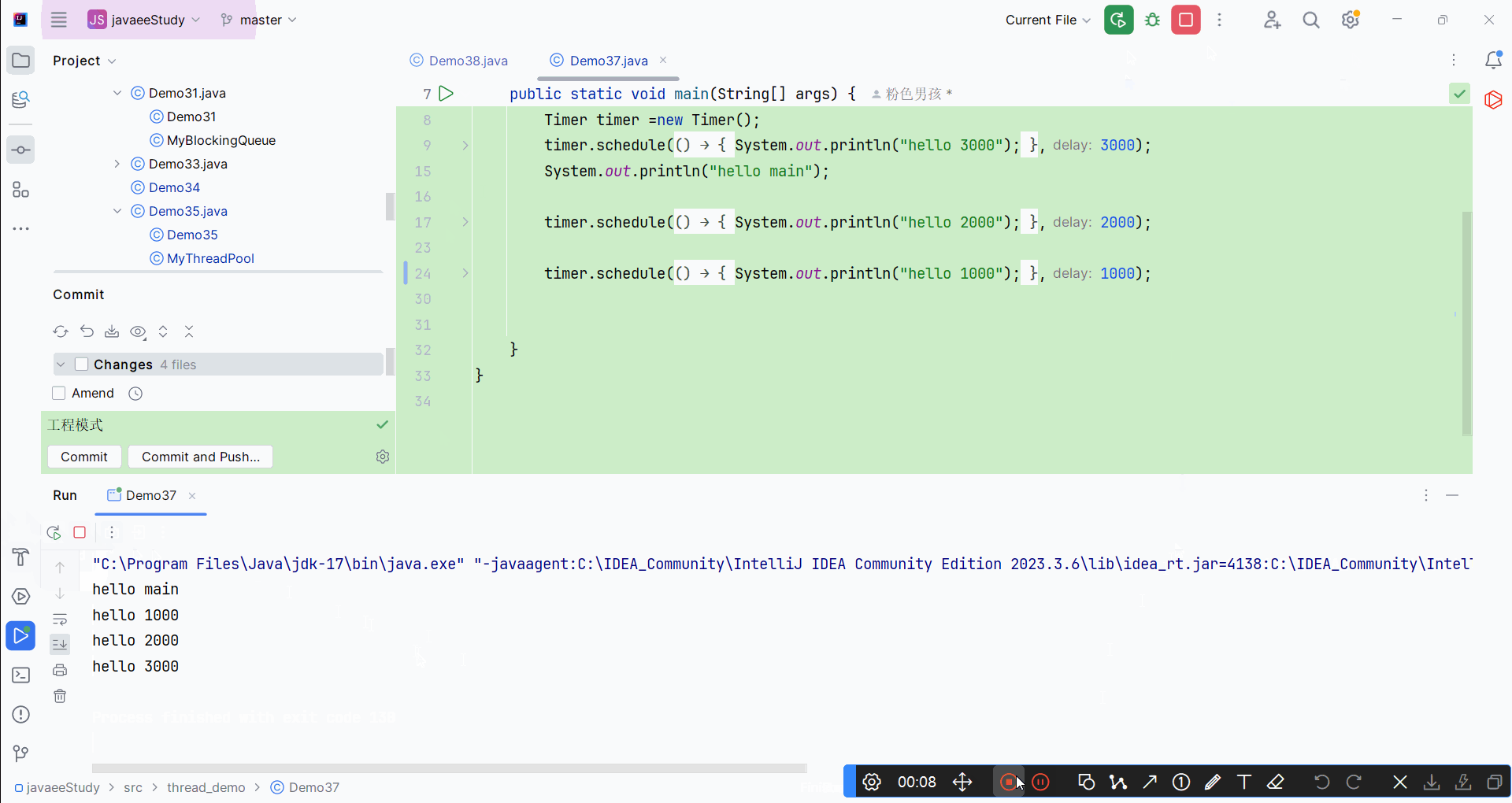
运行结果:
2、模拟实现定时器
定时器的构成
• ⼀个带优先级队列(不要使⽤ PriorityBlockingQueue, 容易死锁!)
当管理多个任务的时候,需要确保,时间最早的任务,最先执行,通过遍历的方式,找到时间最早.使用优先队列
• 队列中的每个元素是⼀个 Task 对象.
• Task 中带有⼀个时间属性, 队⾸元素就是即将要执⾏的任务
时间戳:
计算机中,使用时间戳来表示“时刻”
以1970年1月1日0时0分0秒基准时刻
计算当前时刻和基准时刻的,秒数之差 (毫秒/微秒)
• 同时有⼀个 worker 线程⼀直扫描队⾸元素, 看队⾸元素是否需要执⾏
代码实现
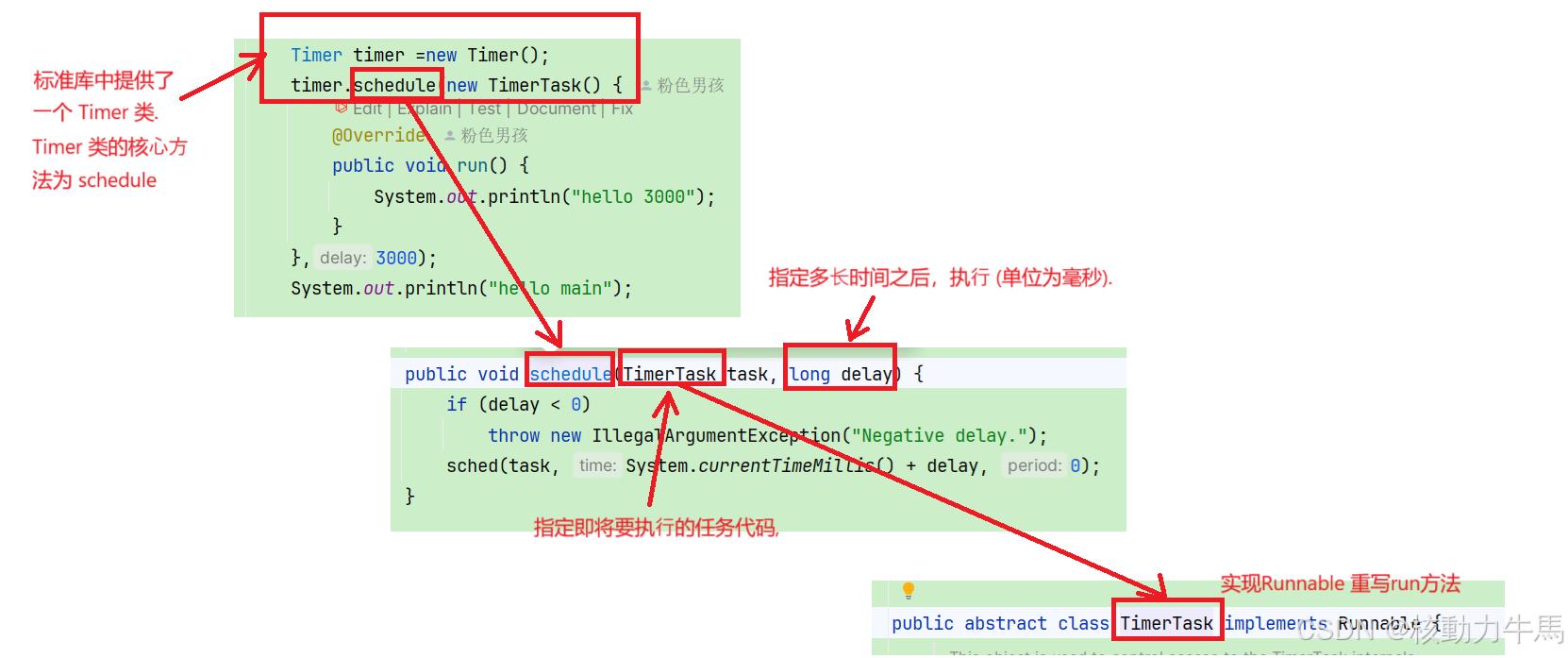
1. Timer 类提供的核⼼接⼝为 schedule, ⽤于注册⼀个任务, 并指定这个任务多⻓时间后执⾏.
class Mytimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
public void schedule(Runnable task, long delay) {
}
}
2. MyTimeTask 类⽤于描述⼀个任务(作为 Timer 的内部类).
⾥⾯包含⼀个 Runnable 对象和⼀个 time(毫秒时 间戳) 这个对象需要放到 优先队列 中. 因此需要实现 Comparable 接⼝.
class MyTimerTask implements Comparable<MyTimerTask> {
private Runnable task;
private long time;
public MyTimerTask(Runnable task, long time) {
this.task = task;
this.time = time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(MyTimerTask o) {
return (int) (this.time - o.time);
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public void run() {
task.run();
}
}
3. MyTimer 实例中, 通过 PriorityQueue 来组织若⼲个 Task 对象. 通过 schedule 来往队列中插⼊⼀个个 Task 对象.
class Mytimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
private Object locker = new Object();
public void schedule(Runnable task, long delay) {
synchronized (locker) {
MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask(task, System.currentTimeMillis() + delay);
queue.offer(timerTask);
locker.notify();
}
}
}
4. Timer 类中存在⼀个 worker 线程, ⼀直不停的扫描队⾸元素, 看看是否能执⾏这个任务. 所谓 "能执⾏" 指的是该任务设定的时间已经到达了.
class Mytimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
private Object locker = new Object();
public void schedule(Runnable task, long delay) {
synchronized (locker) {
MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask(task, System.currentTimeMillis() + delay);
queue.offer(timerTask);
locker.notify();
}
}
public Mytimer() {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (true) {
synchronized (locker) {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
locker.wait();
}
MyTimerTask task = queue.peek();
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < task.getTime()) {
locker.wait(task.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis());
} else {
task.run();
queue.poll();
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
t.start();
}
}
完整代码:
package thread_demo;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
class MyTimerTask implements Comparable<MyTimerTask> {
private Runnable task;
private long time;
public MyTimerTask(Runnable task, long time) {
this.task = task;
this.time = time;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(MyTimerTask o) {
return (int) (this.time - o.time);
}
public long getTime() {
return time;
}
public void run() {
task.run();
}
}
class Mytimer {
private PriorityQueue<MyTimerTask> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
private Object locker = new Object();
public void schedule(Runnable task, long delay) {
synchronized (locker) {
MyTimerTask timerTask = new MyTimerTask(task, System.currentTimeMillis() + delay);
queue.offer(timerTask);
locker.notify();
}
}
public Mytimer() {
Thread t = new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (true) {
synchronized (locker) {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
locker.wait();
}
MyTimerTask task = queue.peek();
if (System.currentTimeMillis() < task.getTime()) {
locker.wait(task.getTime() - System.currentTimeMillis());
} else {
task.run();
queue.poll();
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
t.start();
}
}
public class Demo38 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mytimer mytimer = new Mytimer();
mytimer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 3000");
}
}, 3000);
mytimer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 2000");
}
}, 2000);
mytimer.schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("hello 1000");
}
}, 1000);
}
}





















 1598
1598

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








