Packaging and Storage Technology Learning Notes
Content derived from The Hong Kong Polytechnic University ISE373 course
Content
- Chapter 1: Logistics Functions
- Chapter 2: Plastic and Glass Packaging
- Chapter 3: Glass Packaging
- Chapter 4: Metal Based Packaging
- Chapter 5: Paper Packaging
-
- **
- 1. Basics of Paper and Paperboard
- 2. Properties of Paperboard
- 3. Types of Paperboard
- Selection of Paperboard
- **Types of Paperboard package
- Production and converting operations of Paperboard package
- Paper-based Flexible Packaging
- ** Cost Estimation of Paperboard Container
- Ring Crush Test for Linerboard strength
- Chapter 6: Corrugated Fiberboard Packaging for Storage and Transportation
-
- 1. INTRODUCTION
- Combined boards
- 2. CORRUGATED BOARD SPECIFICATION
- (A) Mullen Burst Strength Test
- 3. SHIPPING CONTAINER STANDARDS
- **(B) Edgewise Compression Test (ECT)
- **(C ) Predicting CS from ECT:The McKee Formula
- **(D) Stacking pattern on the pallet
- In-class exercise
- Maximum Stacking Height
- (E) Rule 41/Item 222 Burst Test Standard
- (4) BOX CONVERTING
- (C) Box Cost Estimation
- In-class Exercise
- Chapter 7: Packaged Product Quality & Shelf Life
Chapter 1: Logistics Functions
1. Packaging Function
Packaging for Food Preservation (preservation function)
Factors affecting food storage and preservation; Product quality and shelf-life; Packaging regulations on food stuff; Refrigeration and distribution of packaged foods
Packaging for Transportation (Transportation / Protecting function)
Preparation for marketing; Wholesales and retail packages; Transportation by rail, highway, air, and sea; Treatment after transportation; hazardous materials; Carrier rules
Packaging for marketing (Marketing function)
Packaging design considerations; Package printing and decorating; Labelling
2. Benefits of and concerns of packaging/ Public concern in packaging
- Prevents or reduces, product damage and food spoilage,
thereby saving energy and vital nutrients, and protecting the health of the consumer - Requires less municipal solid waste disposal since it
promotes processed food residue recycling for use as animal feed. - Open an international market for industries
- Provides functional convenience in use or preparation, Freeing up more time
3. Packaging Design and Development Framework
- Packaging litter and the volume of packaging waste
- Legibility of labels, Integrity of information on labels
- Perception of over-packaging due to apparently excessive ullage (free space) resulting from product settlement\
- Accidents involving packaging
4. Packaging & the Environment
Product needs
Nature of product
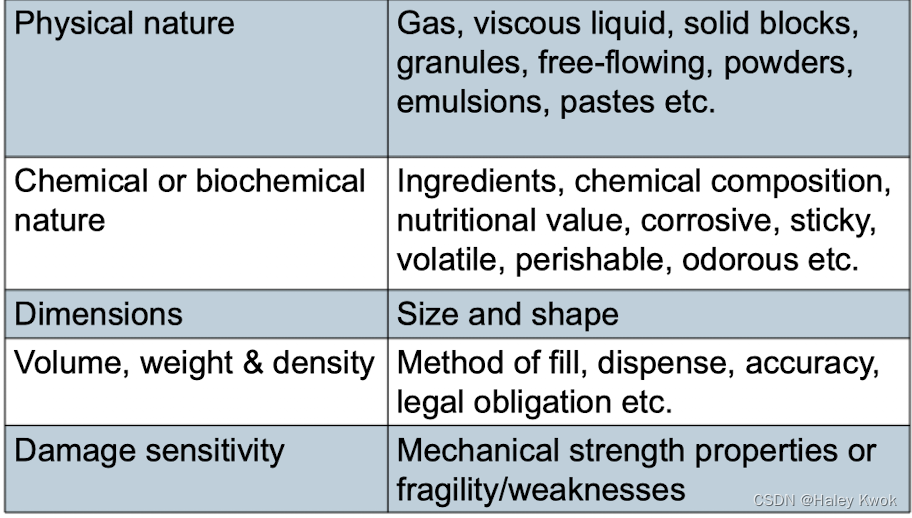
Product deterioration: Intrinsic mechanisms
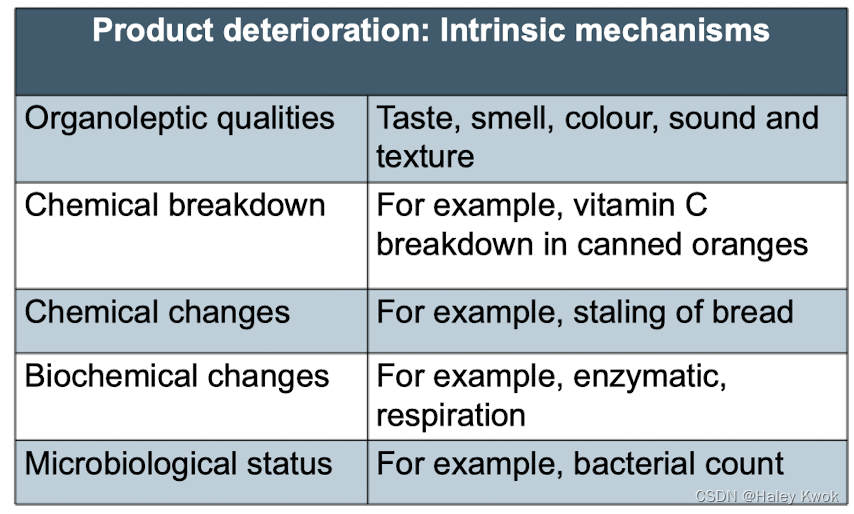
Product shelf-life requirement
Consumer needs and wants
● A product’s brand is generally used by purchasers as a
guide in assessing quality.
● Packaging which makes the sale.
● An interesting or visually attractive pack can give the crucial
● Packaging should accurately reflect product quality/brand
● Packaging is critical to a consumer’s first impression of a marketing edge. values, encourage repeat purchase and build brand loyalty. product, e.g. healthy lifestyle image etc
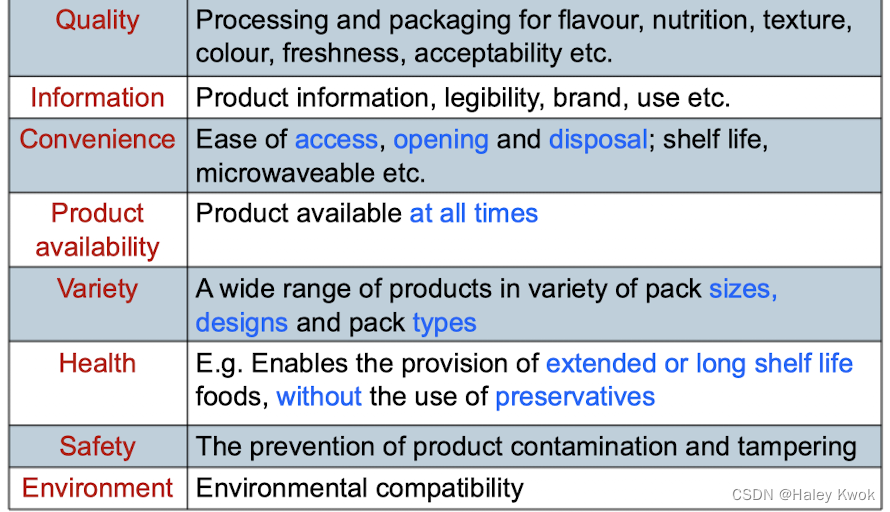
Shelf life: the time during which a food product can maintain satisfactory eating quality in the packs.
● Proper shelf life:
the time convenience of product use and
a reduced risk of food wastage.
● Packaging conveys important information about the product:
product facts such as weight, volume, ingredients, the manufacturer’s details, nutritional value, cooking and opening instructions.
● Labelling
● Convenience
Distribution needs and wants
Distribution: refers to the journey of the pack from the point of filling to the point of end use, packaging reuse, waste recovery and disposal.
● A thorough understanding of the distribution system is fundamental for designing cost-effective packaging
● Three distribution environments:
climatic
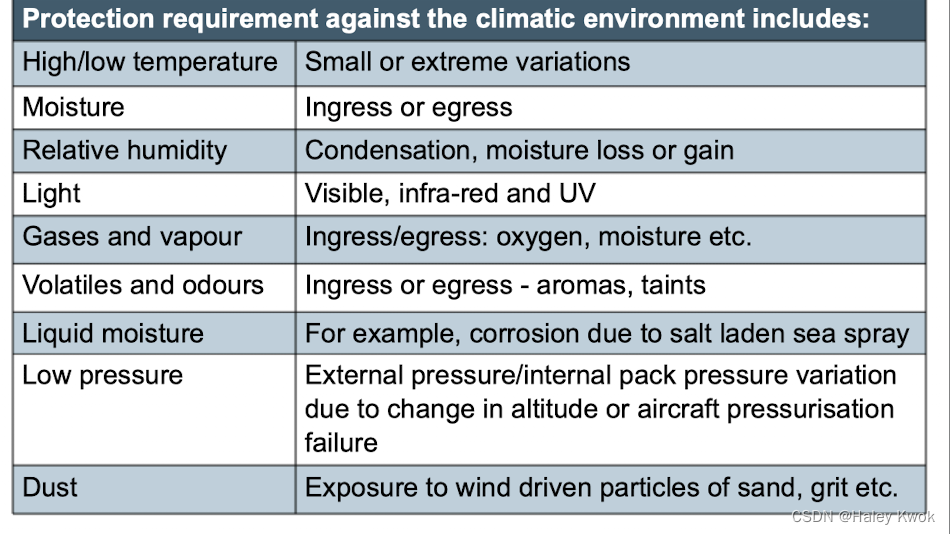
physical
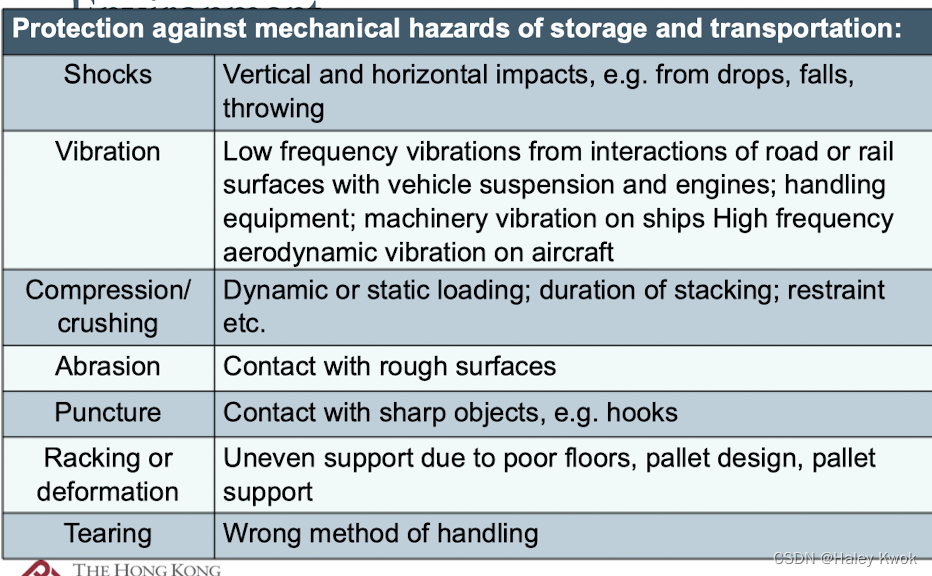
biological

Market needs and wants
● Packaging: a key to the evolution of modern fast-moving consumer goods retailing.
● Emergence of large retail groups: exert enormous influence
and control over what is produced, how products are presented and how they are distributed to stores.
● Manufacturers need to modify their distribution and
packaging operations in response to structural changes in retailing.
4R
- Reduce: use the least material consistent with fulfilling
its basic function - Reuse: Where practical, containers or packaging
components should be reused. - Recycle: Where practical, packaging should be
collected and the materials recycled for further use. - Recover: Before consigning packaging to a landfill,
some thought should be given to possibly recovering
other value from the waste

5. Historical Development of Packaging
6. Packaging Logistics
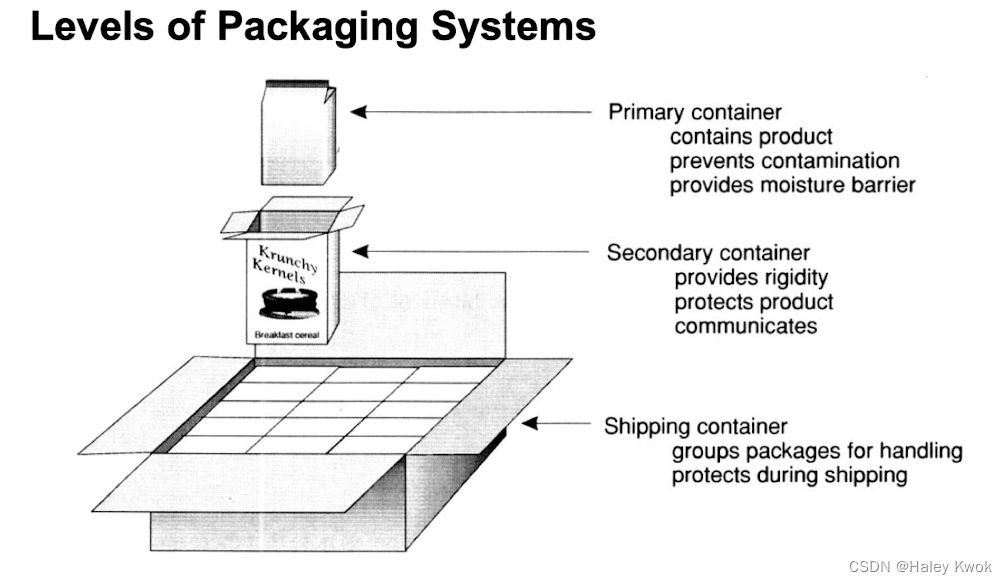
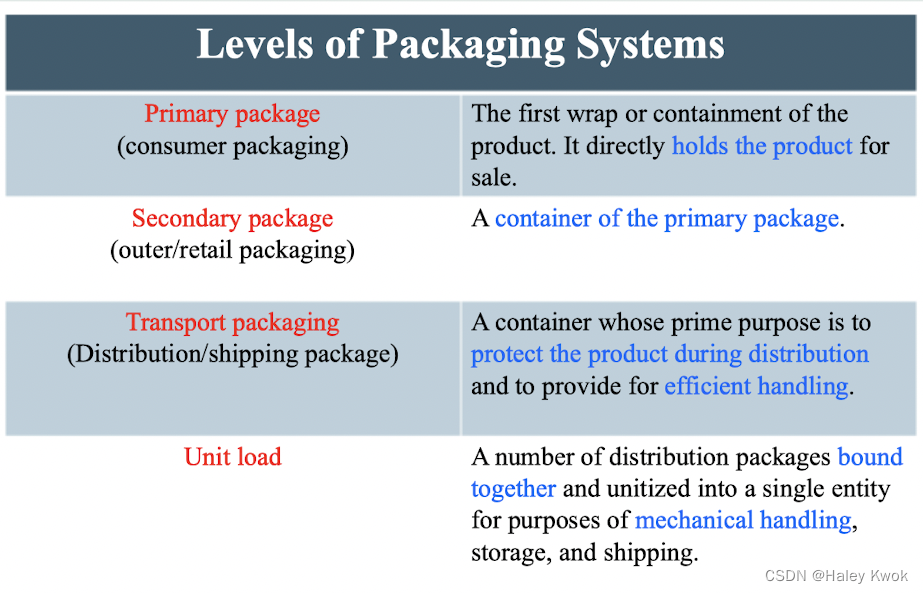
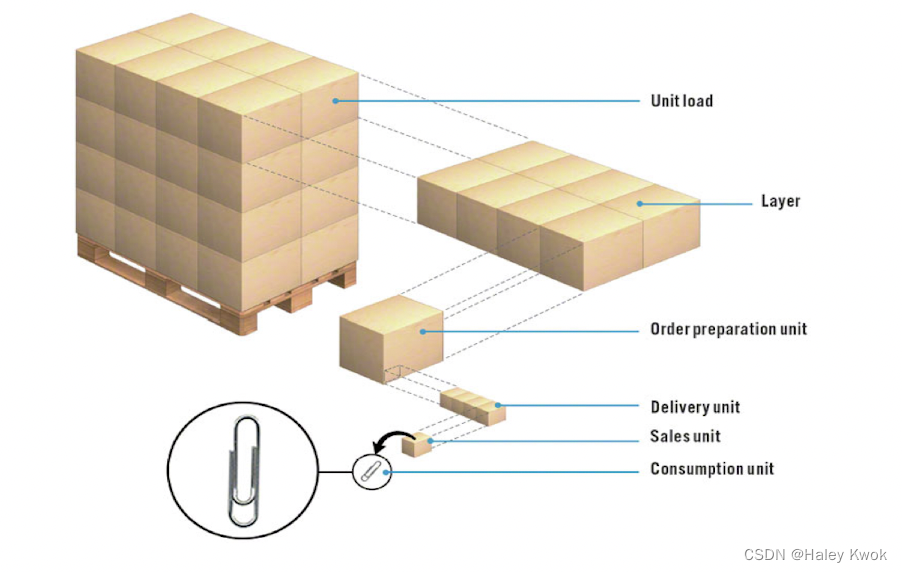
Chapter 2: Plastic and Glass Packaging
1. Role of plastic in packaging
The term plastics is used instead of polymer to indicate a specific category of high molecular weight materials that can be shaped using a combination of heat, pressure, and time. Polyethylene (PE) remains the leading packaging plastic because of its low raw material price, versatile properties, and its ease of manufacture and fabrication
In addition, plastic packages are usually thinner than their counterparts in glass, metal, paper, or paperboard.
Plastics are a special group of polymers.
- Thermoplastics: are able to repeatedly undergo this shape-changing treatment
- Thermoset: can be shaped only once. Thermoset polymers tend to have relatively
high chemical resistance and excellent mechanical properties. - However, the vast majority of plastics used in packaging are thermoplastics.
2. Plastic Injection Molding
Injection molding is the process in which melted plastic is forced into a mold where it is shaped and cooled. In packaging, it is the usual method for manufacturing closures (caps and lids) of various types of bottle.
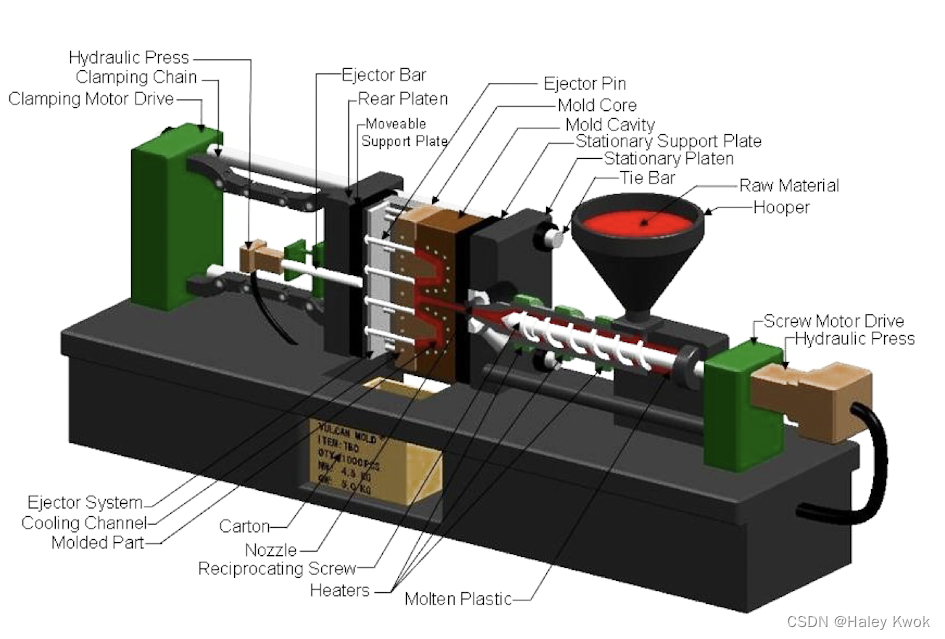
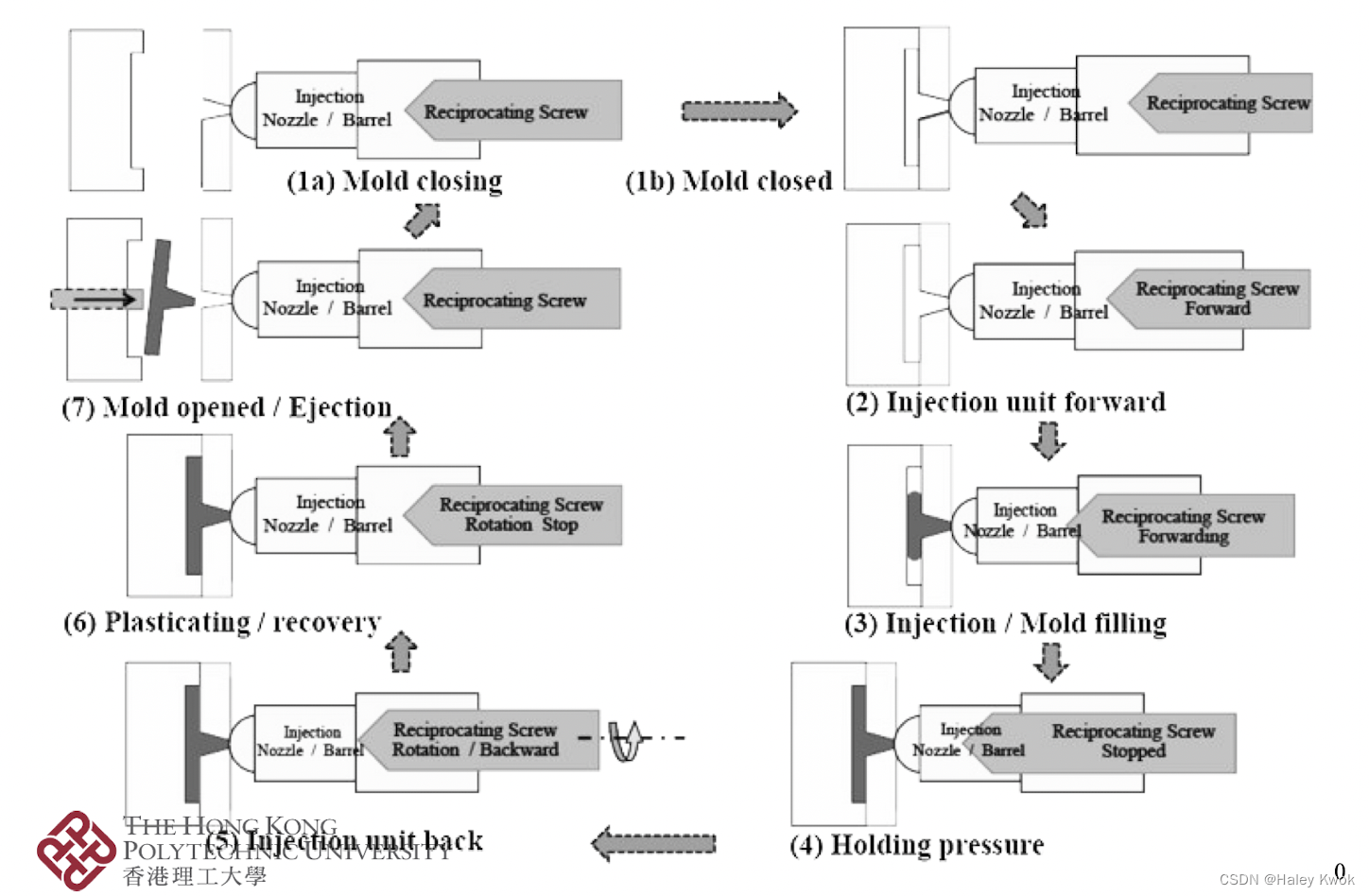
Injection molds have two main parts, or platens.
- Typically the half containing the hollow cavity side is attached to the injection molding machine, and is referred to as the fixed platen.
- The section of the mold containing the convex core is usually the piece that moves back and forth to open and close the mold, and is referred to as the moving platen.
The clamp unit hold the two halves of the mold together, providing the force needed to keep the mold closed when the plastic is injected. This clamping action is provided using hydraulics or by mechanical toggles.
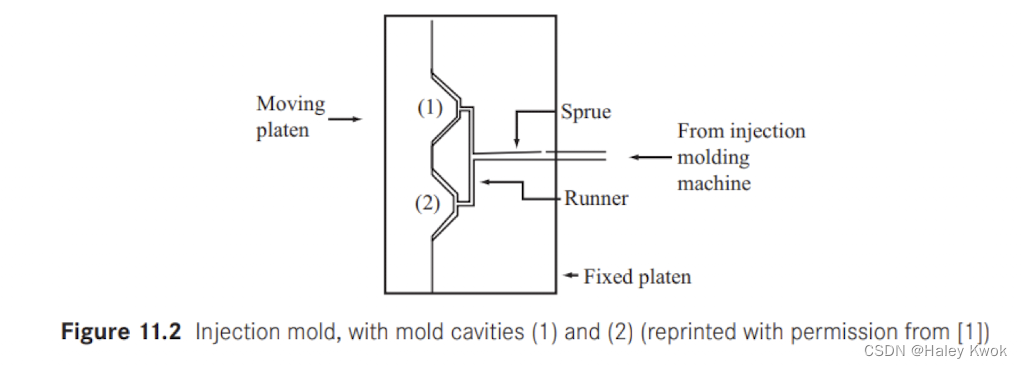
Injection Molding: Mold Design & Making
Weld line
Weld lines are places where the flow of plastic, initially separate, unites
For example, suppose we are molding the cup. When the polymer enters the mold, small temperature differences in the mold walls will cause the polymer front to advance unevenly.
Eventually, when the polymer fronts meet in the flange area, they must join together. At these points, a weld line is formed.

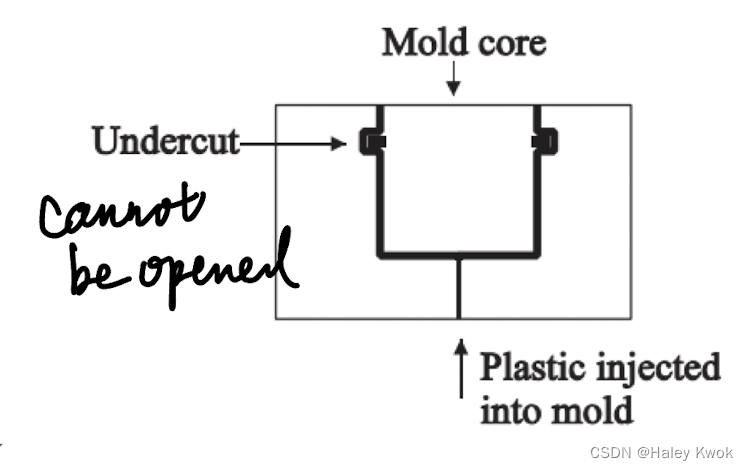
Undercut
Successful removal of the part from the mold is a major factor
in mold design.
Portions of the molded object that protrude into the side wall
of the mold. When these are present, the object being molded cannot simply slide out of the mold, since it is restrained by the protruding area
Closure
Friction
Friction between the outside of the closure and the inside of the mouth of the container provides the force that resists removal of the closure. It is hollow inside, and has a ridged outer surface.

Snap-fit
A snap-fit closure is made of a resilient material and is designed to deform as it passes over a protruding feature on the container
Removal of the closure requires deformation again to “snap” the closure back over the protruding feature, which is typically a retaining ring
One of the major advantages of snap-fit closures is that they can be applied very quickly.
A disadvantage is that they cannot be used for containers with internal pressures exceeding one atmosphere, since the pressure may act to snap the closure back off of the container.

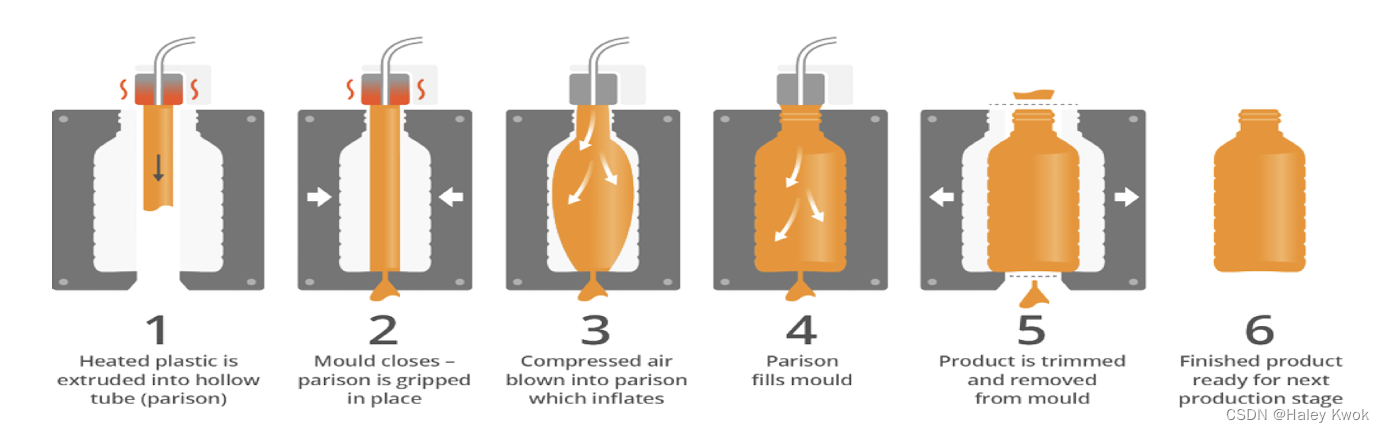
3. Blow Molding
use air pressure to shape the inside of the object
Injection blow molding is more expensive than injection molding alone, since it requires two sets of molds and two molding processes.
It generally cannot economically produce bottles with handles commodity resin such as PE, PP, PVC can be used to produce containers and packaging
Extrusion blow molding
The extrusion is usually in a downward direction for making bottles, and usually in an upward direction for film.
A blow pin or a needle is inserted, and air is blown into the mold, expanding the tube, or parison.
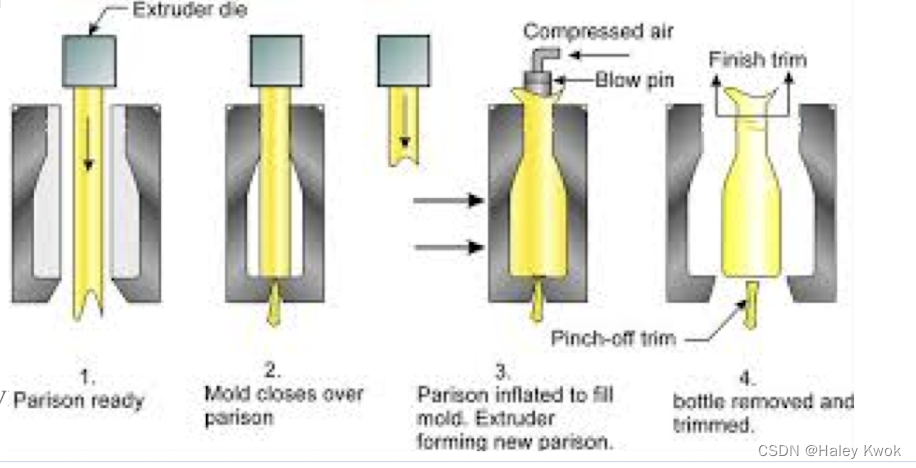
Flash 毛边
The flash (excessive material) is trimmed from the container neck and bottom, as well as from other areas that are pinched off
The marks left from the removal of the flash serve as an easy means for identification of extrusion blow-molded containers. Usually this is easiest to see on the bottom of the container.
It typically appears as a rough area along the mold parting line, centered in the middle of the bottom and running half or so of the distance to the heel of the bottle

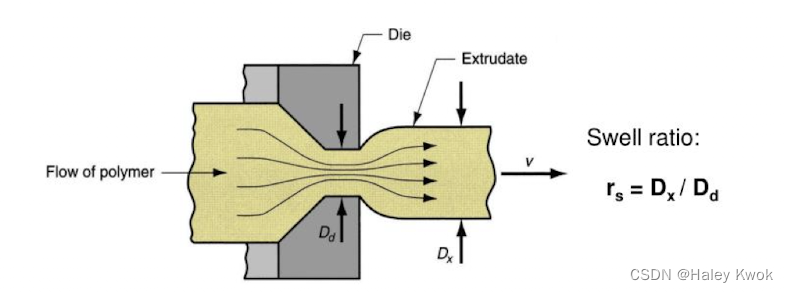
Parison dimension and swell 型坯尺寸和膨胀率
Die swell is a common phenomenon in polymer extrusion.
When a viscoelastic fluid flows out of a die, the extrudate diameter is usually greater than the channel size. This is called die-swell, extrudate swell.
Bottle Paneling
Paneling occurs when the pressure inside a plastic bottle becomes less than the ambient air pressure outside, causing the walls of the bottle to partially collapse inward.
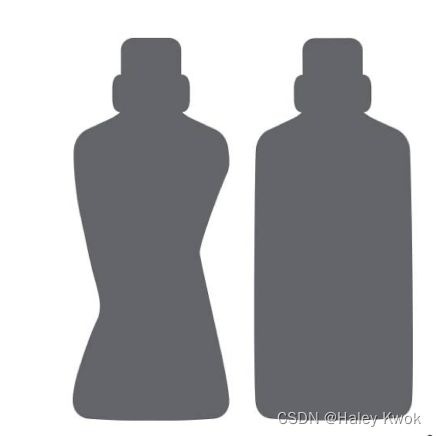

Wall Uniformity
Another design style that presents challenges for wall uniformity is the F-style container, often used for motor oil and chemicals.

Injection blow molding 注射吹塑瓶
Injection blow molded bottles (IBM) are always made in a two-step process.
- First, a preform, or parison, is produced by injection molding
- Next, this preform is placed in a second mold and blown to produce the final
Injection blow molded bottles are generally blown on the same machine as
container shape the one that makes the preforms.
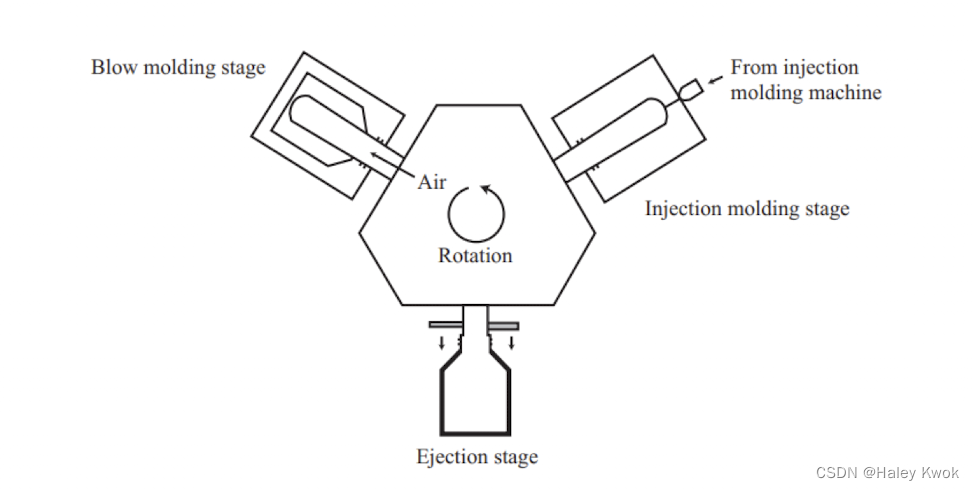
The process is often arranged on a horizontal table
Multiple cavity preform molds and bottle molds can be used in the process
Stretch blow molding
IBM V.S. EBM
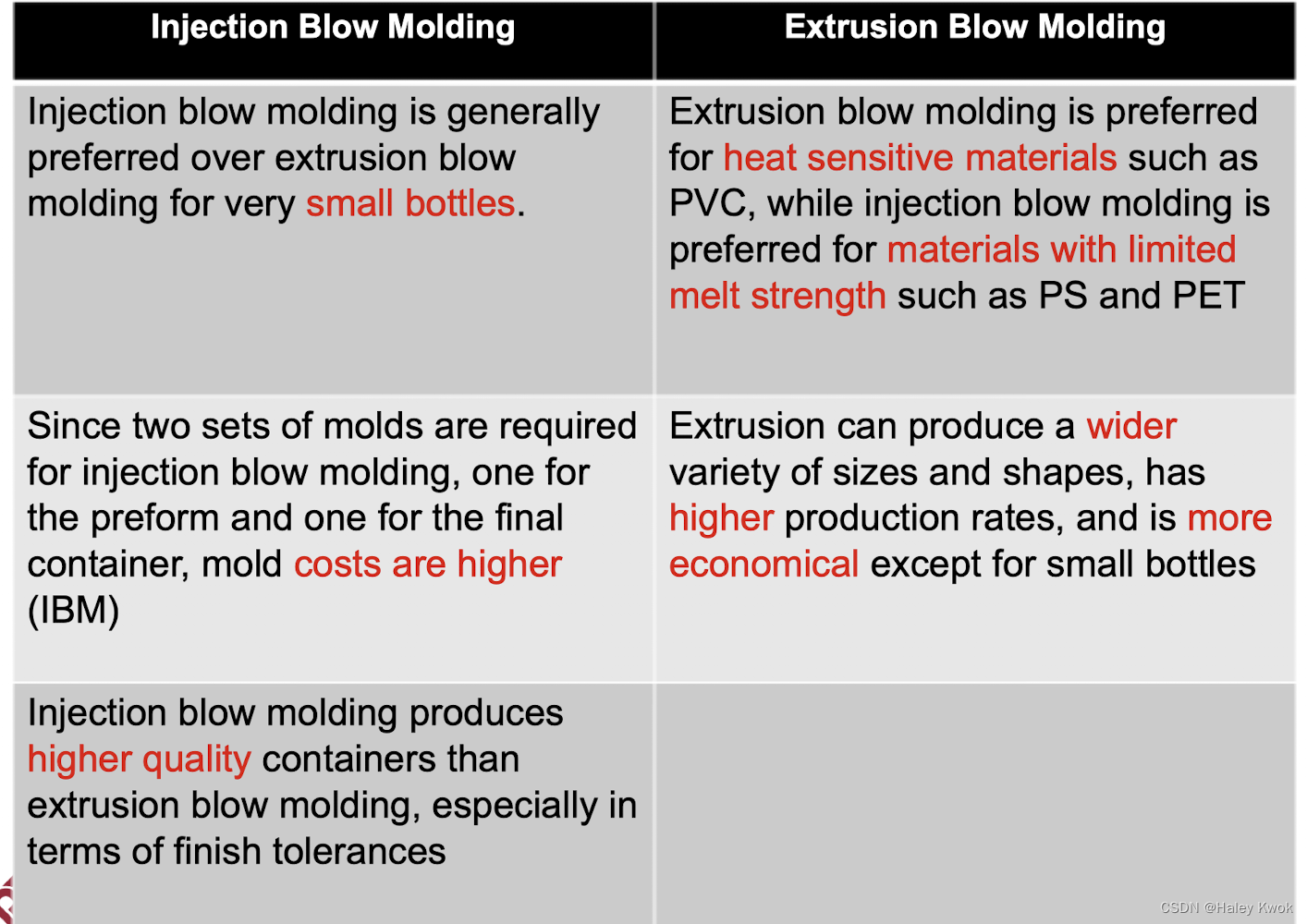
- Products: the principal difference between IBM and EBM is the type of products they create. IBM is typically used to form more solid parts, which can include medical parts, kitchen parts, and other solid components. Meanwhile, EBM is used for manufacturing more hollow parts like bottles and other containers.
- Molds: For IBM, they need to be a high precision match between both halves of the mold to enable total control over the flow of resin. In EB, there is a higher level of design flexibililty between both mold halves since each half forms its own wall shape.
- Types of Materials: EBM is most commonly used to form products out of:
High-density polyethlene (HDPE)
Polypropylene (PP)
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
IBM is most commonly used to form products out of:
Acrylic
Polycarbonate
Polyoxymethylene (POM)
Polyethylene (PE)
4. Thermoforming 热成型
The thermoforming process has three basic steps: heating the sheet, forming the sheet, and trimming the part.
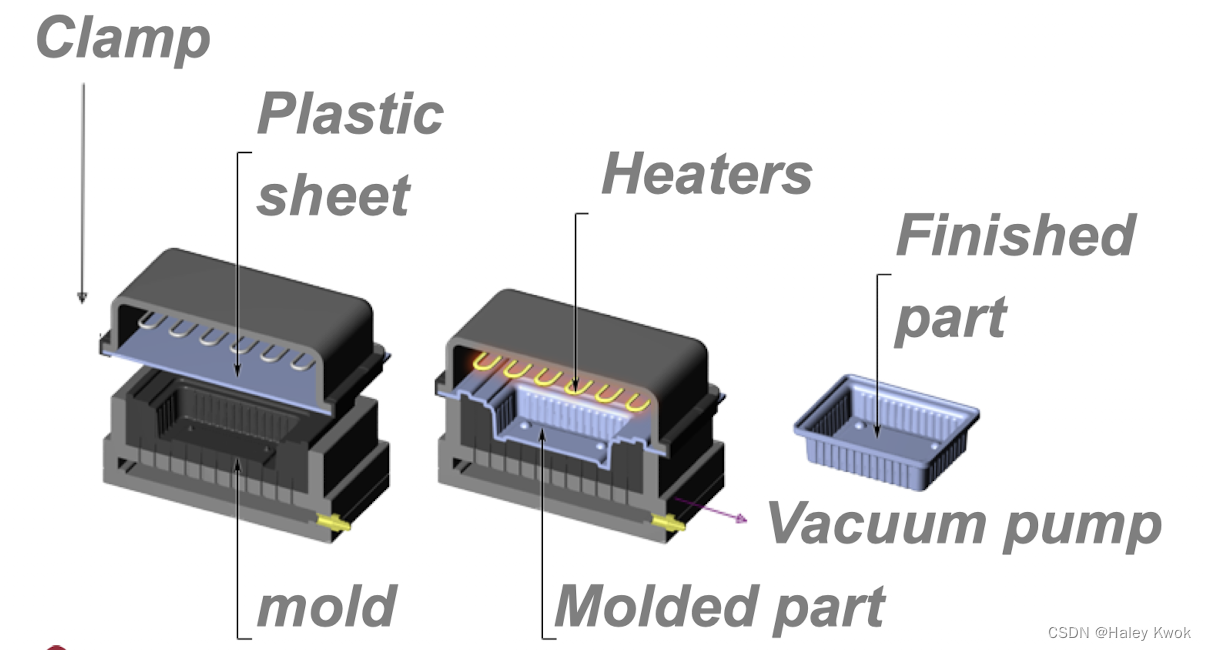
Temperature and heating: The polymer sheet must be heated to get it to the proper state for forming. The optimum temperature is dependent on the polymer and on the mold design that is being used to make the part.
Heat can be transferred to the sheet in several ways. The most common for thermoforming is radiation from heater elements.
In some thermoform/fill/seal equipment, heating is by conduction. In this case, the sheet is pulled up against a heated plate, and heated by contact
Pressure forming
Pressure forming uses additional pressure to form the sheet. Most often air pressure greater than one atmosphere is supplied to one side of the sheet, while a vacuum is drawn on the other side. Pressures of 20 to 80 psi are common, but pressures as high as 500 psi are sometimes used.
Matched mold forming
In matched mold thermoforming , matched sets of negative and positive molds are used to form the part from the softened sheet. Vacuum is generally applied through the negative cavity, as well. The result is excellent dimensional control, and the ability to form very complex shapes. This method is most often used in thermoforming of foams, due to their tendency to deform if not restrained
Vacuum forming
Vacuum forming, the main forming force is air pressure, caused by normal atmospheric pressure on one side of the sheet and a near vacuum on the other side
5. Packaging adhesive
An adhesive can be defined functionally as any substance capable of holding two materials together. Adhesives, typically referred to as glue, are used to join together materials
Reactive Adhesive
Chemically reactive types of adhesives usually involve the polymerization of low molecular weight components that are applied as liquids.
● These form a polymerized adhesive with good cohesive strength after curing.
● Uses in packaging include bags, pouches, wraps, and boil-in-bag food pouches.
● Reactive adhesives typically can be used to bond very dissimilar materials. They are usually flexible, though epoxies are rigid.

Hot Melt Adhesive
Hot melt adhesives are the fastest growing adhesive group for packaging applications. They are 100% solids and do not require any type of solvent. Hot melts have to be applied hot (above melting temperature) to wet the surface of the substrate. Then on cooling, the molten polymer returns to its solid form, providing good cohesive strength to the bond. They set very quickly after they are applied, do not chemically react with the substrate, and do not generate solvent emissions.

Solvent-borne Adhesive
Solvent-borne adhesives consist of








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章














 1735
1735











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








