目录
例题分析
参考百词斩app,打开界面如下,大致画一下UI界面的结构。
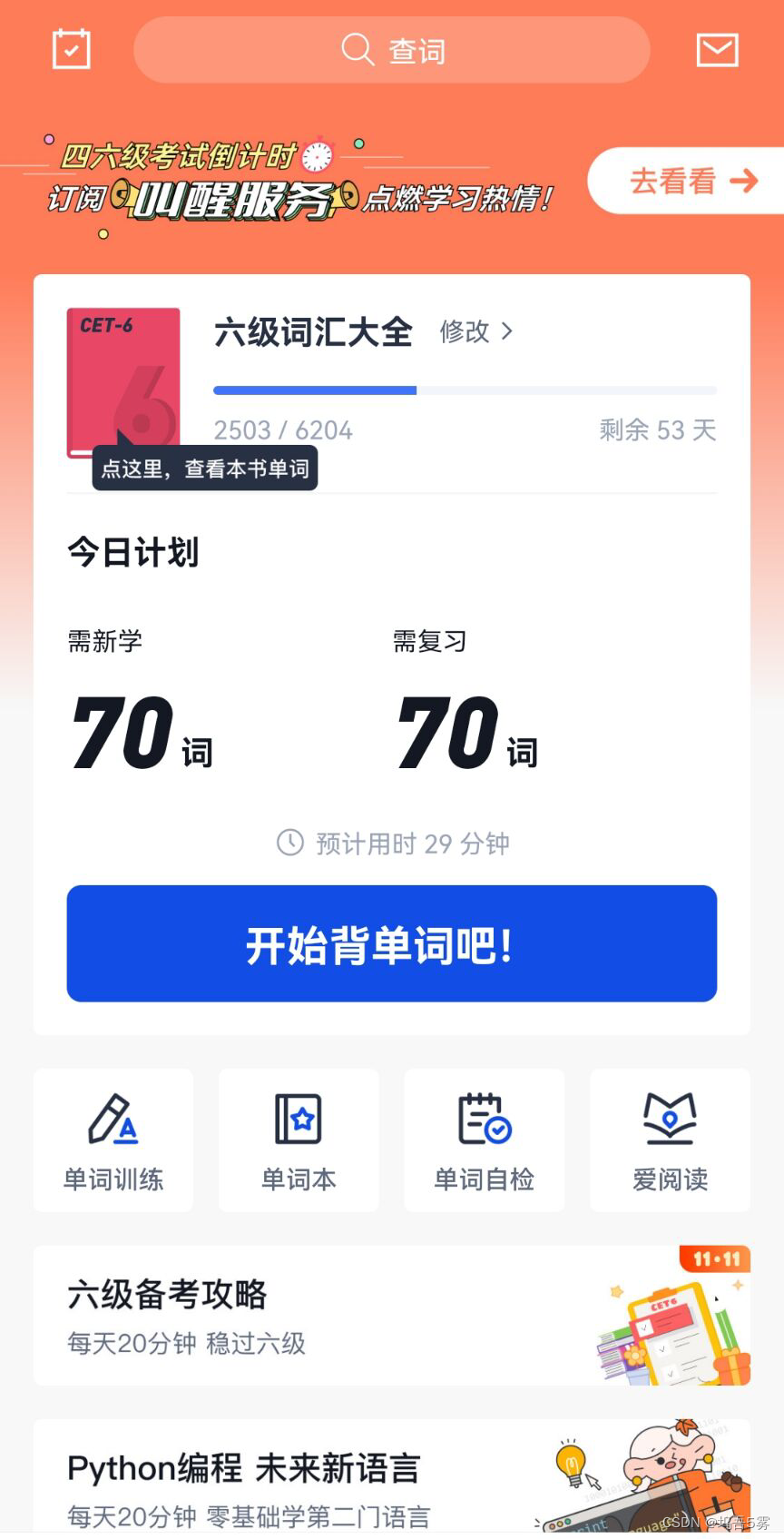

代码实现
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="120dp">
<View
android:id="@+id/view_1"
android:layout_width="30dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:background="#d9ead3"
android:layout_marginVertical="10dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_2"
android:layout_width="290dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view_1"
android:background="#d9ead3"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="17dp"
android:layout_marginVertical="10dp"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_3"
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view_2"
android:background="#d9ead3"
android:layout_marginVertical="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_4"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_below="@id/view_3"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:layout_marginStart="5dp"
android:background="#bfedae" />
</RelativeLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:layout_marginRight="10dp"
android:background="#3c78d8"
android:orientation="vertical">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<View
android:id="@+id/view_5"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:background="#c9daf8"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_6"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view_5"
android:background="#c9daf8" />
<View
android:id="@+id/view_7"
android:layout_width="380dp"
android:layout_height="90dp"
android:layout_below="@id/view_6"
android:layout_marginStart="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="10dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:background="#c9daf8" />
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
android:background="#fff2cc"
android:orientation="vertical">
<RelativeLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<View
android:id="@+id/view_8"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:background="#ed9494"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_9"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view_8"
android:background="#ed9494"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_10"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view_9"
android:background="#ed9494"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_11"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view_10"
android:background="#ed9494"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_12"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:layout_margin="15dp"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/view_11"
android:background="#ed9494"/>
<View
android:id="@+id/view_13"
android:layout_width="380dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_below="@id/view_9"
android:layout_marginStart="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="8dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="15dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="15dp"
android:background="@color/white" />
<View
android:id="@+id/view_14"
android:layout_width="380dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_below="@id/view_13"
android:layout_marginStart="15dp"
android:layout_marginTop="3dp"
android:layout_marginEnd="15dp"
android:background="@color/white" />
</RelativeLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>实际效果


颜色取色器网站:在线颜色选择器 | RGB颜色查询对照表





















 181
181











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








